How thin or fat dinosaurs?
Karl Bates and his colleagues from the paleontological and mechanical research group have recently recreated the bodies of five dinosaurs, including two typhoon T. rex (Stan specimen of the museum). Manchester and the MOR555 specimen of the Rockies Museum), one of Acrocanthosaurus atokensis, one Strutiomimum sedens and one Edmontosaurus annectens.

Tyrannosaurus rex dinosaurs.(Photo: arizonaskiesmeteorites.com)
The team discovered the T. rex dinosaur in the Rockies museum with smaller sizes weighing between 5.5 and 7 tons . Meanwhile larger specimens weigh up to 8 tons.
Acrocanthosaurus atokensis is a large-sized predatory dinosaur that looks like the T. rex dinosaur but has large spikes on its back. It also appeared on Earth much earlier than T. rex in the middle of the Cretaceous, about 110 million years ago. The team thinks that Acrocanthosaurus atokensis is probably the same size as MOR555 and other mature T. rex dinosaurs have an average size of about 6 tons.
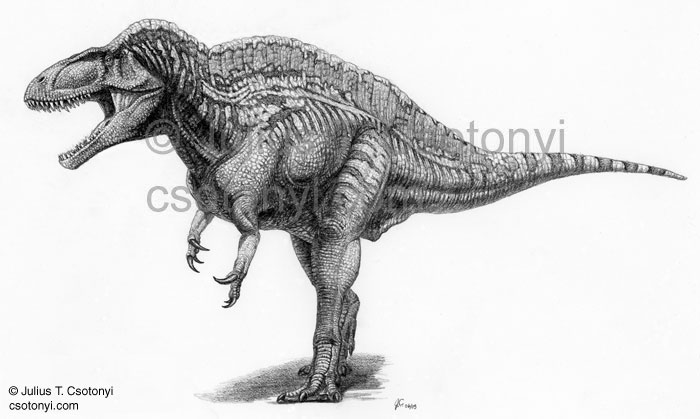
Acrocanthosaurus dinosaur atokensis.(Photo: csotonyi.com)
Strutiomimum sedens, this name means 'ostrich imitator', lives with T. rex in the late Cretaceous period, perhaps they weigh between 0.4 and 0.6 tons.
The emulator of the ostrich.(Photo: Pangeaindustries.com)
The reconstruction of the Edmontosaurus annectens dinosaur, a plant-eating dinosaur, is based on relatively small specimens but still weighs 0.8 to 0.95 tons. When it comes to adult size, some herbivorous dinosaurs can be as big as the T. rex dinosaur and also live in the late Cretaceous period.

Edmontosaurus annectens herbivorous dinosaurs.(Photo: marshalls-art.com)
The team used laser scanning techniques and computer modeling methods to create 3D models of specimens, in an attempt to reproduce their body sizes and their true shape. The laser scanner establishes a full skeleton image, thereby creating a detailed 3D model in which every bone has its spatial and spatial alignment. This work creates a high-resolution skeleton whereby the body cavity and organs such as the stomach, lungs and air sacs can be reused. This allows to calculate the body part mass, the center of gravity as well as the inertial movement of each animal. All of the above information is necessary in analyzing body movements.
After reconstructing the image of each animal, the group will change the volume of the body and respiratory organs to find out the best weight for them. Even scientists cannot be sure of the true size of dinosaurs like T. rex in reality. Therefore, the research team is very interested in the search for the dinosaur body mass value. They believe that low-weight weight estimates seem to be the most accurate because there is no reason to force dinosaurs to be heavier than what they need because this will affect speed and energy. amount of use and demand for their respiratory system.

The reconstructed image of Tyrannosaurus rex BHI 3033 looked from the right (A), from the back to the back (B), from the front of the skull (C) and from the skull to the corner.( Photo: Bates et al., DOI: 10.1371 / journal.pone.0004532)
The team also determined ostrich body weight - a living specimen to verify their accuracy for the technique and found that the results were accurate. They will use these results for later research on dinosaur movement, especially on how they run.
Karl said: 'Our technique allows us to look and decide for ourselves the actual fatness of the dinosaurs. We can observe the skeleton has a belly. Anyone from a 5-year-old child to a professor can look at it and say, 'I think this reconstructed image is a little fat or a bit thin.' Karl added: 'This research will help us conduct studies on how dinosaur runs based on 3D models, not 2D as previous studies'.
'Reconstructing many dinosaur specimens with such details allows us to examine changes in body weight, especially when they evolve. As we know, dinosaurs evolved into birds. In this process, the center of gravity will move forward, which will also evolve. Although the dinosaurs we recreated are not close relatives of the birds, however, we can see the small movement forward in the central position from Acrocanthosaurus atokensis to the tyrant dinosaur T. . rex, this central position is quite close to modern birds on the evolutionary path. '
Refer
Bates et al.Estimating Mass Properties of Dinosaurs Using Laser Imaging and 3D Computer Modeling.PLoS ONE, 2009;4 (2): e4532 DOI: 10.1371 / journal.pone.0004532
- 10 weird, hard to imagine dinosaurs
- Arctic dinosaurs are only 20 years old
- 10 misconceptions about dinosaurs
- What if dinosaurs live with humans?
- 70 million years old dinosaurs
- How does the dinosaur learn to fly?
- Erotic dance of carnivorous dinosaurs
- 6 things you read about dinosaurs when you were young, but are no longer true
- Discovered 2 new dinosaurs that hurt archaeologists
- New theory reverses the truth about dinosaurs
- The process of world domination and the destruction of dinosaurs
- The reason you eat so much is still thin
 Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old
Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China
Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast
Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils
Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils