Nerve cells remember fear
The memories of fear were imprinted in our brains, through newly formed neurons, as a result of new research by neurologists, working at the University of California, Berkeley, USA.
Scientists have long known that fear and intense emotional experiences often leave unforgettable impressions in our minds. The results of this new study are published in the Journal of Molecular Psychiatry, issued on June 14, 2011, by Daniela Kaufer, working at UC Berkeley University, USA and colleagues, this is a broadcast. New to the way in which emotions are remembered: The center that controls the emotions of the brain, the amygdala, affects the hippocampus, a transitional center for memory to create new neurons.
In a situation that scares you, newborn neurons will be activated by the amygdala and may provide a " white area " on which your memory of the situation really scares you. fear can be strongly imprinted. In terms of evolution, this means that new neurons can help you remember things like you were almost killed by a lion.
" We tend to remember events that have given us more powerful emotions than our daily experiences, and for a long time we know that the connections between the amygdala and the hippocampus, help coding these emotions, "said Kaufer, associate professor of integrated biology, a member of the Wills Neurological Institute, UC Berkeley University, USA. " Our study shows that data entering the hippocampus amygdala cause new neurons to be born from one of the original neurons. This provides completely new cells. activated to respond to emotional input. "
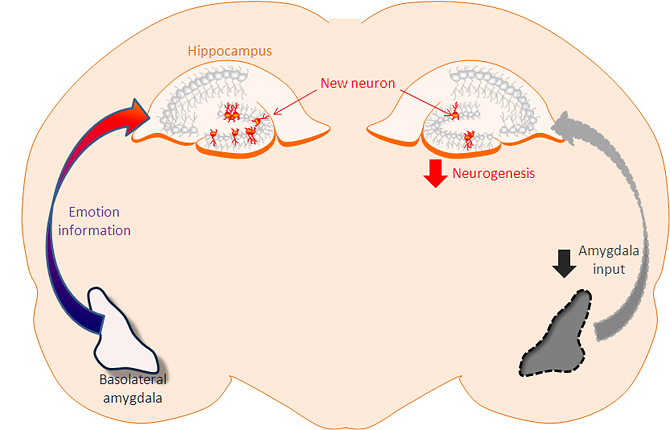
See the section of the rat brain showing how emotional information from the amygdala, helping to develop new neurons from mature neuronal stem cells in the hippocampus (left) . This newborn neuron can be triggered by fear for 2-4 weeks of critical period after birth, helping to record memory, the imprint of the frightening situation that mice encounter. No data entered from the amygdala (right) , the hippocampus region produces less new neurons.
This finding is significant for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder and other problems of memory disorders caused by emotions.
" Many disorders are related to past emotions such as post-traumatic stress disorder, depression and anxiety. We think newborn neurons can play a role in creating make these emotional memories , "Kaufer said.
In 2010, brain researcher Fred Gage, working at the Salk Biological Research Institute, in La Jolla, California, USA, demonstrated the formation of new memories associated with increasing the activation ability of Neurons born about two weeks old in the hippocampus region are originally derived from mature neuronal cells. Adult neuronal cells appear continuous differences to form new neurons, nearly 100 new neurons a day, but half of the newborn neurons are expected. Will die within 4 weeks after being born. But if new neurons are activated, however, as in complex information systems, new neurons will survive and help establish new memories in the brain.
Kaufer, who conducts research on the effects of stress on the brain, knows that many types of positive and negative experiences, such as exercise and stress, affect the rate of neurons in the hippocampus. Along with graduate student Elizabeth Kirby, the study's lead author, Aaron Friedman, was intrigued by the idea that emotions could affect neurons in the hippocampus, since the brain's information center Acquiring emotions, amygdala, is connected to the hippocampus region through many nerve circuits. To test, Kirby focused on the amygdala basolateral, the area of almond-shaped structures to handle negative emotions, including stress, anxiety and fear.
Using experimental mice, Kirby cut and destroyed the basolateral almond nodes and found that the production of new hippocampus neurons was reduced. To be sure the cell damage created when the surgically damaged amygdala did not affect the experiments, the researchers borrowed gene therapy techniques from Robert Sapolsky's laboratory, University. Stanford, USA, puts potassium channels into the amygdala, closing neuronal activity without causing damage. This also reduces neurons in the hippocampus.
Researchers have experimented with the theory of Gage: New neurons are particularly sensitive to emotions first two weeks after they form . Kirby and Kaufer marked new neurons in the hippocampus, created in a 3-day period in a group of mice, and about 2 weeks later they carried out activities that caused fear in those mouse. Later, the researchers continued to endure the mice with fearful situations with the same context the next day. When they examined the brains of the group of experimental mice, they found that the newborn neurons were activated by the scary specific situation. However, when experimental mice destroyed the basolateral amygdala, new neurons were no longer activated in response to fearful memories.
" This study shows that newborn neurons play a role not only in the formation of memory, but also in creating the emotional context of memory ," Kirby said. It also shows that the basolateral almond lymph nodes dominate the ability of newborn neurons as part of emotional memories.
The team is planning to see if other negative stimuli, such as stress and anxiety, are similar to co-operating with amygdala to change nerve cells in the hippocampus.
Co-authors of the study together with Kaufer, Kirby and Friedman are: David Covarrubias, graduate student, UC Berkeley University, United States and students Carl Ying and Wayne G. Sun; Ki Ann Goosens, Associate Professor of Brain and Cognitive Science, works at McGovern Brain Research Institute at Massachusetts Institute of Technology; and Sapolsky of Stanford University, USA.
- How do we remember memories?
- 7 most common fears in the world! Try reading if you have a friend in it?
- Fear of confusion
- 6 ways to help you control fear
- 8 bizarre fears of humans
- Strange fear syndrome that you may be suffering from but don't know how to call
- Detecting brain cells regulating memory
- Nerve cells help form the salivary glands
- Stimulating nerve impulses with nanoparticles
- Transform skin cells into neurons
- Hair follicle germ cells help to recover nerve damage
- Memory of the digestive system helps us remember where we used to eat
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum?