The cause of the fire and how to survive from a scientific perspective
Victims' lives in fire accidents are usually measured in minutes. In many cases, they will have to cope on their own before any rescue units can arrive on the scene.
Formation of fire
Fire is a visible effect of combustion, which exists as a special type of chemical reaction between oxygen in the air and certain substances that act as "fuel".
The first condition of a fire is that the fuel must be heated to the ignition temperature for combustion to occur. Fuel can be solid, liquid or gas.
During the chemical reaction that produces fire, the fuel is heated to the point that gases are released from the surface.
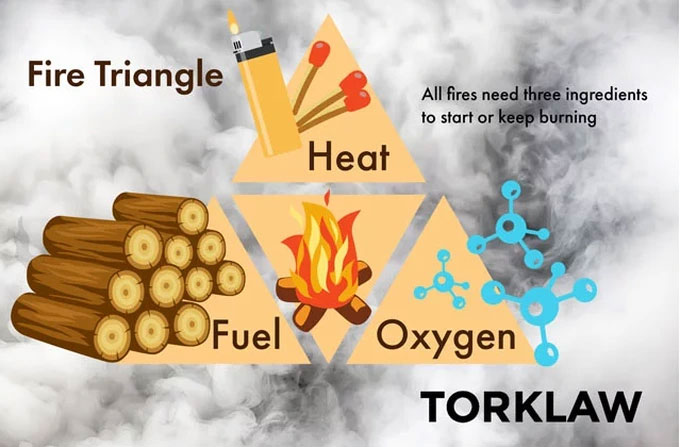
Fire triangle, with the participation of heat, fuel and oxygen.
At that time, a combustion is formed that also releases heat energy. Combustion can be slow or fast depending on the amount of oxygen available. But usually, the burning process produces a very fast, continuous flame.
The danger of a fire is that they will not stop, as long as there is enough heat, fuel and oxygen. These three elements form a "fire triangle". Since the above 3 factors are inseparable, eliminating any one of them can prevent or completely extinguish the fire.
A common method is to use water to water the fire. In some cases, water acts as a heat absorber and extinguishes wood or paper fires.
Small fires can also be easily handled by covering them with a tight blanket. As a result, oxygen is removed from the combustion process, causing them to gradually extinguish.
What kills the victim?

Fire burns and asphyxiation are the main causes of death for the victims.
In large fires, there are usually two main causes of death for victims. It is fire burns and asphyxiation.
The first group of causes comes from burn injuries. These burns are not only caused by fire in direct contact with the human body, but also occur as respiratory burns, when the victim inhales hot vapors into the lungs.
The second group is much more common, which is death from asphyxiation or poisoning. According to Science Direct, fires suck up oxygen, and cover space with carbon dioxide (CO2). This causes the victims to fall into a state of asphyxiation, leading to confusion, disorientation, and even unconsciousness.
At the same time, when the toxic gases directly affect the body, it will cause the body to collapse and die quickly on the spot. The scary thing is that this process of asphyxiation happens very quickly, usually just a few minutes when the body does not have access to an adequate oxygen source.
How to survive the fires?
Victims' lives in fire accidents are usually measured in minutes. In many cases, they will have to cope on their own before any rescue units can arrive on the scene.
Therefore, being aware of the danger and making countermeasures is considered a decisive factor between the life-death boundary. Even in a critical situation, it's important to stay calm, evaluate your options, and don't forget to warn those around you.

Victims' lives in fire accidents are usually measured in minutes.
The simplest thing we can apply, is to use familiar items such as towels, pieces of cloth, or maybe wet clothes themselves. The water molecules and the fabric will help to reduce the impact of toxic gases on the body, and help prevent burns to the respiratory tract.
In addition, the victim should also try to find sources of "clean" air, which means crouching low (because toxic gases tend to rise up high), trying to run against the place where the fire occurred, or to a safe exit.
Absolutely do not hide in the room, in the toilet, or use the elevator because the risk of getting trapped is very high.
In case the fire situation is not yet dangerous and has a large outbreak, you can try basic fire fighting measures, such as using fire extinguishers, water, blankets. In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to moving items. flammable away, and close doors on the way to limit the spread of fire.
If you cannot escape the fire in a high-rise building, quickly move to open and visible areas such as terraces and balconies. This will help you limit smoke inhalation and be rescued faster.
- All things about love from a scientific perspective
- How to survive when jumping from a burning building
- Scientific perspective on apocalyptic hypotheses
- Milk looks from a scientific perspective
- Scientific tips help you survive in life
- Teamwork helps fire ants to die in floods
- Scary 'sparks' in the ocean
- Amazingly huge ants fire floating in the super typhoon in America
- 100 scientific experiments can be done at home
- How was the old man against 'Ms. fire'?
- Things to know about the Fire - The difference between people and things
- Correct response when suddenly caught fire
 The most famous scientific failures in history
The most famous scientific failures in history Mysterious genius mechanic and the machine froze time
Mysterious genius mechanic and the machine froze time The son carries the 'bad gene' of genius Albert Einstein
The son carries the 'bad gene' of genius Albert Einstein Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton