Detecting new black holes with very strong firepower
Astronomers discovered a small but extremely powerful black fire, with two heads emitting a stream of air that stretches 20 light years.
Lead researcher Roberto Soria of Curtin University (Australia) said that to observe the MQ1 black hole in the galaxy M83 , the team of experts including American and Australian astronomers has used a variety of the most modern tools. currently, from Hubble telescope, Magellan, Chandra X-ray observatory, Australian observatory and large telescope.
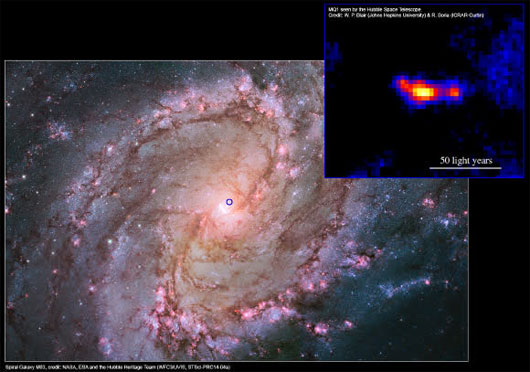
MQ1 is located in the middle of the galaxy M83 blue dot spot (Photo: NASA)
When analyzing MQ1 under normal light, radiation and X-rays, experts discovered that the black hole was smaller than it thought, with a diameter less than 100km.
The M83 galaxy is located about 15 million light-years from Earth, in the constellation of the Serpent.
Like the Milky Way, M83 is a spiral galaxy, and MQ1 forms when a star collapses, with a mass of 5 to 10 times the sun, according to Space.com.
According to expert Soria, MQ1 is a sub-standard, ie, a black hole absorbs matter from a companion star, and possesses two jet currents that emit material stretching across 20 light years.
- Millions of black holes are hiding in our galaxy
- Decoding mistakenly thought that the black hole of the universe is
- Discover the mystery of the most exotic black holes in the universe
- Detecting black holes
- Detecting new gravitational waves from two colliding black holes
- Three huge black holes are about to collide in the universe
- Why can black holes glow?
- Unexpectedly discovered 5 mysterious black holes in the universe
- Detecting black holes 'monsters' 350 million times more massive than the Sun.
- The galaxy has 3 black holes
- Detected stunned the power of the supermassive black holes
- For the first time, two black holes revolved around each other
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people