Still other jelly meteorites like?
There is much confusion between still jellies and meteors making many you still think both are the same. In fact, these are two completely different concepts.
is a natural object from outer space and impacts the Earth's surface. When an asteroid from outer space falls into the Earth's atmosphere, the compressive pressure causes the meteor to heat up and emit light, possibly with the burning of the outer layer.

Meteors are a natural object from outer space and affect the surface of the Earth.
Meteors can be small asteroids or dead comets, weighing between 10 từ10 and 104kg and diameters ranging from a few μm to meters. Small meteorite particles are called meteorites. Larger meteorites are remnants, fragments of comets or asteroids. The remaining fragments of old comets, all of which glow, continue to move in the original elliptical orbit of the comet. Only when Earth's orbit intersects with these invisible meteorites, its existence is discovered. When penetrating into the Earth's atmosphere, they caught fire at an altitude of 150 - 120km, causing meteor phenomenon; Special bright meteors are called fireballs (English: bolide) .
An asteroid with a size of only 30 to 40 cm creates a region of burning air around it several hundred meters wide. The meteorite surface temperature can reach 1,600 ° C and at an altitude of over 100km, its surface melts, turns into gas, evaporates quickly and glows. The meteorite must have a sufficiently large mass, a high density and a relatively slow motion (velocity less than 20 km.s − 1) will not be completely burnt in the atmosphere. And the Jellystone is the rest of the meteorite that comes from the space between planets flying into the atmosphere, being partially burned and falling to the surface of the Earth.
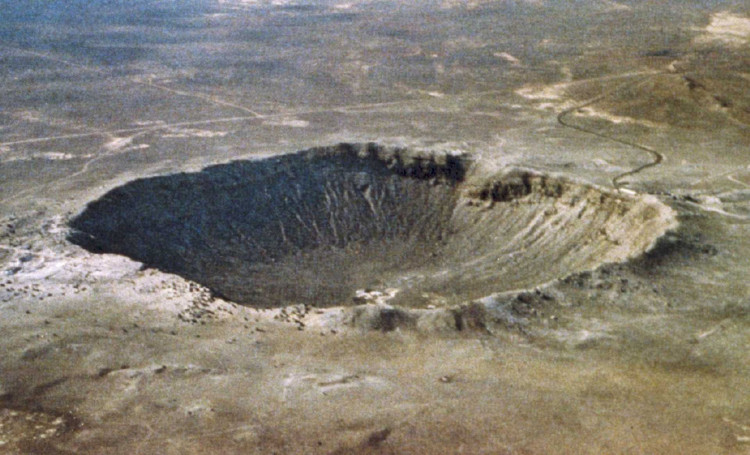

The jelly hole is divided into two groups according to its forming sequence.
According to Wikipedia, you also have a concept that the Hole is still alive. Pits are still pits on the Earth's surface, planets, satellites with hard surfaces . created by colliding with the jelly. The jelly hole is divided into two groups according to its forming sequence. The pit is still crippled by the head with the excavated meteorite. The still-spotted pits appear due to debris from the first collision falling back to the planet's surface. Previously, still holes were considered to be separate points of the Moon, and the few holes still on the Earth's surface were considered rare.
From Earth can be observed on the surface of the Moon with binoculars about 300,000 Pits still jelly. In fact, the results from the images of the Moon's artificial satellites or its surface landing devices estimate the number of 3,1012 holes still in diameter greater than 1 m (not even visible on the face). of the Moon). The density of still holes in Mercury is similar to that of the Moon.
In general, when in outer space, it is called meteorite. Once it is over the atmosphere, leaving the ground until now, it is called still jelly.
- Giant Jelly Robot
- The secret in royal jelly quickly heals wounds
- 'Jelly Battle' mysterious 7500 years: Astrology station or tomb?
- Lake water turns into 'jelly' because of pollution
- Watch Japanese people craft fruit knives
- Russian meteorite rain brings virus to Earth?
- The surface of the 'giant' meteorite landed on Earth
- New Choice taro extract recall contains toxic additives
- The origin and name of meteorite
- Argentina: A family hides up to 2.5 tons of meteorites
- Huge meteorites will graze the Earth
- Detecting algae-like fossils in meteorites
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Mud Volcano in Indonesia - A Devastating Natural Disaster from Both Natural Force and Human Greed
Mud Volcano in Indonesia - A Devastating Natural Disaster from Both Natural Force and Human Greed  Rare photos from the surface of Venus
Rare photos from the surface of Venus  First detection of traces of CO2 and H2O2 on the surface of the moon Charon
First detection of traces of CO2 and H2O2 on the surface of the moon Charon  Find out the reason for the nightly migration of trillions of zooplankton
Find out the reason for the nightly migration of trillions of zooplankton  Sensors quickly detect pesticides in fruit
Sensors quickly detect pesticides in fruit 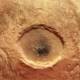 The rover found the scary 'evil eye' on Mars
The rover found the scary 'evil eye' on Mars 