Amazing gas molecules in NGC 5908 spiral galaxy
The team of astronomers used a 30m IRAM radio telescope in Spain to conduct observations of its stream of carbon monoxide and isotopes from NGC 5908 spiral galaxy.
It is known that NGC 5908 is a giant spiral galaxy with a very high tilt of about 170 million light-years from Earth, with a stellar mass of about 8.3 billion solar masses.
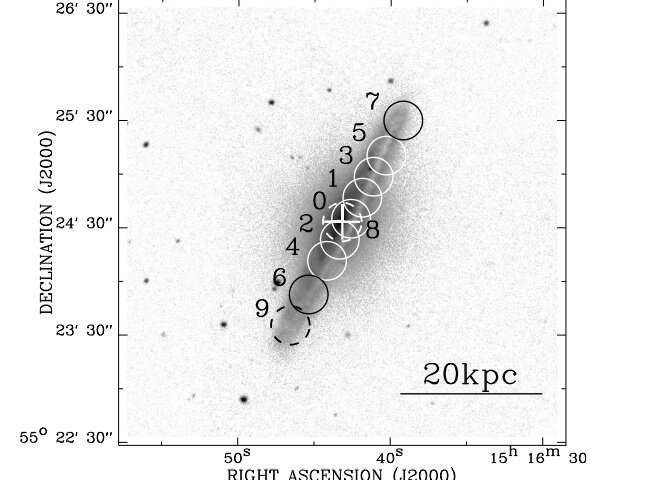 Image source: Phys.
Image source: Phys.
The results also show that the radiation of the galactic environment is not enough to compensate for the amount of gas, energy consumed for star formation. The researchers found that one of the carbon monoxide molecules and its isotopes participate in relatively weak star formation in NGC 5908. Therefore, experts no longer see any new moves from this galaxy.
Therefore, the experts concluded that NGC 5908 is not completely shut down and may be in the period of 'hibernation' before waiting for 'turning' back from a certain impact.
- Discover the oldest universe spiral galaxy
- Detecting spiral galaxies in the early universe
- Hold your breath in front of the magnificent image of the galaxy 30 million light-years away
- The collision of the galaxy is 80 million light-years from Earth
- Hubble discovered the galaxy with brilliant lenses
- Photo of spiral galaxy 65 million light-years away
- The shape of the galaxies depends on the speed of rotation
- Shining spiral galaxies in the universe
- Revealing the largest galaxy in the universe
- Close-up of the Milky Way's twin brothers
- Huge 'flying saucer' in the universe
- The galaxy deforms 100 million light-years from Earth
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people