Small bowel obstruction: causes, symptoms and treatment
Small bowel obstruction is an uncommon but dangerous disease only after acute appendicitis. Therefore, understanding the disease situation, causes and symptoms will help patients cope and have effective treatment for this disease.
What you need to know about small bowel obstruction
1. What is small bowel obstruction?
Small bowel obstruction is a condition in which the small intestine is blocked by substances in the intestinal lumen, leading to vomiting, abdominal pain, and constipation. This is one of the most unpredictable dangerous symptoms, especially for babies and young children. If not detected in time, it can lead to intestinal perforation, and leakage of gastric contents into the abdominal cavity, causing the contents of the intestine where many bacteria are present, to spread to the cavities of the body. The disease then becomes life-threatening.
2. Causes of small bowel obstruction
There are many causes of small bowel obstruction such as:
- Extra-intestinal causes: Due to adhesions, abdominal wall hernia, intestinal volvulus, intra-abdominal abscess, and intra-abdominal hematoma
- Causes in the intestinal wall: The patient has tumors, stenosis, hematoma in the intestinal wall, intestinal lumen, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Causes in the intestinal lumen: The patient has tumors, gallstones, foreign bodies in the intestinal lumen such as food residues and worms.
Signs and symptoms of small bowel obstruction:
With bowel obstruction, patients often experience pain in the abdomen and abdominal distension. Constant pain, sometimes spasms in the epigastrium or around the navel. When obstructed, the abdomen is often distended, which is due to the reflex of the small intestine
Patients often have vomiting and constipation, defecation. Vomiting is often delayed, if the vomiting is due to an obstruction in the terminal portion of the small intestine. Constipation, defecation is most obvious when all stools in the bowel below the obstruction are enemas removed. When complete small bowel obstruction is in its early stages, it can be difficult to diagnose.
In the case of patients with only partial small bowel obstruction, bowel movements often continue to occur and there are few stools. However, in the early stages of partial or complete small bowel obstruction, both have similar symptoms, so it is necessary to pay more attention to distinguishing them.
When the intestines are blocked, it becomes malabsorption, thus creating fluid to fill the intestinal lumen and increase secretion. The secretions of the stomach, pancreas, and bile also gradually form and accumulate in the intestinal lumen. Fluid can seep through the intestinal wall causing edema of the intestinal wall and may leak into the peritoneum.

Inflammatory bowel disease is the cause of small bowel obstruction.
3. Diagnosis and treatment of small bowel obstruction
Diagnosis of small bowel obstruction
Small bowel obstruction can be diagnosed by the following methods:
Clinical diagnosis method: The doctor will examine and monitor the patient's health status through signs of observation, hearing, touching.
Subclinical diagnostic methods: Including a lot of techniques, but to see the best, the doctor will give x-rays
X-ray image: The X-ray image of small bowel obstruction shows air-fluid levels and fluid retention. The specific sign of intestinal obstruction is the water vapor level. The steam level can be just a little or a lot, depending on the location of the bowel obstruction. The lower the occlusion, the later the patient arrives, the higher the steam level is. In small bowel obstruction, the water level is in the middle of the abdomen. X-ray image of large-legged small bowel loops. The mucosal folds of the small intestine run the entire length of the intestine. The mucosal folds of the small intestine are very close together, except in the ileum. Small bowel obstruction usually has little or no gas.
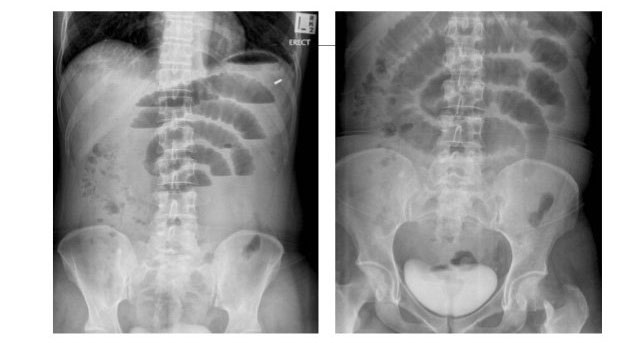
X-rays help diagnose small bowel obstruction.
Treatment of small bowel obstruction
- Medical treatment: For patients with small bowel obstruction due to adhesions or inflammatory bowel disease
- Surgical treatment: For patients with complete small bowel obstruction without any cause or when medical treatment is unsuccessful.
Depression, suicidal thoughts common among high school students during the pandemic
What is fear of ghosts? How to stop being afraid of ghosts?
Strange hair syndrome that can't be combined, disappears on its own as an adult
- There has been a new breakthrough in bowel cancer treatment
- Never let your belly encounter this condition
- Detected two culprit genes causing bowel cancer
- 3 signs that many people often confuse bowel cancer and hemorrhoids
- Aspirin prolongs the life of bowel cancer patients
- Going out several times a day, what is the cause?
- The incidence of bowel cancer increases in China, the US, Australia and Europe
- Going to the toilet - should my gong be flushed and strained or not?
- Prevention and treatment of chronic pancreatitis
- Correctly use An medicine to help save the stroke
- Good news for sick men 'powerless'
- Allergic rhinitis: Causes, symptoms and treatment
 13 causes of non-itchy rash
13 causes of non-itchy rash How the mouse with human ears changed the world?
How the mouse with human ears changed the world? The truth about 'fried rice syndrome!
The truth about 'fried rice syndrome! What is dental implant?
What is dental implant?