70% of emerging infectious diseases are caused by animal transmission
Vietnam has been identified as one of the global hotspots at high risk of emerging infectious pathogens.
National and world environmental changes are happening quickly. The risk of emerging infectious diseases and animal-to-human diseases tends to increase.
Vietnam is one of the three countries participating in the Action Package to prevent infectious diseases from animals to people (Vietnam, Indonesia, Senegal). The three countries are the focal point of cooperation with 13 other member states to strengthen detection, prevention and response to public health threats globally.
In recent years the world is facing the risk of emergence and spread of emerging or re-emerging infectious diseases in people, animals and wildlife. These diseases stem from human-animal interactions - ecosystems and are likely to cause immeasurable consequences for human health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 70% of emerging dangerous infectious diseases in humans come from animals. Vietnam has been identified as one of the high-risk global hotspots emerging emerging infectious pathogens including diseases spread from livestock, wildlife or ecosystems.
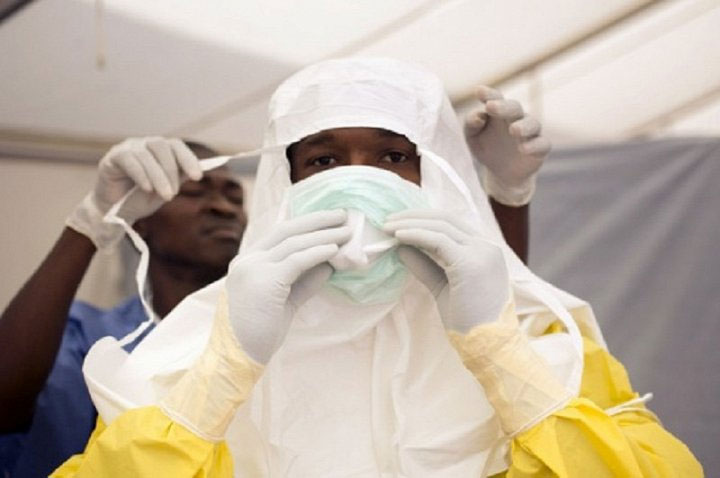
Ebola epidemic in West Africa spreads strongly due to weak health system.
Emerging infectious disease has been reported in Vietnam recently in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS, 2003), avian influenza A / H5N1 in 2003 (mortality rate of about 50%), pandemic flu (Influenza A / H1N1, 2009).
Besides, our country is still facing long-standing infectious diseases such as rabies . Rabies is currently one of the most serious infectious diseases with the leading number of fatal cases in infectious diseases. More than 90% of human rabies cases are caused by dogs. The disease can be effectively prevented by vaccination promptly, properly and in sufficient doses, but every year our country still has about 100 rabies deaths.
Human streptococcal disease is also complicated with the number of cases and deaths every year because the people still keep the habit of eating broth. The clinical situation is severe, expensive treatment, high mortality rates and, if they are, leave many serious sequelae.
With avian influenza A / H5N1, from February 2014 until now, no new cases have been detected. However, the risk of infection from poultry to humans is always present due to bird flu outbreaks in many localities throughout the country and the habit of close contact between humans and animals.
Recently, Vietnam is also at risk of infiltration of some emerging infectious diseases originating from dangerous animals such as Mers-CoV in the Middle East and South Korea, Ebola in West Africa, plague in Africa, A / H7N9 bird flu in China .
- Infectious diseases and unexpected effects
- The main semen is a virus reservoir.
- Special test system for diagnosing infectious diseases
- The reason for infectious diseases is increasing
- Decoding the genome of the mosquito species Quinquefasciatus
- Vitamins and infectious diseases
- Ebola nightmare turned around: 19 people died
- Use geographic zoning techniques to combat the spread of disease
- Prevent pets from spreading infectious diseases to their owners
- 3 dangerous diseases spread from mice
- Debate about children created by three people
- ADB helps Vietnam control infectious diseases
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking