Learn about the Louvre museum
It used to be present in many novels and movies, typically the Da Vinci Code of Dan Brown.
The Louvre Museum is probably the name that is no stranger to us, this is a famous cultural spot of the world. It used to be present in many novels and movies, typically the Da Vinci Code of Dan Brown. This place holds a lot of artifacts with great cultural value, from paintings, art to painting, decorative arts to sculptures. The Louvre Museum is not only a place to keep typical cultural and historical values of mankind but also a cultural center, demonstrating the history of France in particular and the world in general. In this article we will learn about the Louvre museum.
Original foundation
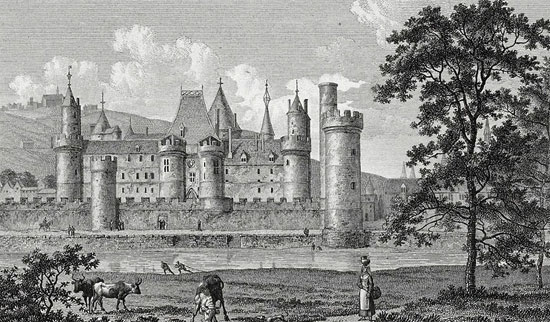
The starting point of the Louvre is from a defensive fort on the banks of the Xen River. King Philippe Auguste built the Louvre in 1190. By the 14th century, the Louvre had another function to become the royal palace under King Charles V. In the following years, the Louvre was repaired. , expanding, investing through many dynasties. This remodeling is done at the hands of leading French and European architects. This time is considered the golden age of the Louvre as a palace. However, since 1672, after the Palace of Versailles was completed, the place was deserted for some time. But it was at the same time that the Louvre began his transformation to become a museum like the present.
The birth of the museum
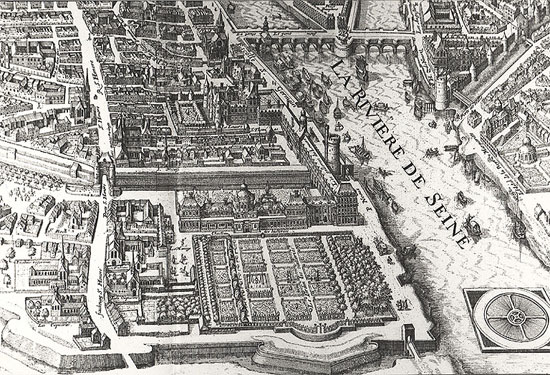
French people carry in themselves the characteristics of elegance and respect for culture. It was during this period that Louvre was 'exposed to dust' when France realized the need for heritage development and preservation. Many cultural conservation management agencies were born during this period. A solid, well-built and luxurious place like the Louvre itself cannot be left empty, so there is a combination of the Louvre into a museum.
The Treaty of Campo-Formio in 1797 gave France many valuable works from the Veneza and the Papal collection. Among them, paintings and ancient sculptures were transferred to the Louvre. On November 9, 1800, Napoleon and his wife unveiled the Ancient Museum. Since then, the Louvre has constantly received more artifacts thanks to the expeditions of the French army. Also under the First Empire, the museum was named Napoleon. Between 1804 and 1811, it was expanded by Architect Fontaine, redecorated and Napoleon built the Carrousel triumph between Louvre and Tuileries (a palace). By the time the First Empire collapsed in 1815, nations had regained their possessions, directly affecting the Louvre's collection. This is a period of many ups and downs of the museum but it was also the time when Louvre was given his real name.
For the next several years, the museum continues to hold many precious artifacts brought from everywhere. During the Second Empire, the Tuileries palace was expanded and was first connected to the Louvre. In 1871, the Tuileries was burned and destroyed later. The Louvre was repaired by architect Hector-Martin Lefuel.
Modern times

By the 19th century, the Louvre museum became a famous and prestigious place. Many of the great painters spent their time studying here, including Edgar Degas, who was allowed to make copies of museum paintings.
In 1905, a collection of decorative art was brought from the Palais de l'Industrie to the Louvre and in 1922, the Islamic art gallery was opened in the Horloge building. Since 1930, some spaces have been remodeled for the purpose of sculptures. Cour du Sphinx is roofed with glass for ancient sculpture. European sculpture is in the Flore house. Ancient Egyptian and Eastern rooms were also repaired.
The Second World War broke out, Louvre artifacts were hidden in sandbags and sent everywhere. Although almost empty, in 1940, when the German Army occupied Paris, the Louvre was reopened. In 1945, the collections were gradually brought back.

