10 million deaths are one of the startling numbers about 'Antibiotic resistance'.
Every day in the world, about 1,900 patients die from antibiotic resistance, equivalent to 700,000 people die each year due to the use of excessive antibiotic-induced antibiotics.
However, AMR figures show that this figure can be up to 10 million people every year by 2050, higher than the number of deaths from cancer every year.
In 2014, former British Prime Minister David Cameron published a report on the impact of antibiotic greasy status on the global economy. Accordingly, the annual GDP of the world will decrease by 2-3.5% from now until 2050 if countries do not have countermeasures, equivalent to 60-100 trillion USD of lost GDP.
A recent report from the World Bank (World Bank) also identified the world economy will be significantly affected if the situation of antibiotic lubricants is not resolved thoroughly.
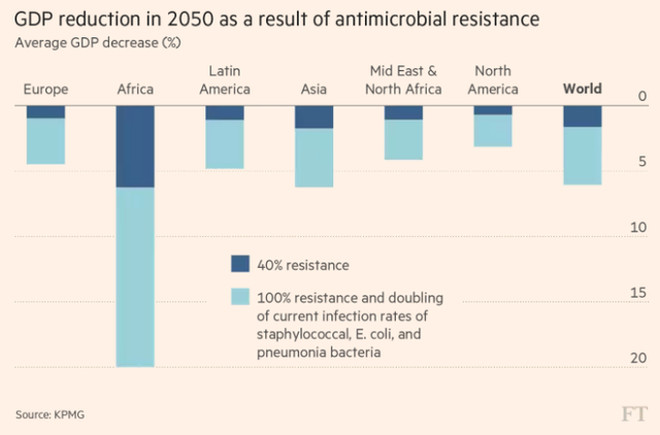
GDP in many areas declined because of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Since 1928, human life has changed radically when antibiotics were invented and especially when they were widely commercialized in the 1940s. However, the widespread use of antibiotics in medicine Animal husbandry and agriculture are making the situation worse when bacteria and viruses start to lubricate.
The situation became so serious that antibiotic lubricants became the main subject of the UN Annual Meeting (UN) in 2016 and also a key issue of G20 health ministers meeting. in last May.
Despite government calls and warnings, pharmaceutical corporations still ignored the antibiotic segment due to the low profit. Currently, the drugs for diabetes, cancer . are the main direction of these companies because they bring many benefits.
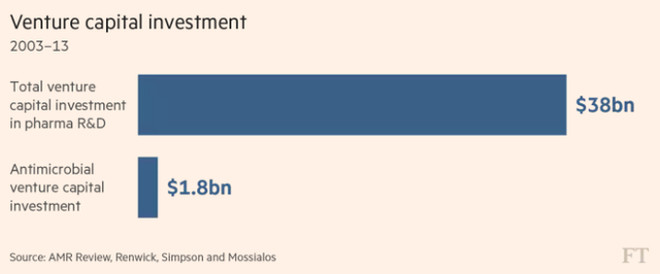
Amount of investment in medical research and antibiotics (billion USD).
Antibiotic development is now less profitable than the popular and popular treatments for chronic diseases such as cancer or diabetes. The 2011 study of the London School of Economics showed that the NPV (net present value) ratio of the injectable antibiotic segment was only about $ 100 million, much lower than the $ 1 billion of the musculoskeletal treatment line. or chronic arthritis.
As a result, many older antibiotics that have not been studied develop the virus to lubricate the drug, while the patients who use it extensively in non-designated antibiotics make the situation worse.

The number of people killed by the greasy virus in 2050 (million people).
At the beginning of the invention of antibiotics, the problem of unnoticeable drug-resistant viruses by humans constantly created new drugs in the 1950s-1980s. However, the rate at which new antibiotic strains slow down, the number of cases of greasy drugs increases and the supply shortage of older antibiotics is causing a headache for the health sector.
Data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP), the country has only 9 new antibiotic lines developed in 2005-2014, much lower than 27 types in the 1980s. The QuintilesIMS Institute report showed that in 2,240 new pharmaceuticals in 2016, only 8% were in the antibiotic line.
Meanwhile, the 2015 study of CDD Center showed that the amount of antibiotic use in society has increased by 30% in 2000-2010, especially in the health sector as well as livestock.

Patients in the US are taking a variety of antibiotics that are not needed to treat them.
How is the poultry market poisoning itself?
In countries with diverse ethnicities and religions like India, poultry meat is the safest food when they are not only cheap but also suitable for all kinds of religions. Figures from the US Department of Agriculture show that India consumes 4.5 tons of chicken from the beginning of the year and the consumption growth rate reached 30% in 2013-2017, the strongest increase in the world.
However, the country's livestock industry is facing a major crisis in the country when antibiotics are abused too much, damaging the environment for consumers.

The highest amount of antibiotic greasy virus in India.
Studies at the 18 largest farms in Punjab-India state show that two-thirds of poultry contain enzymes against most antibiotic strains. Of the birds tested, 87% of the samples contained antibiotic greasy bacteria.
The World Health Organization (WHO) said that poultry currently consume twice as many antibiotics as humans due to the need for industrial production and meat consumption in many countries, especially those with many religions such as India. .
The danger of abuse of antibiotics in livestock is that they do not kill the pathogens, causing the bacteria to survive and develop their own mechanism of greasy medicine, thereby spreading and staying in the consumer body. as well as water, soil and air.
The World Bank's September 2016 report showed that the antibiotic greasy crisis could have a very bad impact on the global economy, even worse than the 2008 crisis. The world may have to lost $ 1 trillion for medical expenses between now and 2050 without countermeasures.
In the Punjab farms survey, all farmers admitted to taking antibiotics said they were used for prevention as well as stimulating growth for poultry.

Growth in demand for poultry meat in countries during 2003-2017.The Chinese market decreased due to bird flu.
The consequences of this abuse are enormous when more than 56,000 babies die from infections every year without effective antibiotic treatment.
A 2015 report shows that the use of antibiotics in livestock in some Indian states may increase fourfold between now and 2030 due to increased demand for poultry.
Currently, not only India, large poultry consuming countries such as China are also increasing the use of antibiotics for livestock to meet the food needs of a very large part of the population with up income. when the economy exploded.
- The CDC report states: The United States has entered a post-antibiotic period
- £ 10 million for anyone to find a solution against antibiotic resistance
- 10 reasons why antibiotic resistance is scary right now
- Bio-nano robot will help end the antibiotic resistance crisis
- WHO put recommendations on what to do to prevent the spread of resistant bacteria
- How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics?
- Antibiotic resistance can be passed from mother to child
- Learn about the phenomenon of antibiotic resistance
- The principle you must remember in an age of nightmares 'antibiotic resistance'
- Solving the phenomenon of drug resistance by giving bacteria 'fighting' together
- Vietnam appears to be resistant to all antibiotics
- Latest weapons against antibiotic resistance - Platypus milk
 The United Nations' all-human warning: All antibiotics are becoming useless
The United Nations' all-human warning: All antibiotics are becoming useless How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics?
How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics? Learn about the phenomenon of antibiotic resistance
Learn about the phenomenon of antibiotic resistance 7 principles when using antibiotics
7 principles when using antibiotics