Hypothesis of black plate formation on the Moon
By using images taken by pairs of twin-spacecraft GRAIL projects implemented by NASA since 2012, a group of researchers have been able to decipher the origin of the black dimples on the Moon. Accordingly, this may be the result of massive lava eruptions on the ancient Moon, rather than merely being hit by other planets according to the widely accepted hypothesis. .
>>>Close up of 3 mysterious holes on the Moon
For years, people often look up on dark spots on the Moon and imagine it as the image of a man's face. Previously, scientists have shown that the dark spots are the circular basin areas of the volcanic terrain. The largest basin area named Oceanus Procellarum , is thought to form after a strong collision between the Moon and large-size asteroids in space. However, the dimples only focus on one side of the Moon while the opposite face is almost absent. That is the question that scientists have not yet been able to provide a valid answer.
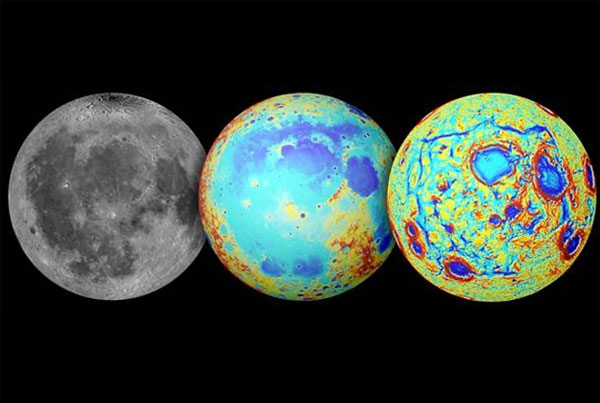
By studying the image captured by twin spacecraft pairs in the Gravity and Structural Recovery Laboratory (GRAIL) project, the team of scientists led by Professor Maria Zuber at MIT discovered that the Large protruding black spots on the Moon are traces of an ancient lava flow with huge masses.
GRAIL is a project launched to understand the origin of the Moon, using pairs of two spacecraft to fly at opposite sides at different distances to measure the difference in gravity of the Moon. The difference in the material density of the Moon will cause a very small change in gravity, which will change the velocity of the spacecraft when flying around. From the results of gravity measurements, the researchers will create an accurate map of the Moon's surface.
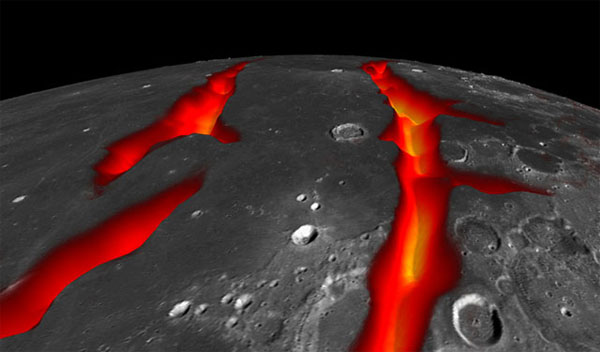
Procellarum is a large circular area of nearly the size of the United States. The current topography of this area with large craters is very similar to the result of a collision with a large asteroid plus meteorites later. However, the results of gravity analysis have shown that not all craters are the result of a collision. Instead, the team discovered that many craters have sharp edges, long-running fractures rather than a smooth circle.
Finally, the team formed a hypothesis that black patches on the Moon were the result of lava eruptions of the Moon billions of years ago rather than merely craters due to collision. touch. The study, published in the latest issue of Nature, raises a wave of public opinion around the world. Hopefully in the future there will be more studies with new approaches with higher accuracy to help people understand more about the Moon, the object always evokes curiosity of people in for thousands of years.
The title has been reset by repository.
- History of Moon formation
- New theory of Moon formation
- The new discovery supports the hypothesis of the formation of the Moon
- New hypothesis about the origin of the Moon
- New hypothesis of cosmic formation
- Revealing the mystery of the dark spots on the moon
- New hypothesis about the solar system
- Explain the phenomenon of Black Moon
- The truth about the strange shadow on the Moon
- Unable to find a more reliable theory than Big Bang
- New hypothesis: Black holes in the universe turn into
- The rare black moon phenomenon will appear on the evening of September 30
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people