The danger is greater than cancer: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Antibiotic resistance is becoming a global threat and according to estimates by the World Health Organization, antibiotic resistance will become more terrible than cancer.
The warning is not redundant
The case of 23-year-old Natalie Silva, Texas America, died of antibiotic-resistant virus after giving birth to her first son in Texas. The type of bacteria she had was MRSA, short for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus).
This bacterium causes an "staph" infection that does not respond to conventional antibiotics.
When MRSA infection will lead to serious and life-threatening infections such as septicemia, wound infections and pneumonia, no antibiotics can be treated.
Little Josiah Cooper-Pope died when he was only 17 days old, had an infection in the hospital and could not save his life because of the viruses and no antibiotics could cure the virus.
These are just two of millions of deaths each year due to antibiotic resistance.
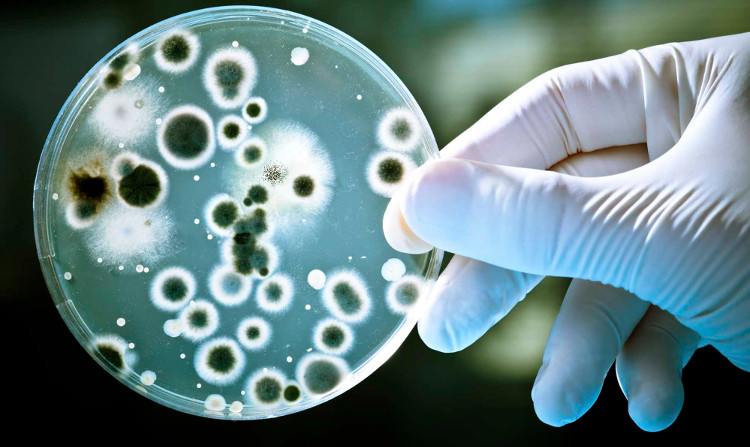
Super antibody bacteria contribute to the death of 10 million people every year worldwide by 2050.
"We are losing our ability to treat infections ," said Keiji Fukuda, WHO's special adviser . "It not only leads to high mortality rates, but also treatment." For patients who are also threatened, even providing enough food is not guaranteed. "
This refers to viruses that can affect both plants and animals.
A recent British study shows that the development of super antibody bacteria contributes to the death of 10 million people worldwide each year by 2050 and a large number of patients die from cancer. different.
Currently, the number of deaths per year worldwide is thought to be due to the absence of anti-bacterial resistance of 700,000, including 23,000 in the United States.
WHO believes that the prevention of antibiotic resistance requires community involvement, not sharing antibiotics with others.
Antibiotic resistance is every threat to health and food. Current antibiotics are no longer treatable because of drug resistance. By 2050 each year more than 10 million people die from bacterial infections and we don't have drugs to treat it.
Heartbreaking death in Vietnam after only 1 week of cough, fever
Antibiotic resistance in Vietnam has also increased to the level of red alert, making the number of patients hospitalized and drug resistant no longer a chance to live up every day while the race between people and bacteria is bacteria. also won.
The case of Nguyen Hai H., 21, a mother who is raising a 5-month-old baby who resides in Truong Dinh, Hanoi, leaves a memory of her family. H. sniffles, cough and signs of fever. On the 3rd day, the infusion fever did not go away, H went to Thanh Nhan Hospital for examination.
While waiting for the examination, suddenly she fainted and the doctors put in emergency and then transferred to Bach Mai Hospital. After 1 week of treatment at the intensive care unit, Bach Mai H. Hospital has taken its last breath.
The doctor diagnosed H. had a blood infection, multiple organ failure because of the virus . During a week of treatment at Bach Mai Hospital, the cost of treatment for H. is up to VND 300 million because of the expensive modern dialysis costs but in the end H. still did not survive because the bacteria she had acquired were drug.

Antibiotic resistance in Vietnam also rose to red alert levels.
The story of H. pity her friends and colleagues.
In Vietnam, TS. Nguyen Vu Trung, deputy director of the Central Hospital of Tropical Diseases said, in our country, not only one but several "viruses" are resistant to all antibiotics. The most common are intestinal gram-negative bacteria.
Not to mention the risk of spreading multi-drug-resistant "viruses" globally due to increasingly widespread world exchanges. Therefore, antibiotic resistance is a global problem that no country is outside.
Meanwhile, the history of antibiotic inventions and its development process shows that the speed of finding new antibiotics is not timely compared to the increasing level of drug-resistant bacteria.
Accordingly, in the 1940s, the first antibiotic was invented as penicillin, but only 10 years later, there appeared bacteria resistant to this drug.
According to Dr. Nguyen Vu Trung, antibiotic resistance is really alarming to every citizen.
- The danger that people still misunderstand can kill 10 million people every year
- The scary truth about antibiotic-resistant bacteria
- WHO put recommendations on what to do to prevent the spread of resistant bacteria
- Five types of antibiotic-resistant bacteria are particularly dangerous
- The principle you must remember in an age of nightmares 'antibiotic resistance'
- Experts have warned about antibiotic resistance
- New antibiotic resistance
- Vietnam appears to be resistant to all antibiotics
- Bacteria resistant to all drugs discovered in the US
- Bacterial bacteria eat DNA to evolve into antibiotic resistant strains
- Find a mechanism to help bacteria not only resist but also antibiotics
- New bacteria in the nostrils will lead humanity through the era of antibiotic resistance
 The United Nations' all-human warning: All antibiotics are becoming useless
The United Nations' all-human warning: All antibiotics are becoming useless How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics?
How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics? 10 million deaths are one of the startling numbers about 'Antibiotic resistance'.
10 million deaths are one of the startling numbers about 'Antibiotic resistance'. 7 principles when using antibiotics
7 principles when using antibiotics