What will happen when the Sun goes through its entire life cycle?
Our sun looks like a giant balloon that is always on fire, but that is not forever, everything has its limits and the sun is not out of that rule.
If the Sun's life cycle ended, that would have been very bad for life on Earth, everything would have evolved to adapt to darkness or perish forever.
According to a study published in the journal Nature, after the end of its life cycle, the Sun will no longer burn like it is currently , instead the planet will turn into a giant block of quartz, but This quartz will be completely different from what we still see every day.
Before discussing the quartz crystals at this super-massive star, we need to understand how stars like the Sun live.

If the Sun's life cycle ended, that would surely be bad.
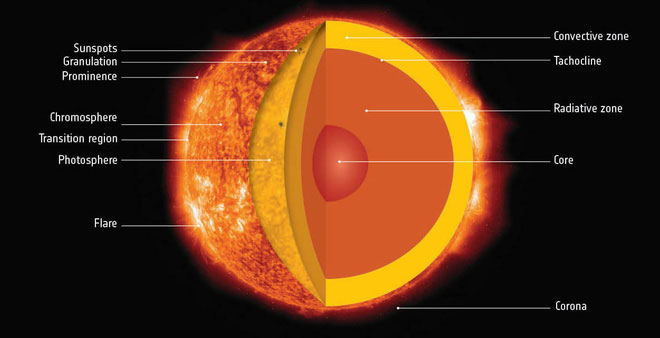
The Sun generates energy through the fusion of atoms, and its massive gravity squeezes and compresses hydrogen atoms together, condenses into helium atoms and releases large amounts of energy. amount and release of tremendous amounts of light and heat.
And as long as there is enough hydrogen fuel to support this process, the size and temperature of the solar core will still be maintained (about 15 million Kelvin). The energy generated by nuclear fusion is radiated to the entire solar system and eventually spawned the evolution of life on our planet.
In the life cycle the Sun experiences, this hydrogen burning period lasts about 90% of the time and stars in this life cycle are called "sequence-sequence stars" . Currently, this period of the Sun has passed 4.5 billion years - about half of its life.
Heavier helium nuclei will begin to unite, maintaining a balance for the Sun.
So what happens when the hydrogen atom on the Sun gets depleted?
Without the external pressure of the energy generated by hydrogen fusion, the Sun's gravity will weigh on its core, which will make the Sun's core smaller and its temperature will be lower. 10 times increase. Heavier helium nuclei will begin to merge and once again exert external pressure to maintain the Sun's balance. It is predicted that this will begin to happen in about 5 billion years and marked by an unexpected energy explosion called "Helium flash" . During helium synthesis, carbon and oxygen are formed, and the core's temperature will return to its original level.
Soon, heavier elements will begin to merge again and cause the Sun to begin to change its appearance. It will begin to swell, intense solar winds will sweep through the interstellar space and the planet's surface layers will begin to flake. However, the mass of the Sun is not enough for it to explode to become a supernova - a transient astrophysical event that occurred in the final stages of stellar evolution in stellar stars. The mass marked the destruction of that star. Instead, the Sun will probably extend beyond the Earth's orbit and burn down our planet.
Then, the remaining gas in the outer layer of this star will be blown into space by the solar wind and ionized into the solar plasma , forming a beautiful planetary nebula. The nebula is rich in newly formed heavy elements and will continue to be used to create subsequent generations of stars and planets. After the outer layer detaches, the rest and core will be hot enough for 5-10 thousand years and called white dwarfs. This is a small star that's high in density and very heavy, but will gradually cool down and cool.
White dwarfs will quench and fade over billions of years, but this is not the end of the story. Researchers at the University of Warwick, UK, stumble upon a secret hidden behind it.

After the deaths of stars like the Sun, it is not over yet.
Immediately after formation, the white dwarf will become very hot, radiating powerful energy from the core of the star of the main sequence ever. Over the billions of years after formation, white dwarfs will slowly cool down and at some point, the oxygen and carbon inside will undergo a change - similar to the freezing of water.
"All white dwarfs will crystallize at some point in their evolution and larger white dwarfs will undergo this process faster," said Pierre Emmanuel, head of the department of physics and research at University of Warwick said.
His team analyzed the observations and measured the brightness and color of 15,000 white dwarfs within 300 light years of the Earth, showing that many stars have only a certain color and brightness. They realized that this group of white dwarfs represents a similar stage in the evolution of stars.
The researchers also discovered that some of these stars lived longer than 2 billion years.
"This is the first direct evidence of white dwarf crystal, or the transformation of a liquid into a solid," adds Pierre Emmanuel.
A crystalline white dwarf is not just a star. When the matter of the white dwarf crystallizes, they will be arranged in a quantum level and the atomic nucleus is arranged in a three-dimensional lattice, forming a metal oxygen core and carbon-rich outer layer.
So, after the deaths of stars like the Sun, their story is not yet over. All white dwarfs will go through this crystallization phase, leaving behind a lot of debris-like stars in the galaxy.
- 8 steps of the Sun before death
- What happens when the Sun fades and swallows the Earth?
- The process of turning the sun's corpse into a glowing nebula
- New finding: The solar cycle affects human life
- Video: Life disorder phenomenon in North America
- Cold in the Middle Ages is returning to Earth
- Trust in time affects your savings
- Close-up of the 'life cycle' of dandelion makes many people surprised
- The life cycle of a protein observed by a single molecule solution
- The process of pupating molting into cicadas
- New forecast on the solar cycle: fewer black spots, but not necessarily less active
- Life cycle of a mobile phone
- What will happen to mankind in 3000?
- Discover the mystery in the sun
- The encyclopedia of life has achieved 170,000 titles
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people