Discovering a new giant storm appeared on Neptune
A new storm appeared on Neptune with nearly the same size as Earth is a big surprise for astronomers.
Astronomers have just observed Neptune and were surprised to discover the occurrence of a 9,000 km 2 (equivalent to ¾ diameter of the Earth) storm , as well as spreading up to 30 degrees on the whole chain. the sutra and the declination, so it is very large when compared to the main Star King
The storm is in an area close to the equator of this giant gas planet. Astronomers began to observe from June 26 and July 3 through a telescope at the WM Keck Observatory on Mount Mauna Kea, Hawaii, and they found it getting better and clearer every day.
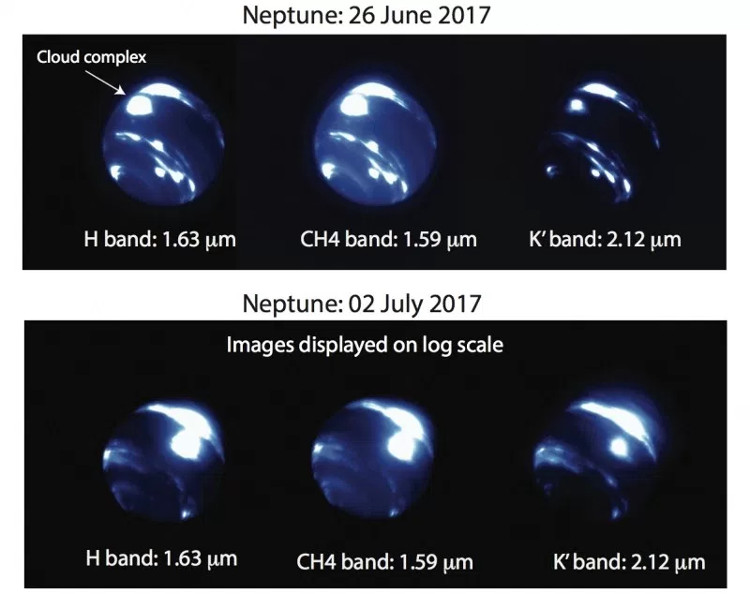
The researchers observed Neptune at Keck Observatory and found a giant, glowing storm cloud in the equatorial equator.Its brightness gradually increases day by day.(Image: N. Molter / I. De Pater, UC Berkeley / C. Alvarez, Observatory M. M. Keck).
'The emergence of a storm in this area is really surprising, because often storms appear only in the two hemispheres and not near the equator like this storm,' graduate student Ned Molter at the University of California, Berkeley said.
In the past, many storms on Neptune were also observed and photographed by professional observers on Earth. The Voyager 2 spacecraft was able to capture the Great Black Storms in 1989, and then the Hubble Space Telescope re-observed and photographed it more clearly in 1994.
Astronomers are still wondering about why big storms occur across a wide area of the hemisphere. Because Neptune is the coldest planet in the Solar System, it has different winds at different latitudes, so storms can be made up of large swirls.
Tornadoes appear everywhere in Neptune's atmosphere, they will intensify as the air warms up, while if the temperature drops, they will condense and form large clouds. This process is similar to Earth, but clouds on Neptune are probably made of methane.
Or another theory given by astronomers, that this storm is a giant convection cloud. Convection will appear to cause the cloud of gas to rise high as the surroundings warm up. Convection clouds were discovered on Saturn in 2010.
On Earth, convective clouds are cumulus clouds or cumulonimbuscus clouds (cumulonimbusc cloud) . Astronomers say that if the storm on Neptune is now convection clouds, it will quickly dissipate about a week later.
'This discovery shows a dramatic change in Neptune's atmosphere, perhaps this is a seasonal weather event that lasts for decades , ' Ned Molter said.
Astronomers will continue to observe this storm again in the fall, to learn more about the storm, see how it is progressing. This study not only gives us a clear view of Neptune's atmosphere, but is more broadly speculated about the atmosphere of exoplanets because most of the planets outside the Solar System are found to be of size. equivalent to Neptune.
In recent years, scientists have been constantly searching for new planets outside the Solar System but because they are too small and far away, they don't know much about them. Understanding the mechanism of Neptune's atmosphere will open up the opportunity to better understand the atmosphere of these exoplanets.
The latitude or the latitude is an astronomical term that refers to one of the two coordinates of a point on a celestial sphere using the equatorial coordinate system. The remaining coordinates are called ascension or longitude.
The latitude is similar to the latitude, projected on the celestial sphere, measured in the north corner, calculated from the equator. Specifically, the declination of a celestial body is equal to the angle between the earth connecting the celestial body and the center of the Earth with the equatorial plane. This angle is conventionally positive when the celestial body is north of the equatorial and negative planes in the south.
Ascension is similar to longitude, measured from a definite method called the spring equinox to the east. Specifically, the equator of a celestial body is equal to the angle between the body connecting the celestial body and the Earth's center with the plane containing celestial polarity and the equinox. This angle is conventionally positive when the celestial body is on the eastern side of the equinox, and the negative when the celestial body is in the west.
- Giant hurricane on the star of the Neptune's sights on Hubble's sight
- Discovering new features of Neptune
- Overview of Neptune
- Rediscover the missing moon of Neptune
- Little is known about Neptune and the legendary love of Galatea
- A new storm appeared on the east sea, storm Pakhar
- A strong storm of level 14 appeared in the South China Sea
- A new storm appeared near the East Sea
- Hai Vuong star has 'eaten' a planet
- The difference between the names of storms
- Can the Mars probe ship be hit with dust?
- The technology of sound transmission through bone
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Mysterious dark spot in Neptune's atmosphere
Mysterious dark spot in Neptune's atmosphere  Unrevealed Facts About Triton - Neptune's Mysterious Moon
Unrevealed Facts About Triton - Neptune's Mysterious Moon  China uses nuclear power to launch a mission to Neptune
China uses nuclear power to launch a mission to Neptune  James Webb Glasses will restart studies of 'ice giants' in our Solar System
James Webb Glasses will restart studies of 'ice giants' in our Solar System  Why Neptune and Uranus have different colors?
Why Neptune and Uranus have different colors?  The 'youngest' planet Earth is stuck with a paradoxical summer lasting 40 years
The 'youngest' planet Earth is stuck with a paradoxical summer lasting 40 years 