Discovering the Milky Way's new black hole
NASA said the Swift satellite had captured X-ray beams from a place near the center of the Milky Way, evidence that the existence of a previously unknown black hole. The new black hole has been named Swift J1745-26.
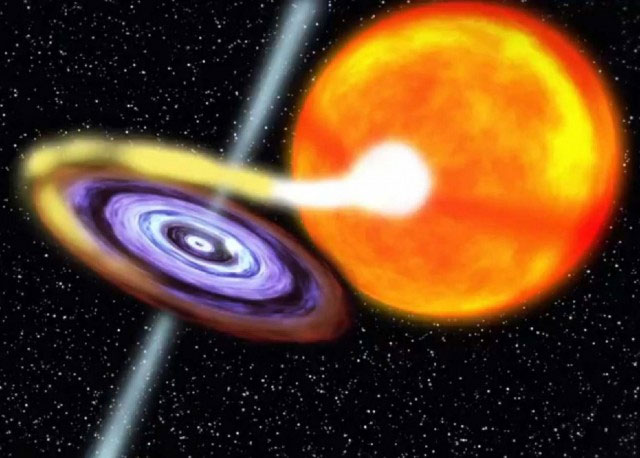
Conceptual illustration of a black hole that draws gas from a companion star
'Dazzling X-ray bursts are so rare that they are events that can only be met once in research missions, and this is the first time the Swift satellite has witnessed such an incident ,' according to Nasa.gov's website quoted Neil Gehrels, Swift's mission leader at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The newly discovered black hole has a companion star. Air flows from this star to the disk around the black hole.
Unlike the giant black hole in the center of the Milky Way, Swift J1745-26 has masses many times lower, often equivalent to only a few stars.
Experts hope that when the X-ray beam fades, they can measure the mass and confirm its official identity, whether or not it is a black hole.
- Monster black holes are 100,000 times bigger than the Sun.
- Discover the mystery of the most exotic black holes in the universe
- The center of the Milky Way may contain thousands of black holes
- Discovering 'super black holes' is 12 times bigger than the Sun.
- Witness the 'meal' of the super black hole
- The endless dance between the Milky Way
- Close up of the black hole of the Milky Way
- Detecting a black hole
- 10 fascinating facts about black holes
- The star flies more than 1,000 km / sec after 'hiding' from the black hole
- The supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way is 'hungry' like never before
- The supermassive black hole closest to Earth glows intensely
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people