7 irreplaceable roles of the Arctic sea ice
Arctic sea ice regulates the Earth's climate through circulation of the atmosphere and ocean currents, providing habitat for humans and animals.
Global warming phenomenon is causing ice in polar regions to melt at unprecedented speed. Scientists think this will greatly affect the environment on Earth, because ice in the Arctic has extremely important roles that cannot be replaced.
Reflection of sunlight

The projection angle of sunlight combined with albedo from sea ice helps keep the polarity cold.(Photo: NASA).
The polar region of the Earth has a cold temperature because it receives less direct sunlight than low latitude. Another reason is because the giant white ice blocks act as reflectors for most sunlight returning to space, according to Mother Nature Network. This reflex is called albedo, which helps keep the two poles cold by limiting their ability to absorb heat.
The narrow area of Arctic sea ice exposes more seawater. The ocean absorbs more heat, causing the ice to melt and albedo to be reduced. This creates a vicious cycle that causes the temperature of the Earth to heat up.
Influence the sea currents
By polarizing air conditioning, Arctic ice has an impact on the weather all over the world. Ocean and air act as heat engines, transporting heat to the poles regularly through circulation of the atmosphere and ocean currents to create balance.
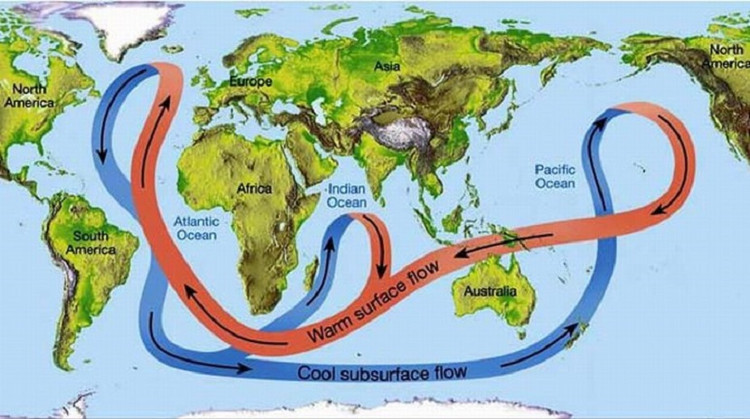
Sea ice affects weather around the world through circulation of the atmosphere and ocean currents.(Photo: NASA).
The reduced sea ice area affects these processes. Warming polar temperatures break down the Earth's overall heat flow, while wind directions change pushing more ice from the Arctic Sea toward the Atlantic Ocean. Here, they will melt into cold water and prevent warm currents from flowing from the tropics.
Insulated with air
The ocean water in the Arctic Ocean is very cold but still warmer than the air in winter. The ice acts as an insulating layer between seawater and air, limiting the amount of heat released. Along with albedo, this is another way to help sea ice maintain the cold climate of the Arctic.
Melted ice or many cracks will form gaps, allowing heat to escape from the sea into the air. About half of the total amount of heat exchanged between the Arctic Ocean and the atmosphere occurs through openings on the ice, according to the US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Limit the release of methane into the atmosphere
Scientists have long known that the Arctic tundra contains large frozen methane gas fields. In 2012, researchers at the Aerospace Agency of NASA's Jet Engine Laboratory discovered a new source of methane emissions in the Arctic, the Arctic Ocean.
In the north of Chukchi and Beaufort, scientists discovered methane rising, but they did not originate from common sources of waste, such as wetlands, reservoirs or industrial facilities. They are not sure why there is methane in the Arctic seawater, but most likely due to bacteria and seabed sediments.

Holes and cracks in the ice could release methane gas from the Arctic Ocean into the atmosphere.(Photo: iStock).
The sea ice is like a surface that separates methane gas from seawater from the air."As the Arctic ice area continues to decline due to the warming of the climate, this source of methane may increase , " said Eric Kort, a researcher at NASA.
Minimize extreme weather
According to NSIDC, loss of sea ice is responsible for the creation of major Arctic storms. The sea ice limits the amount of water vapor rising from the ocean into the atmosphere, making it more difficult to form and develop. As sea ice falls, storm formation is easier and large waves can erode the coast.
Support the life of indigenous people
Many people living in the Arctic mainly hunt seals and other native animals for food. The reduced sea ice area makes hunting more difficult and dangerous.
Offshore, reduced sea ice is considered good news for the oil, gas and maritime industry. However, an increase in these activities may pose specific risks, such as the mass whale death due to sea oil spills.
Habitat of wildlife
Although the Arctic is one of the harshest climates on Earth, there are still many wildlife that live like white bears, seals, snow, foxes, arctic rabbits . Global warming Demand is melting more ice, causing some animals to lose their habitat and lack of food, leading to the risk of extinction.
- Interesting facts about animals living in the Arctic
- Arctic sea ice area is at a record low
- Every second 14,000 tons of water flows into the sea because the Arctic ice melts
- The volume of ice in the Arctic drops to a record low
- The Arctic lost three times as much ice as Belgium every day
- The extraordinary journey of the Arctic fox
- Arctic ice is melting record fast
- Perennial ice in the Arctic is disappearing
- Volcano under the Arctic ice
- Ice in the Arctic is likely to disappear by 2030
- The Arctic temperature is the highest in 44,000 years
- Earth warms, the Arctic will explode vegetation
 Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity?
Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity? Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer
Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer Lightning stone - the mysterious guest
Lightning stone - the mysterious guest Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance
Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance