The brain is bigger, but why are elephants not smarter than humans?
Each species on Earth has a special skill that distinguishes them from other species: the lion roars, the dances dance, the snakes crawl, the mice chew, and the humans think. However, what makes humans low and light can become the dominant species?
According to ScienceABC, many chemists have argued that there is really nothing special about our species. They claim that the pinnacle of human civilization - language, the child of awareness and creativity - is just a mere skill. Compared to other creatures like elephants, humans do not have taps to help lift heavy objects or store drinking water, or compared to carnivores, humans do not have sharp claws and the ability to run fast to catch and kill children. bait.
However, we can create tools to perform similar tasks!

The elephant's brain is large but the density of neurons on the cortex is much lower than that of humans.
So where does intelligence come from?
Awareness , that's what distinguishes primates and other animals.
When talking about the ability to make complex decisions, plan and solve problems ., no animal can overcome people. These capabilities are all derived from the perception, thinking and calculation of the human subconscious. But where does real perception come from?
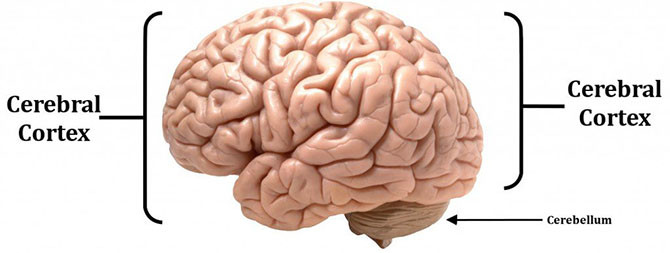
The brain is divided into many areas, and the identification of each region is really not easy. There are still many ambiguities surrounding this issue because of the diversity of the brain. However, science has basically determined that awareness and intelligence come from two areas: cerebellum and cortex.
Cerebellum (Cerebellum) responsible for regulating basic human emotions such as pain, hunger, sexual needs, drowsiness . It is quite small and is often called the "reptilian brain" for its functions. Its basic, as well as the position which is inherently hidden deep in the bottom of the brain.
Cerebral Cortex is responsible for more advanced functions, such as thinking, imagining, grasping language and expressing emotions.
Theoretically speaking, but the human brain is not quite the same as a computer. There is no specific brain area responsible for a certain function. In contrast, all areas of the brain coordinate harmoniously to control different human abilities. So, both the cerebellum and the cortex are equally important, because they are responsible for producing the majority of neurons in any brain.
The human brain is not quite the same as a computer.
So the bigger the brain, the more intelligent it is?
If awareness arises from the brain, then the bigger the brain, the more awareness there is? Because the bigger the brain, the more neurons, leading to increased intelligence, the ability to do more things? African elephants have brains three times larger than humans, so why don't they dominate humans?
Such an observation stems from the misconception that every brain has the same structure, and the size of the cerebellum and the cortex also increases proportionately. Of course not so.
Evolution says simply the summation of microscopic changes over the millennia. Primate species have smaller brains, fewer neurons, but what makes them different is how neurons are distributed.
As mentioned above, most neurons are distributed in the cerebellum and cortex. However, their distribution density in any area is not the same, or in other words asymmetric. And here is the answer to the question posed in the article title.
Why does size not matter?
Suzana Herculano-Houzel - a Brazilian neurologist - joined her students in an experiment to count the number of neurons on the brain of an African elephant, specifically the number of neurons located in the cortex ( especially the prefrontal cortex - where she believes is the source of intelligence. She used a knife to cut the elephant's brain into parts and count the neurons on each part.

The density of neurons is what determines the level of intelligence of an organism.
According to her prediction, although the brain is large, the density of neurons on the cortex will be much lower than that of humans, and it is the density of neurons that determines the level of intelligence of an organism , not the size of the brain that these neurons reside. And that's exactly what she discovered after the elephant brain surgery experiment: the total number of neurons on the elephant's brain is about 257 billion, three times the figure of 86 billion of the human brain. However, 98% of those 257 billion neurons are in the cerebellum, only 5.6 billion neurons are located in the cerebral cortex. In humans, there are 16 billion neurons on our cortex!
Suzana's experiment has shown that human superior intelligence comes from the enormous density of neurons on the cerebral cortex, instead of the cerebellum. The number of human cortical neurons far exceeds all other organisms on this planet!
Humans have been very fortunate to evolve from primates - the first species to develop neurons in this direction. And over time, our father's technological improvements add to human intelligence.
The fact that people cook food is an important factor in the development process, because it helps create more energy than raw food. Eating ripe, boiled drinking is probably the reason why neurons on the human cortex grow in such a large quantity.
- 10 things about the brain
- Do you believe men's brains are really bigger than women?
- Big brains don't mean smarter
- Seven characteristics prove that elephants are extremely intelligent animals
- Elephants speak because they are so close to people
- Elephants turn into 'murderers' when migrated
- Why are humans smarter than chimpanzees?
- Marvel at the 300 elephants who cried at the
- New discovery: Elephants hear with .. legs!
- The higher the latitude, the bigger the brain
- Human neuron detection in monkey brain
- The truth about people is the smartest
 Animal 'suffering' after hibernation
Animal 'suffering' after hibernation Why do goats climb well?
Why do goats climb well? Scientists were surprised to see chimpanzees eating turtles
Scientists were surprised to see chimpanzees eating turtles Giant catfish died deadly due to drought in Thailand
Giant catfish died deadly due to drought in Thailand