In 1981, the French President announced that the entire Louvre palace space would be reserved for the museum. The project called "Grand Louvre" was started. By 1983, the famous architect Ieoh Ming Pei was chosen to implement this project. In 1986, the Orsay Museum opened. European art collections from 1848 to the start of the cubism were transferred from the Louvre to the new museum.
On March 30, 1989, the controversial Pyramid project was unveiled on Napoleon. A large space is opened underground under the pyramid, becoming the museum's main entrance. This large hall is also for services of sending clothes, bookstores, restaurants, and cafes. In 1993, the series Richelieu opened to the public. The three roofed inner courtyard became the ideal space for large works. By 1997, a number of Sackler sequence rooms were reserved for the Ancient East and 1998, the École du Louvre was opened in the Flore range with 5000m² for sculpture.
Art gathers about the Louvre

Overall, the artifacts in the Louvre are rich and diverse, coming from all over the world. The Louvre collection contains more than 380,000 artifacts, but only about 35,000 artifacts are displayed regularly. The entire Louvre is 210,000m² wide, of which 60,600m² is for display and is divided into 8 zones: Ancient Orient; Ancient Egypt; Ancient Greece, Rome and Etruria; Islamic art; Art; Sculpture; Art and decoration art. According to the arrangement and organization policy of the French national museum system, many valuable Louvre collections have been transferred to other museums. Currently, the Louvre artifacts include Western artworks from the Middle Ages until 1848, ancient civilizations and Islamic art.

In addition to the eight main collections, the Louvre has a historic display of the palace itself and an art gallery in Asia, Africa, America and Oceania.
All art objects in the Louvre were nationalized after the monarchy. However, it must be said that the kings' passion for art helped the Louvre have a wealth of precious collections. François I is the one who collected the works of Raphael, Titian, Leonardo da Vinci and other modern Renaissance artists. Some cases like Michelangelo's statue - "The Slave" are donated by the author himself.

Napoleon Bonaparte is also a character who has contributed a lot to the Louvre collection. His conquests brought the museum many spoils. Under the direction of Dominique Vivant Denon, the Louvre collection is also greatly expanded. Denon goes to the conquered areas by Napoleon's army to select items to bring back. Agreements with countries like Germany, Austria and Spain all have control over artworks. And of course they are all gathered in the Louvre. Napoleon himself also paid for a few collections to bring back to the museum.
Famous works

In the opinion of the majority, the most famous work kept in the museum is Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa, also known as La Joconda. The Mona Lisa has its own mailbox at the Louvre. This is a symbol of national pride but also contains painful memories. In 1910, a man abandoned by his fiancée had committed suicide before the painting. The following year, a supervisor at the museum tried to steal this painting, resulting in a wave of annoyance before the security here. The Mona Lisa is also the target of some malicious tricks, some visiting have thrown acid and sprayed red paint on the painting area.

Another famous work is the statue of Venus de Milo - the female guardian of Milo. This is an ancient Greek statue and is the most famous ancient Greek sculpture, portraying Aphrodite - the goddess of love and beauty of the Greeks. The statue is sculpted in marble material, slightly larger than the real one with a height of 203cm (80 inches), but has lost two hands and original pedestal. The statue was found on Melo Island in 1820 and soon reached the Louvre.

After the arrival of the Venus statue for 60 years, the statue of the victorious god Samothrace was found. This is an ancient Greek marble sculpture, depicting the deity symbolizing victory. The statue was discovered in 1863 by French diplomat Charles Champoiseau, in the island of Samothrace, eastern Greece, in a state of being broken into pieces. Champoiseau identified this as a god statue of Nike with a winged woman. Fragments were sent to Paris, assembled and displayed at the Louvre.
One of the most valuable artifacts of the Louvre is the Stone of Hammurabi Code. This is one of the oldest laws found, dating back to King Hammurabi, around 1760 BC. Another valuable artifact is the Mesha stele, from the 9th century BC.
Conclusion
The Louvre Museum has existed and developed for centuries. The historical ups and downs have created this place with a great culture. Artworks from painting, sculpture and a variety of other types are carefully preserved. Every year the Louvre museum welcomes millions of tourists from all over the world. In addition, this place is also sponsored by many international organizations as well as individuals. In the future, the Louvre will continue to retain its position as a leading museum in the world.
- The architectural works are most welcome in 2017
- 7 most horror museums in the world
- How was the picture theft Mona Lisa decoded?
- Strange feeling in the dark night at the museum
- The $ 1.8 million statue was forgotten in the old warehouse
- Museum 800m2 on top of Chinese cliffs
- Tracing the origins of the Speaker of the Rooster, the symbol of France
- Promotion of the construction of the country's first science museum
- Why did Mona Lisa become the most famous painting in the world?
- 10 interesting things about 2 great scientists of humanity
- Things that make Abu Dhabi better than Dubai
- The security bar helps European unified owners
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum?