The most beautiful sun is the most dangerous time
Launched into space in February 2010, data obtained from sensitive devices of NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory reshaped what we knew about the solar process and the cause of the current. weather space " space weather ", according to Alan Title, senior specialist working at the Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center in Palo Alto, USA, and a professor of physics working at Stanford University, United States
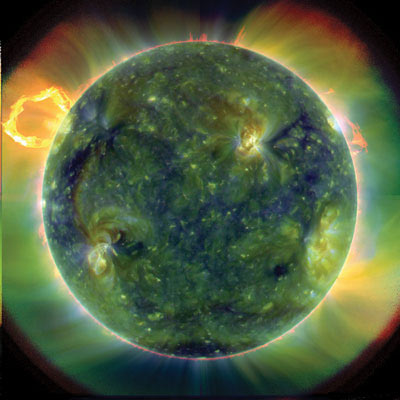
The most beautiful sun is the most dangerous time. It is then that we see the light of the sun shining down on the earth in the form of light in the north and south, appearing when magnetic particles come from the sun hitting the upper atmosphere of the earth. . But in space, the results of the Sun cause harmful weather phenomena: high-energy particles, X-rays and gamma rays emitted from the Sun can harm sensitive electronics, computer, causing accidents and deadly situations affecting astronauts.
Most of the time, the Earth's atmosphere and magnetic fields protect us from violent events that occur in the solar atmosphere, such as explosions near the surface of the Sun or incidents. eruption of large air bubbles from inside the sun (called CMES). Even so, when charged particles from the Sun hit the Earth's magnetic field, the magnetic field is distorted and compressed . The accompanying consequences are a change in the density of charged particles in the Earth's upper atmosphere that can produce significant effects, radio communications can be interrupted, sometimes that change can cause high-energy currents to cause long-term damage in power lines, buried cables and oil pipelines, huge diffusion levels even destroy power transformers and low-voltage power grids.

Fire circle
However, like the aurora screens, solar processes that cause space weather are also stunningly beautiful. The images on the left show a prominent ring-shaped eruption from the Sun's surface, sending a pulse of plasma material out rushing at a speed of about 300 km / s. Before the eruption, this striking sight existed as a relatively cool long tube, material containing magnetism on the visible surface. It is an instability that the cause of what mechanisms are still mysterious. Such mechanisms are important because they can produce CMES, can start up to 10 billion tons of hot plasma into the heliosphere, causing serious consequences for any object, person . on Earth.
One of the main goals of NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory mission is to explore instability mechanisms . To learn more about these mechanisms, and the phenomena they cause, we need to observe solar eruption events as they occur. This is not an easy thing. The spread and eruption of large air bubbles from inside the sun CMES can happen almost anywhere at any time, so we need a surveillance system that can observe the whole The surface of the Sun continuously.
Furthermore, rapid solar explosions at speeds of 1000 km / s, are uncommon, such images must be collected and with exposure time to capture the evolution of events. complicated facts. Sending data from many images to Earth and then distributing them to the scientific community is also very difficult. Finally, there are all the common problems associated with working in space: You only have one chance, so if the device doesn't work, then you can't fix it; All equipment has been carefully selected because it costs £ 200,000 / kg only to start a test, and sensitive devices and computers must be able to withstand extreme weather conditions, with that is to study, without the protection of the Earth's magnetic field.
The results from these tasks were previously provided with an inviting view of how the Sun works. However, this new mission will give us more sun than our predecessor. All previous images of the sun halo were three major limitations. One is that the image does not combine with high spatial resolution, so it is impossible to observe the entire disk of the Sun. Secondly, the instruments cannot take many consecutive pictures because the rate limits of data can be sent to Earth. And finally, because previous devices couldn't capture images on a range of different wavelengths, and at a rate comparable to the development of corona rings, it was impossible to distinguish whether the events The observed event is due to heat, cooling or changing density.
- Admire the beauty of Bac Son at the time of entering the crop
- 10 dangerous flowers
- Beautiful pictures of African images, surprised from above
- Time stopped when we met danger
- 10 most dangerous viruses of all time
- Taking many drugs at the same time is dangerous
- The motorbike line in Phan Thiet is on top of beautiful photos taken from flycam
- Ha Giang yellow sunshine in the early winter days
- The first baby from deadly liver disease thanks to new technology
- Inside the world's most dangerous city
- Watch the most beautiful meteor shower of the year on the morning of December 14
- The reason for 'beautiful boys' refuses to confess
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Top 5 lands where the sun never sets, where 'sunset never reaches'
Top 5 lands where the sun never sets, where 'sunset never reaches'  Rare detailed image of sunspot
Rare detailed image of sunspot  Why are the sun's outer rings so much hotter than the inner core?
Why are the sun's outer rings so much hotter than the inner core?  'Planet 9' left its mark on Earth before disappearing?
'Planet 9' left its mark on Earth before disappearing?  Could the Sun Capture a New Planet, Changing Life on Earth?
Could the Sun Capture a New Planet, Changing Life on Earth?  Mysterious comet flies close to the Sun without melting, leaving scientists puzzled
Mysterious comet flies close to the Sun without melting, leaving scientists puzzled 