The artificial object rotates 300 billion times every minute
A "dumb-shaped" nanoparticle is powered by the force and light torque that set the world's fastest spinning object record.
Researchers led by Associate professor of astrophysics Tongcang Li from Purdue University, USA created a tiny nanoparticle rotating at an amazing speed of up to 300 billion rounds per minute, half a million faster times the speed of a dental drill, making it the fastest spinning object, as well as the world's most sensitive torque detector.
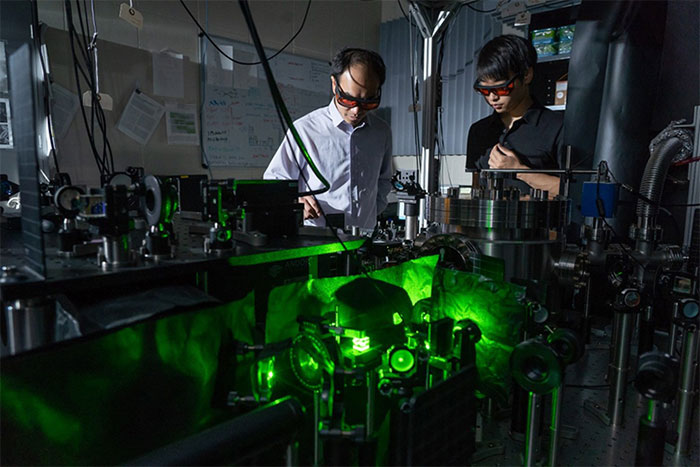

The team uses lasers to spin nanoparticles in a vacuum.(Photo: Newatlas).
The nanoparticle, made of silica (silicon dioxide) , looks like a microscopic dumbbell with two spheres connected to each other when viewed under a microscope. To create the rotation of the object, the team uses only the power of light. They first fired the nanoparticle into a vacuum with a laser, then used another laser to accelerate it, according to research published in Nature Nanotech.
Light particles, or photons, always exert a force on every object they come into contact with. This force is known as the light radiation pressure. Normally, it is too weak (millions of times smaller than gravity) to create any noticeable effect, but in a vacuum with very little friction, radiation pressure can cause an object to move.
In 2018, Li and colleagues created a similar nanoparticle that set a record rotation of 60 billion cycles per minute. The object in the new experiment is about 5 times faster in rotation speed. In addition, it also has the ability to detect torque 600 to 700 times more sensitive than previous tools.
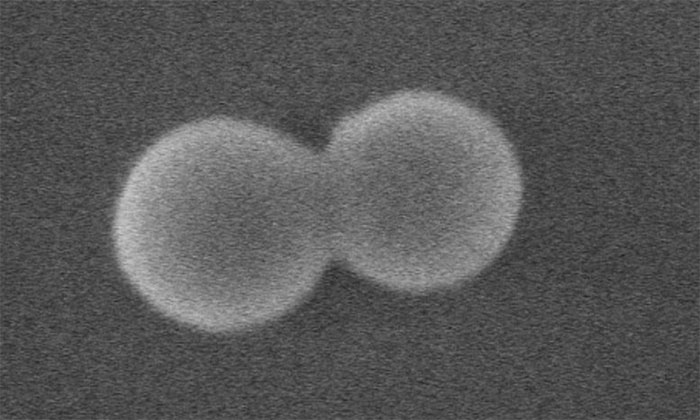
Silicon nanoparticles seen under a microscope.(Photo: Newatlas).
The idea of using light radiation pressure to make object movements is being used to test new methods of operating space engines. Last year, the Planetary Society successfully launched its self-propelled LightSail 2 spacecraft by harnessing the energy of photon particles from the Sun, similar to using a wind-driven sail. to push the boat.
- Method of manufacturing nanoparticles of hard magnetic materials in a simple way
- Successfully fabricated nanoparticles with many cancer treatment drugs
- The mysterious artificial flying object is about to crash into Earth?
- The galaxy cluster is 500 billion billion times heavier than the Sun.
- Why is the Earth rotating?
- New infantry armor: 240,000 rounds per minute
- What would happen if one day the Earth suddenly turned faster?
- Russia solves the object 'E' to explore the Moon
- The artificial brain project receives 2 billion euros
- Pioneer 10 - the mission of the pioneer
- Video: UFOs are 100 times faster than aircraft in Australia?
- The artificial mechanics lift 1,000 times heavier objects, opening the future for robots that are just like humans
- China invested 2 billion USD to build AI research park
- 3D printing artificial leather - a new step for cosmetics industry
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum?