SpaceX tested the space shuttle Crew Dragon, which had eight engines
On January 18 (local time), SpaceX Group will launch a non-carrying shuttle Crew Dragon. If all goes well, business opportunities will open up for SpaceX.
10 months after the first successful launch of the space shuttle Crew Dragon , in March 1919, Elon Musk's SpaceX Group (based in California, USA) is preparing to launch a launch. Testing is important.
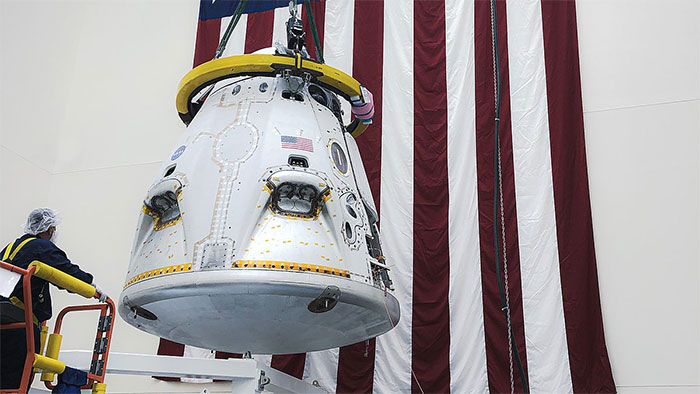
Space Shuttle Crew Dragon - (Photo: SPACEX)
On January 18 (local time), SpaceX will test the space shuttle Crew Dragon (also known as Dragon 2) not carrying people, separating the Falcon 9 launch rocket during the flight to protect the safety of the home. traveling back to Earth.
12 minutes of decision
The test is expected to last 12 minutes under conditions similar to the space shuttle Crew Dragon has been carrying.
1 minute 30 seconds after the launch of the Falcon 9 rocket is the most important moment in the launch process due to the intense pressure acting on the launch missile.
The test this time (at the request of the security partner of NASA) was that the launch failed, the engines of the main missile floor will stop working.
At that time, the 8 SuperDraco engines of the shuttle would perform the task of replacing the shuttle from the malfunctioning rocket (or exploding) and slowly slowing the brakes down and even though it exploded, landing on the surface. sea water, ensuring the safety of astronauts' lives.
In today's test, if everything goes as planned, the space shuttle Crew Dragon will crash into the Atlantic, which will then be recovered by SpaceX. In contrast, the Falcon 9 launch rocket will explode while flying and debris will also fall into the Atlantic.
This test is very important for SpaceX Group. This is the last step for the US space agency (NASA) to nod to allow SpaceX to send astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS).
NASA and Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley are expected to have to visit the International Space Station (ISS) as early as the summer of 2020 on a 14-day mission.
If the test fails, the space shuttle Crew Dragon must wait even an entire year.

Astronauts Bob Behnken (left) and Doug Hurley will board the ISS as early as the summer of 2020 - (Image: SPACEX).
Run against Boeing
The Russian space shuttle Soyuz and China's Shenzhou use the rescue tower as a detachment and safely move away from the launch rocket in an emergency that occurs while on the ground or during flight.
In contrast, SpaceX Group's Space Dragon shuttle uses two types of inboard engines including eight SuperDraco engines and 16 Draco engines.
Liquid-fueled SuperDraco engines can only be used to send the Crew Dragon space shuttle if the launch rocket fails. And the Draco engine is used for orbit operations and direction adjustments.
Since the end of the space shuttle program in 2011, NASA has had to rely on the Russian Soyuz space shuttle to put people on the ISS.
In 2014, SpaceX Corporation signed a contract with NASA to transport astronauts.
Initially, the launch was planned for 2017 but the delay was long. In April 1919, a space shuttle engine explosion resulted in a public tension between NASA and SpaceX.
If SpaceX continues to delay, competitor Boeing will benefit because Boeing has been developing the Starliner space shuttle for six years.

Space Shuttle Crew Dragon will be launched by space rocket Falcon 9 - (Image: NASA).
In fact, Boeing is also struggling. On 20-12-2019, during a test flight without people, Starliner could not fly to ISS due to a computer error.
- SpaceX revealed the Crew Dragon spacecraft interior
- SpaceX tests the spacecraft's escape system
- SpaceX tested new engines to bring people to Mars
- SpaceX successfully launched Dragon 2 ship
- Private ship having trouble in the air
- Discover the first private spacecraft into space
- SpaceX completed the 2nd resupply mission for ISS
- Dragon ship left the launch pad on October 7
- Dragon Train can carry up to 7 people to the ISS in 2016
- ISS becomes the 'spaceship' on Earth's orbit
- SpaceX will bring the supply ship to ISS
- Space shuttle Endeavor completes its final mission
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people