SST telescope monitors cosmic garbage and foreign objects
The US Defense Advanced Projects Agency (DARPA) is currently preparing to transport the space monitoring telescope (SST) to Western Australia to serve the monitoring of small satellites and garbage. The universe is flying in Earth orbit. SST is able to search in an area larger than the United States in just a few seconds and the system will be operational by 2016.
>>>Video: Introduction to SST telescope
Satellite orbits have become vital to many civilian and military applications. However, establishing and maintaining a network of satellites around the Earth also presents potential dangers of space debris and the ability to collide between satellites. Therefore, tracking what is flying in space has become a top concern for the US Department of Defense in order to avoid a similar disaster like the 2009 Iridium 33 and Kosmos-2251 satellite collision. .
The problem is that there is a lot of space in the space and most satellites are flying in orbit (GeoSynchronous Orbit - GSO) about 35,000km from the earth. This is quite a distance from ordinary telescopes with a narrow field of view - not enough to track small objects. Therefore, DARPA plans to develop a completely new ground telescope to perform the search and tracking of small objects in deep space.
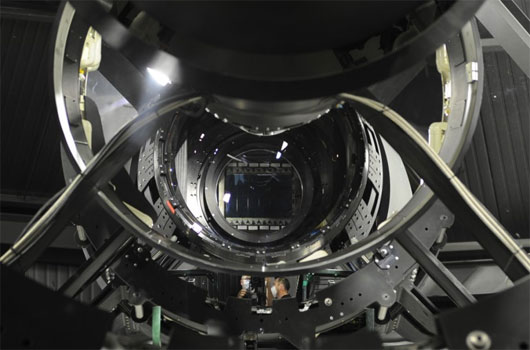
The result as mentioned above is the birth of the Space Surveillance Telescope (SST) . Developed in 2002, SST is a telescope built according to the Mersenne-Schmidt design with a wide field of view and limited aberration. Like telescopes of the same type, SST has the main mirror of the concave parabolic form, the second mirror of the convex bridge and the third mirror of the concave bridge. However, the difference of SST is that the faces of the mirrors with the largest aspherical curves ever built and this feature make SST the fastest telescope in the same aperture class, according to DARPA. In addition, SST is also the first telescope to be equipped with a large focal surface consisting of many CCD charge couplers for recording astronomical images.
"Fast" in the telescope refers to the focal length of the objective lens or mirror with a short reflector and a wide field of view. The "fast" element is borrowed from photography - a telescope with an aperture of f / 5 can take a photo with an exposure time of only one fourth of that of a camera with an aperture of f / 10 .
With the support of servo control technology , SST is a powerful telescope with short focal length, wide viewing field, compact and able to catch fast movements. According to DARPA, SST can detect the light of a laser point projected on the Empire State Building in New York from Miami, Florida.
SST's optical capability allows it to observe a large area in just a few seconds. DARPA says it can scan the entire orbital belt synchronously multiple times in just one night and can detect smaller, darker objects and appear faster than previous telescopes. This means not only detection of objects, SST can also collect data to make quick and accurate predictions about their trajectories.

SST is currently being tested and evaluated at the White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico state. The system has been scheduled to be moved to Harold E Holt Naval Da Nang Center in Exmouth, Western Australia and here, SST will monitor the Southern hemisphere sky. Based on the MoU (Memorandum of Understanding) contract signed on November 20, DARPA will transport SST to Western Australia and the government will build a protective infrastructure for telescopes as well as operate the following system. when the transfer is completed in 2016.
Once in operation, SST will become part of the space monitoring network (SSN) - a US Air Force system, using a global radar network and optical telescope to identify and List dangerous objects for countries that own air space programs. In addition, astronomers can use SST to hunt for meteorites and supernovae.
Colv Travis Blkae - program manager at DARPA said: "The SST program has revolutionized the technology of monitoring space on the ground. At the new location, SST can expand the capabilities of the United States, Australia and other countries to secure their space assets ".
- Europe studies the project of clearing cosmic garbage
- America - Japan cooperates to monitor pillar garbage
- Turn garbage in the universe into radiation shield
- Clear up garbage on the vast universe
- The danger when cosmic garbage returns to devastate the Earth
- Cosmic garbage!
- Effective way to deal with cosmic garbage
- Japan intends to clean up cosmic garbage with lasers
- Russia developed a system to eliminate cosmic garbage
- Two 10-year-old prodigies want to build a space garbage cleaner
- Which country discharges the most waste into the universe?
- 'Overload' cosmic garbage
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people