Venus is about to be a
is considered the 'brother' of the Earth because there are many similarities to Earth. However, at present, human knowledge of this planet is quite limited.
The main reason is that projects always focus on the Moon or other stars. Also because it's too hard to "visit" , according to Science magazine.
Previously, after the relentless efforts, the Soviet Union had a robot on Venus but the robot could only "live" for a few hours because it could not bear the pressure and temperature here.
Hope from silicon carbide
Phil Neudeck, an electronics engineer at NASA's Glenn Research Center, is trying to make a technological advance when building a simple robot that conquers Venus.
Previous robots did not tolerate terrible temperatures and pressures on Venus. In particular, high temperatures make silicon - an indispensable component in electronic circuits, losing semiconductors.
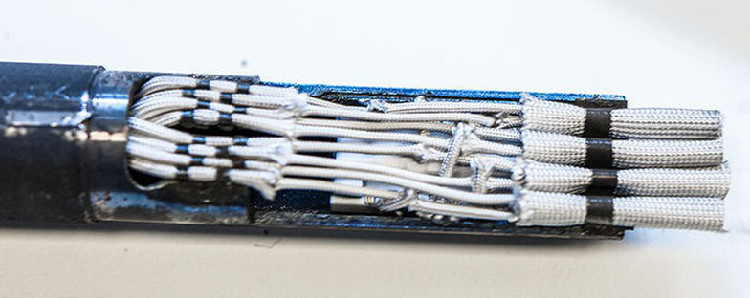
Electronic circuit has a chip made from silicon carbide - (Photo: NASA).
Neudeck happened to notice silicon carbide (SiC), which is used as an abrasive (eg in sandpaper) or as a component of rhinestones.
Specifically, holes in silicon carbide crystals are wider than silicon. This means its electron must absorb much more energy to become a conductor. As a result, it can maintain semiconductor properties at higher temperatures.
With the help of NASA and the Naval Research Office, researchers have found a way to make silicon carbide circuits with a diameter of 150mm and it is still being shrunk.
Neudeck continued to add transistor to the circuit to build a more complex system. Later, the team began developing a complete computer circuit chip from the above sections.
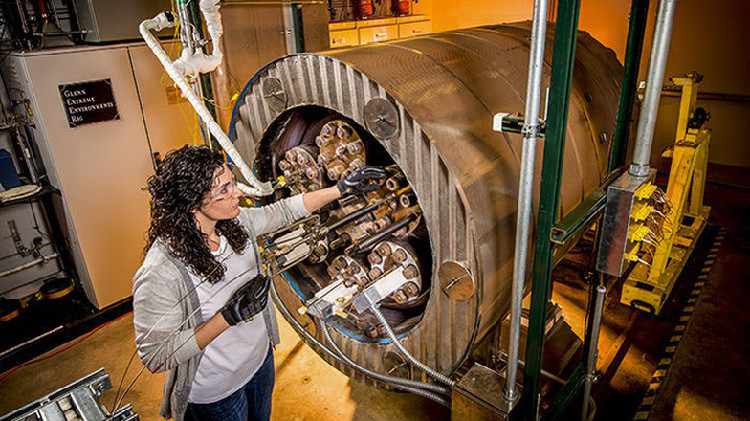

The new chip can operate for 2 months in the Venus atmosphere simulation environment - (Photo: NASA).
Neudeck hopes this robot can survive for months instead of just being able to live for a few hours as before.
"We don't have the fastest processor chip in the world, nor the most complex chip. But in Venus's environment we have the best," Neudeck said.
Its mission is to measure wind, temperature, chemicals, pressure and geological waves on Venus.
The topography of Venus shows that there was volcanic activity here. Scientists believe that Venus once had the same number of volcanoes as Earth, about 167 volcanoes with a diameter of over 100km.
"Guys" strange differences

Venus and Earth - (Photo: NASA).
Venus has longer days . years. One day on Venus (rotation time around the axis) is 243,018 days on Earth. Meanwhile, one year on this planet (the time around the Sun) is only 224.698 days on Earth.
Also, in, and absolutely no natural satellites.
Venus is also the only planet in the Solar System that rotates around its opposite axis with the other planets. Specifically, Venus spins from east to west while other planets rotate from west to east.
On Scientific American page, two researchers Alexandre Correira and Jacques Laskar of CNRS center (France), said that perhaps at the beginning, Venus had a very tilting axis.
They proposed two hypotheses for a special spinning axis. One is because of the chaotic movement of the atmosphere on the planet causing its axis to rotate and then reverse.
The second is the outer thickening of the atmospheric movement, which causes the inner solid structure to be attracted and turned in the opposite direction while the axis of rotation is constant.

Whether Venus is now geologically active is still a question mark - (Photo: NASA).
With an average surface temperature of 462 ° C, Venus is the hottest planet in the Solar System.
Some scientists have suggested that Venus has had oceans in the past, but because there is no carbon cycle to bring carbon back to rock, carbon exists in the atmosphere causing uncontrolled greenhouse effect, causing the crystals get hot and dry.
Finally, Venus's entire surface becomes an arid desert with rocks and dust.
The air pressure on the surface of Venus is extremely large, about 92 times higher than the pressure of sea level on Earth.
- Overview of Venus
- Venus can stay?
- NASA wants to bring people to Venus
- Venus Experss are about to plunge into the Venusian atmosphere
- After 8 years of Venus exploration, Venus Express has run out of fuel
- 10 most interesting things about Venus
- Plan to conquer human Venus
- The ocean may exist on Venus on Earth about 700 million years ago
- Video: Unusual midnight in hell Venus
- Venus has volcanic eruptions
- Century astronomical banquet: Venus passes through the Sun.
- Science explains why Venus has so few volcanoes
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people