How does wireless power work?
Nikola Tesla always dreamed of being able to supply electricity around the world without having to pull wires. Finally, the inventor also came close to dreaming, when his experiments produced the "Tesla coil" (Tesla coil).
As the first system that can transmit wireless power, Tesla coils are really a revolutionary invention. Tesla developed these special coils in 1891, before using traditional transformers to power everything like lighting systems to telephone circuits. But these transformers cannot withstand high frequencies and currents like Tesla coils. The idea behind this coil is actually quite simple, which is to take advantage of electromagnetic force and resonance. Using copper wires and glass bottles, an amateur electrician can also make a Tesla coil that can produce ¼ million volts of electricity.
Structure of Tesla coil
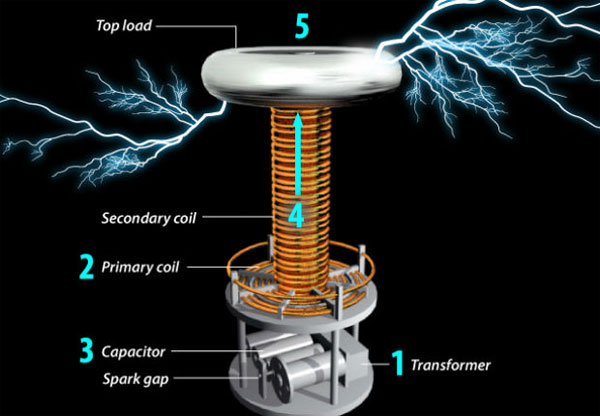
The structure of Tesla coil consists of 2 parts: a primary coil and a secondary coil.Each coil has its own capacitor.
A Tesla coil consists of two parts: a primary coil and a secondary coil, each with its own capacitor (the capacitor stores the same electrical energy as the battery). Two coils and capacitors are connected by an ignition slot - which is the air gap between the two electrodes to generate electrical sparks. Basically, Tesla coils are two open circuits connected to an ignition slot.
Tesla rolls need a high-voltage power source. The normal power source passing through a transformer can produce an electric current with the required intensity (at least thousands of volts). In this case, the transformer can convert the low voltage of the main circuit into high voltage.
How does Tesla roll work?
The power supply is connected to the primary coil. The capacitor of the primary coil acts as a sponge that absorbs the charge. Primary windings must be capable of withstanding very large and many electric waves, so this coil is usually made of copper, the type of wire is very good. Finally, the capacitor accumulates so much charge that it breaks down the air resistance in the ignition slot. Then, similar to squeezing a wet sponge, electricity flows out of the capacitor to the primary coil and creates a magnetic field.
A large mass of energy causes the magnetic field to drop rapidly, creating an electric current in the secondary coil. The voltage compressed through the air between the two coils creates spark in the ignition slot. The energy covered between the two coils, accumulates in secondary windings and capacitors. Finally, the charge in the secondary capacitor is so high that it escapes as an electric arc.
High-frequency voltage can light fluorescent bulbs a few steps away without connecting wires.

In a perfectly designed Tesla coil, when the secondary coil reaches its maximum charge, the entire process will restart and the device will be able to maintain itself. However, in reality, this does not happen. The heated air in the ignition slot will pull some electricity from the secondary windings and return to the ignition slot, so the Tesla coil will eventually run out of energy. This is why the windings must be connected to an external power supply.
The basic principle behind Tesla coil is resonance . Resonance will occur when the primary coil shoots the current into the secondary coil in time to maximize the energy transferred to the secondary windings.
Producing a Tesla coil with a ignition slot helps us better control the voltage of the current it produces. Although Tesla coil (Tesla coil) is no longer practical, but Tesla's invention has revolutionized how we understand and use electricity. Today, radio and TV still use different forms of Tesla coils.
- Electricity will be transmitted as wireless Internet
- Wireless electricity is safe for humans
- How does wireless charging work?
- Wireless charging and things to know
- Power transmission without wires
- Already able to charge wireless phones remotely - Breaking the phone industry
- Wireless Table Light
- A battery-free device can still send messages
- Six steps for wireless network location survey
- Transferring electricity to a moving object, scientists step closer to remote wireless charging technology
- Charge wirelessly for up to 40 phones
- Wireless charging for electric vehicles
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum?