Detected 23 galaxies formed after 800 million years of Big Bang explosion
By using dark energy cameras in Chile, the researchers discovered 23 young galaxies that appeared 800 million years after the Big Bang - the time when the universe was born from darkness.
At this point, the universe undergoes a process called re-ionization . In it, radiating energy from galaxies and the first stars illuminates the surroundings to dispel the mist surrounding young galaxies.
An international team of researchers, including astronomers from Arizona State University (ASU), used dark energy cameras (DECam) to observe galaxies during the dawn of the Universe cylinder.
According to researchers, about 300,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe is dark and filled with neutral hydrogen gas. The first galaxies and stars began to appear in the next half billion years, and when they appeared, ionizing radiation of the space around them caused the universe to change.
It is estimated that this process takes place between 300 million and 1 billion years after the birth of the universe.
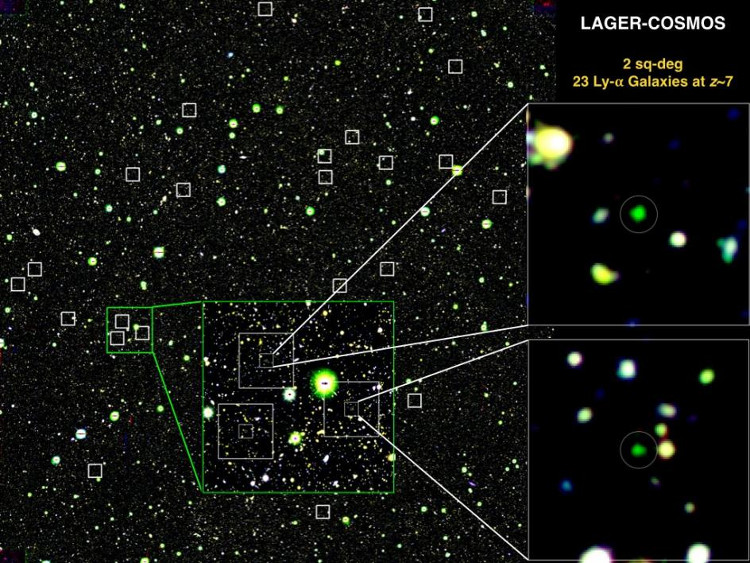
Identifying 23 young galaxies in the universe.(Photo: Zhenya Zheng).
"Before the re-ionization process, these galaxies are difficult to see, because their light is dispersed by intergalactic air, like a car headlight in a fog ," said Professor Sangeeta Malhotra. "When enough numbers of galaxies appear, they dispel the mist, making visibility clearer," the team member said.
According to the researchers, 23 young galaxies discovered by DECam could help better define how the re-ionization process actually took place. DECam has recently been upgraded and equipped with a special narrow band filter designed by ASU researchers.
"A few years ago, we did a similar study using a 64-megapixel camera that covered an area of sky the same as the Moon when it was round. Meanwhile, DECam had a higher resolution. to 570 megapixels and can cover 15 times the area of the full moon in a single image , ' said James Rhoads, a member of the research team.
'We spent several months improving the design of the filter as well as optimizing the camera to get maximum sensitivity during the research', Zhenya Zheng, an astronomer working at the station. Shanghai astronomical observers in China said.
According to the researchers, this is the largest device chosen to be able to observe the time of the dawn of the universe. Malhotra said: "Large-scale surveys have shown that, at the beginning of the universe, common galaxies have low light, while galaxies rarely appear again with intense light. '.
Researchers say that the results of this study could help improve our understanding of the early moment of the universe. According to Junxian Wang, co-author of the study, "the findings in this survey show that most of the first galaxies that were ionized and illuminated for the universe were formed early, less than 800 million years ago. after the Big Bang ".
- The most powerful explosion in the universe after Big Bang
- Spectacular picture of the Big Bang
- Discover the birth of ancient galaxies
- Revealing the first fireworks photo in the universe
- Detecting a bright group of galaxies more than 3 trillion times the Sun
- Detecting exotic galaxies, about 359 million light-years from Earth
- Life evolved through an explosion on earth
- The oldest galaxy formed from 13.55 billion years ago
- Research shows that we all misunderstood the universe
- The knot formed from two galaxies collided
- Unexpected information about the galaxy merged after the Big Bang
- More Cao Bang province has bird flu
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people