Methane hydrate and incidents on the sea
AAG fiber breakage on December 20, 2013 affected tens of millions of internet users in the country. The cause is predicted by human impact (anchor ship entangled in optical cable) or due to seismic activity causing the sea floor structure to collapse. However, there is another factor that needs attention.
Vietnam possesses a coastline of thousands of kilometers stretching from the East Sea through the Gulf of Thailand, the coastline pattern receiving a large amount of sediment from the abundance of organic materials. Over time, organic materials gradually shift to the gases that are most typical of methane gases. Deep in the sea where the temperature drops to a certain extent, methane gas molecules change their physical state and turn into another mechanism - methane hydrate or gas hydrate. Normally methane hydrate is formed at a depth of not more than 1,200m from sea level, with a structure consisting of a methane molecule (CH 4 ) surrounded by water molecules.
Exceeding a certain depth, the geothermal heat of the earth's crust gradually grows larger than the low temperature needed to form methane hydrate, which gradually returns to the basic gas of methane. In general, the insertion inside a thick layer of sediment materials has a higher density than methane hydrate above the lighter density methane gas layers below. This structure constitutes a special form that can be recognized on seismic profiles , namely seismic reflections (BSR - Bottom Simulating Reflector) with an inverse reflection amplitude with a parallel characteristic. operating on the sea floor and cutting through organic sediments.
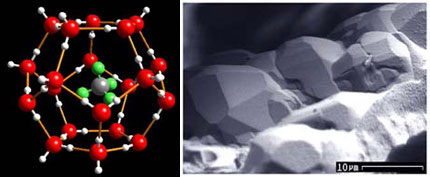
The theoretical structure of methane hydrate and electron microscope imaging
Research on the presence of BSRs on seismic maps will help detect methane hydrate beneath the seabed along the continental shelf. Existing presence of methane hydrate will lead to the following applications: This is a necessary source of fuel (gas) for the future when oil resources are exhausted. In the world, some countries have exploited this fuel source and predicted their location.
Methane hydrate plays an important role in the study of climate change. Warming in the atmosphere will follow the warming of seawater, leading to a return to methane hydrate. Methane escaping into the atmosphere will transform and form carbon dioxide. This gas is the main factor to increase global temperature (greenhouse effect). And so this chain reaction chain is repeated with the intensity of transformation becoming more and more intense.
When the temperature changes, methane will escape to the sea floor and collapse the structure or disturbances on the sea surface. There have been times of mysterious phenomena in Bermuda's 'demon triangle' off Florida (USA), the sudden disappearance of aircraft or ships passing through the region is thought to be due to the sudden escape of methane hydrate below the sea surface. Thereby causing huge whirlpools or abrupt changes in the atmosphere there.
Therefore, when constructing or setting up marine-based systems (drilling rigs, tanks, oil and gas pipelines .) or other works such as fiber-optic cables, electric cables (for example, electric cable to Phu ), The position of these system architectures needs to be studied to stay away from places where methane hydrate is present.
- Experimental new ways to exploit methane hydrate
- Japan exploits natural gas from burnt ice
- Japan is about to exploit gas from
- Gulf Stream warm currents are releasing methane from the sea floor
- Japan obtained about 120,000m3 of gas from the
- Japan drill to prepare to exploit gas in the seabed
- Finding a giant pit in Siberia: The time bomb for our Earth has begun to run
- China discovered large hydrate reserves in the South China Sea
- Japan will promote the development of submarine resources
- Modern mysteries
- Graphene films can turn methane gas into an energy source
- The University of London developed a methane absorption spectrum
 Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity?
Is the magnetic North Pole shift dangerous to humanity? Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer
Washington legalizes the recycling of human bodies into fertilizer Lightning stone - the mysterious guest
Lightning stone - the mysterious guest Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance
Stunned by the mysterious sunset, strange appearance NASA catches biological signs on 1.5 billion year old planet
NASA catches biological signs on 1.5 billion year old planet  Satellite detects 'super pollution' that is warming the planet
Satellite detects 'super pollution' that is warming the planet  Dangerous orange plume covers the planet, UNEP issues urgent report: Action needed now!
Dangerous orange plume covers the planet, UNEP issues urgent report: Action needed now!  Decoding the mystery of the giant 'death hole' in Siberia
Decoding the mystery of the giant 'death hole' in Siberia  NASA robots continuously catch 'unexpected life signals'
NASA robots continuously catch 'unexpected life signals'  NASA found traces of methane gas near a crater on Mars
NASA found traces of methane gas near a crater on Mars 