Venus: images of Oxygen, a year of data collection
A year has passed, since April 11, 2006, when the Venus Express spacecraft, the first European exploration ship to carry out its mission to Venus and is the only spacecraft currently flying around the fund. Venus, landing on this planet. From that time, this advanced ship was built to probe one of the most mysterious planets in the solar system that discovered events that were previously a mystery.
Russian and American space probes have made many visits to the star from the 1960s to the early 1990s, Venus has always been a confusing observation target of scientists around the world. . Venus Express was designed and built in time to record by ESA, with the aim of studying Venus - a place no one has ever been since 1994 - in a systematic and most comprehensive way from So far, to have a long-term good influence on the exciting planet is still a mystery.
Using the most advanced operating equipment, Venus Express is conducting research on Venus on a global scale. The space probe collects information on the ever-changing and poisonous atmosphere of Venus (including clouds and strong winds observed from footage captured by onboard VMC cameras) and Its interaction with solar wind and interplanetary environment. Last but not least, people are looking for signs of surface activity such as volcanic activity.
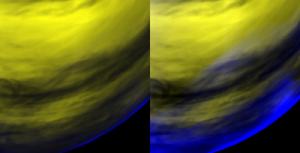
The view of Venus's surface from the south.The horizon seen in the lower right corner of the two pictures is near the equator of Venus.To the left of the top of this photo is about 60 south latitudes, the center of the two photos is located at 130 longitude west.Both images show the phenomenon of oxygen aurora in the atmosphere at night of Venus, only visible at infrared wavelengths.This image was formed by a combination of many colors: blue aurora phenomenon, corresponding to 1.27 micrometers, gold corresponding to 1.7 micrometers and its modulation due to different cloud thickness in different regions. .In the picture on the right, aurora phenomenon appears in the form of an atmospheric structure similar to clouds.In the left-hand image a slightly different color level is used to highlight the halo light on the side of the atmosphere due to the photomultiplier itself.(Photo: ESA / VIRTIS / INAF-IASF / Obs. De Paris-LESIA).
"For a long year of observation, we have collected a large amount of data that we need to explain complex atmospheric secrets such as Venus secrets , " Håkan Svedhem - Scientist of the spacecraft Venus Express project said - "analysis is a great effort of all scientific research groups but clearly responded by the value of research results."
First, the first amazing global images of Venus's southernmost tornado , the first 3D data sets on the structure and dynamics of sulfuric clouds around the planet. The thick screen layer, graphing the temperature of the planet's surface and air at different altitudes from sea level, are just some of the results achieved so far.
'Continuing at the current rate of research, and based on what we can see so far, there is no doubt that the Venus Express spacecraft will help us better understand. about this planet, ' Svedhem added: 'not only is science about the universe generally benefiting from this study but understanding Venus - its climate and atmospheric dynamics will provide a A more comprehensive view of the mechanism that leads to the long-term development of our earth's climate '.
Today infrared ray data can be used to detect oxygen aurora - this phenomenon is detected in the dark area, making the planet light up like a 'space lantern' . "The phenomenon of oxygen aurora was first discovered thanks to ground-based monitoring and also thanks to the observation of other star-star probes such as Russia's Venera spacecraft and Pioneer Venus's spacecraft. America ' - Pierre Drossart, the principal researcher of the VIRTIS department on Venus Express, said, ' However, the comprehensive and detailed image we have is thanks to the Venus Express spacecraft that has never really been word. up to now '.
The fluorescence of aurora is produced when the oxygen atom is present in the 'recombinant' atmosphere into an oxygen molecule (or O 2 ) emitting light. The question is: where does oxygen form?
'Oxygen in the environment is a rare element,' Drossart said. In the high altitude of the atmosphere in the atmosphere, on the daytime of Venus, the intense emission of ultraviolet rays from the sun will break down CO 2 molecules, which is very much present. Much in the air, releasing oxygen atoms. Later, these oxygen atoms are transported by the so-called " solar system " and air circulation " against the solar system " towards the night of Venus. Here, these atoms move from the high air area to the lower layer called ' middle layer ', where they recombine into O 2 molecules. In this way, they emit light at their own wavelength that can be observed by remote sensing from Earth and by Venus Express.

(Photo: Guarniero)
Detecting the aurora phenomenon and being able to keep track of its development in time is crucial because of several reasons:
First , we can take advantage of the dispersal and movement of fluorescent oxygen clouds to understand how the underlying air layer moves and interacts, according to Giuseppe Piccioni, another author of the research group. In this way, oxygen aurora is a true ' sign ' of atmospheric dynamics on Venus.
Second , analyzing this phenomenon will provide new ideas about how the global atmospheric chemistry industry works - a task that is truly challenging and an extensive field of research. By calculating the rate of recombination reaction, in the future we can understand whether there is any mechanism that causes or catalyzes this recombination and knows more about the Birth and recombination of other chemical samples in Venus.
Third , observing the aurora oxygen phenomenon also allows us to better understand the global energy exchange between the central Venus atmosphere - aurora phenomenon appears on the upper boundary of this mid-stratum, with the supernova atmosphere, the higher layer is directly affected by the sun.
Hong Nhung
- Overview of Venus
- 10 most interesting things about Venus
- The Venus probe sent the first images
- Venus suddenly turned slower
- Venus can stay?
- Decode the formation of SO2 gas on Venus's atmosphere
- NASA wants to bring people to Venus
- Venus Experss are about to plunge into the Venusian atmosphere
- Intelligent data collection rain
- Venus is about to be a
- After 8 years of Venus exploration, Venus Express has run out of fuel
- Plan to conquer human Venus
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people