Half a Billion Year Old Monster Appears Intact, Beautiful as a Bas-Sculpture in China
The monstrous ancestor of three animal families alive today was sealed by a rock in China, keeping his features surprisingly intact.
According to Sci-News , the small monster Wufengella bengtsoni , shaped like an armored club with countless spikes growing in clusters around it, is an extinct worm that lived during the Cambrian period.
It lived in what is now China 518 million years ago, belonging to an ancient group of creatures called tommotiids . Although it was only 1.3 cm long, it was the "great ancestor" of three large groups of creatures that now roam the Earth.
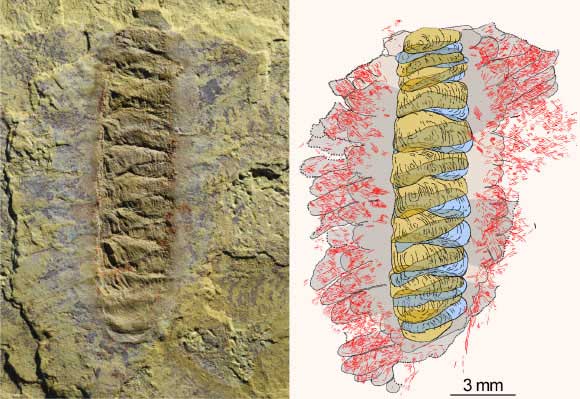
A natural "relief" on a rock in China brings incredible value to paleontology - (Photo: Current Biology)
"It looks like a weird cross between a caterpillar and a mollusk. What's interesting is that it doesn't belong to either group," said Dr Jakob Vinther, from the School of Earth Sciences at the University of Bristol in the UK, a member of the multinational research team.
The surprisingly good specimen of this previously unknown species, unearthed in China, even allowed scientists to identify tiny flat lobes protruding from the sides of the armor, where the hair bundles were attached. The numerous lobes, hair bundles, and shell plates on the back are evidence that the worm was originally divided or segmented, like a modern earthworm.
The animal kingdom includes more than 30 main body patterns, each containing a set of features that make them distinct from one another.
This organism again exhibits several characteristics shared with many of the above groups, demonstrating the rapid rate of evolution in which it is one of the originators, a common ancestor of many species.
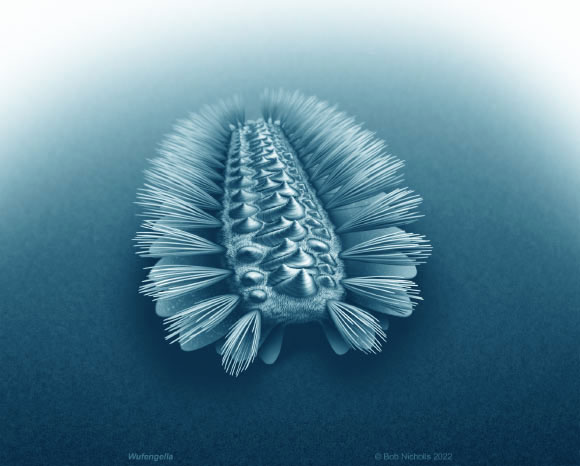
Portrait of a small monster recreated - (Photo: Current Biology).
It also bears features that indicate it is ancestral to the Lophophorata , a general group of horseshoe worms and tiny moss-like animals that are common in the oceans.
The half-billion-year-old worm is also the ancestor of brachiopods, a group of clam-like creatures that live attached to the seafloor and coral reefs.
Its third group of descendants is even more famous – the arthropods. 'Biologists have long noted that arthropods have multiple paired body cavities, unique kidney structures, and bundles of hairs on their backs as larvae,' Dr. Vinther added.
Arthropods, or arthropods , which include more than 1 million different species ranging from tiny mites to insects, are one of the most diverse groups on Earth. And their ancestral link to the bizarre aquatic creatures of the deep sea is truly astonishing.
So this precious fossil specimen has become a rare, unexpected piece of the puzzle, helping to fill in an important segment in the evolutionary tree of Earth's organisms.
The study was recently published in the scientific journal Current Biology.
- Beautiful sculpture amazingly from eggshells
- The 35 million-year-old 'transfigured monster' appears in the Egyptian desert
- Reveal Chinese art origins in carvings
- Overwhelmed with sculptures from the ultimate paper
- China: Found the female body hundreds of years intact
- The tomb of 1,400 years contains a blue monster figure in China
- Loch Ness monster monster appears in China?
- China: 14 billion messages
- The intact ancient city of the lake is incredibly beautiful
- Big foot monster: The truth or myth?
- Go to the forest, frightened to meet beasts
- First discovery of a 'hiccup' black hole: Double ghost!
 Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old
Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China
Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast
Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils
Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils