Awakening 'dormant' cells helps the brain heal itself
Recently, scientists have discovered a new type of stem cell that can help the brain recover from an injury. It even helps cure dementia - Alzheimer's is common in old age.
This type of cell is named 'G2' stem cell because it is one of millions of sleeping (immobile) cells in our brain. But unlike other cells, this cell has a much greater potential for regeneration. It can create any kind of cell that the body needs.
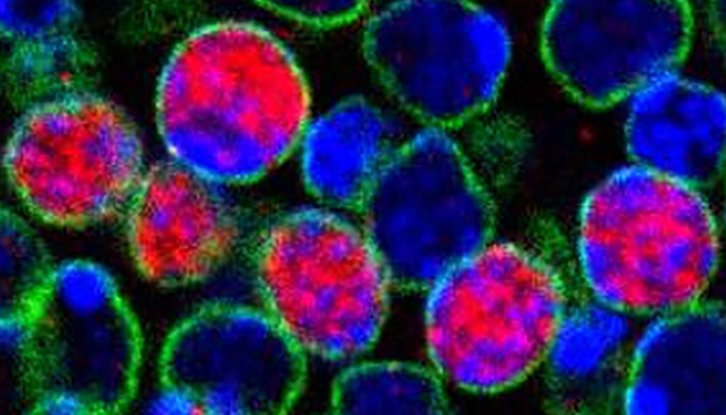
This is one of millions of sleeping cells (immobile) in our brains.
According to two researchers from Cambridge University, UK: "If we can find ways to activate and exploit these stem cells, we can use them instead of complicated surgeries." .
"Although the brain's ability to heal itself is very small, it is possible to find a way to improve this function of the brain in the newly discovered stem cells. The stem cells are in a dormant state when awakened. "It's important to create brain cells. This is the key to developing follow-up research applications , " adds molecular biologist Andrea Brand.
This means that stem cells that are "sleeping" must be awakened from sleep before they are used to create other new cells. However, scientists have yet to find a way to wake them up.
However, the signs of progress are quite good when the study on fruit flies proved that 'G2 stem cells' can be awakened very quickly to start producing neurons, intermediate neurons and Other key cell types in the brain. This fruit fly has a DNA structure very similar to humans with more than 60% of the genetic structure involved in brain diseases. Therefore, experimental research on fruit flies is reliable.
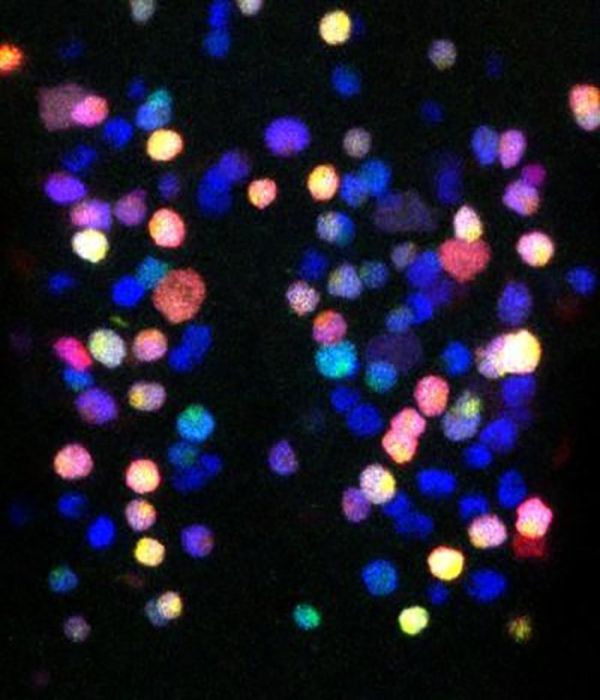
Stem cells begin to wake up in the brain of fruit flies.(Photo: Andrea Brand / Leo Otsuki).
In the fruit fly study, the scientists identified a gene called tribbles that has a key function in controlling G2 cell activity. Scientists believe that there will also be a certain gene that functions similarly to this tribbles gene in humans but at a more complex level.
One of the researchers, Leo Otsuki, said: "We have found a gene that controls hibernation cells to keep them from working. The next step is to study a possible molecular drug. lock this gene to wake up the dormant cells ".
This new study will not only stop inside the human brain because according to scientists, we can find similar types of stem cells in other parts of the body and can control them if find the right chemical signs.
Otsuki said: "We believe that there may be similar silent stem cells in other organs, and this discovery may help improve or develop new regenerative drugs."
There are still many things we don't know about our brains as well as the way they work inside. We don't know how the brain cells are made and where the disease comes from. Once diseases such as Parkinson's (central nervous system disorders) or Huntington's disease (dementia chorea) begin to occur, it is difficult to prevent.
The good news is that science is progressing gradually over time. Although current treatments for brain damage are widely used, research finds that a natural cell within the body is an important contributor to the treatment of future brain damage.
- Sleep helps increase the number of brain cells
- Find out how to heal the heart
- Cell technology breakthrough helps heal large wounds on the skin
- Protein supports the treatment of degenerative brain cells
- Create brain cells from urine
- New vaccine helps the body identify the brain cancer cells
- A breakthrough in transforming skin cells into brain cells
- Shocking facts about the human brain
- Probiotics help heal brain damage
- Human brain stem cells
- Sex helps the brain grow faster
- Discover new brain cells
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking