What is antimatter?
Antimatter is a concept in physics, made up of fundamental antiparticles such as antiparticles, neutron antiparticles, . In theory, if antimatter meets matter, it will explode.
The antiparticle is the particle with the same mass but different from the basic particles that we already know. For example, electrons are also called positrons that have the same mass as electrons but are positively charged.
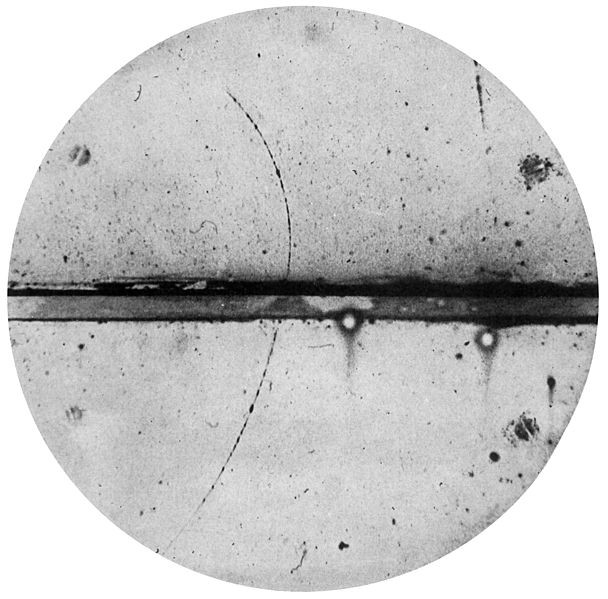
The image of the cloud chamber of the positron was first discovered in 1932.
An antiproton and antiproton can be combined to form an antiparticle molecule in exactly the same way that an electron and proton form normal hydrogen. Therefore, the creation of antimatter and matter will destroy each other like particles and antiparticles, resulting in the release of photons of high energy (gamma rays) or other antimatter-matter pairs. .
Antimatter begins with the imagination of people in the 1930s. Fans of the famous science fiction film Star Trek ("Interstellar Travel") , have known a kind of antimatter. The substance is used as a fuel with high energy to propel spacecraft faster than the speed of light. The most interesting thing is that from the imagination, antimatter becomes reality, and convincing.
Currently, humans have created antimatter such as hydrogen and anti-helium and are very expensive. Antimatter costs about $ 6.25 trillion per gram, the reason for such high costs is because the creation of antimatter is extremely difficult and the demand for antimatter is huge in the medical industry, energy and physical research service.
- The researchers first successfully measured the color of antimatter
- Antimatter bomb - A million-billion-dollar destructive weapon
- Explore the antimatter spacecraft of the future
- Physicists plan to seek antimatter
- The antimatter ring surrounds the earth
- The big mystery about antimatter is about to be explained
- Explain antimatter from the perspective of modern physics
- Uncontrolled antimatter explodes star clusters
- Scientists create matter and antimatter by light
- Antimatter is really meaningful
- Mission refocused gravity
- Neutrino helps explain antimatter?
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people