Common harmful lobster species in the world
Gluttonous nature, earth lobster species become a threat to local animals, ecosystems and irrigation works.
Red swamp shrimp (Procambarus clarkii)
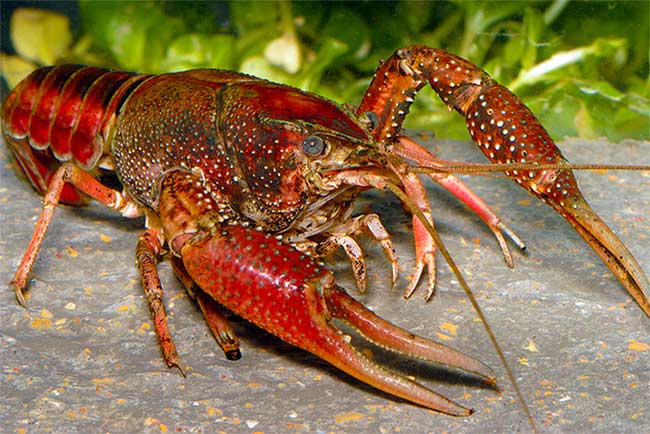

Red swamp shrimp (Procambarus clarkii).(Photo: Flickr).
Procambarus clarkii is also known as Louisiana lobster - native animals in central south America and northeastern Mexico. This is the most widely introduced land lobster in the world, present on every continent except Australia and Antarctica. This species is widely distributed in many US states by being used as bait and released by aquariums.
P. clarkii lives in ponds, marshes, irrigation systems, slow-moving fields or rivers. They are dark red and small dots stick up along the body and a black stripe on the back. Some have blue or blue bodies. Males range from 5 to 12 cm.
P. clarkii usually eats tadpoles, small fish and salmon eggs. They also eat plants that grow at the bottom of lakes and streams. Their activity can cause clear water to become muddy and cause coastal erosion.
In the breeding season, P. clarkii burrows to lay eggs. They are capable of burrowing deeper than crabs, stronger than mice. Their habit of digging burrows up to 2 meters deep can damage dykes and irrigation works. P. clarkii is very aggressive so they can attack native shrimp species in order to scramble for food in the natural environment. This is also an alien species, so the ability to carry pathogens to other species.
Lobster of rusty (Orenectes rusticus)
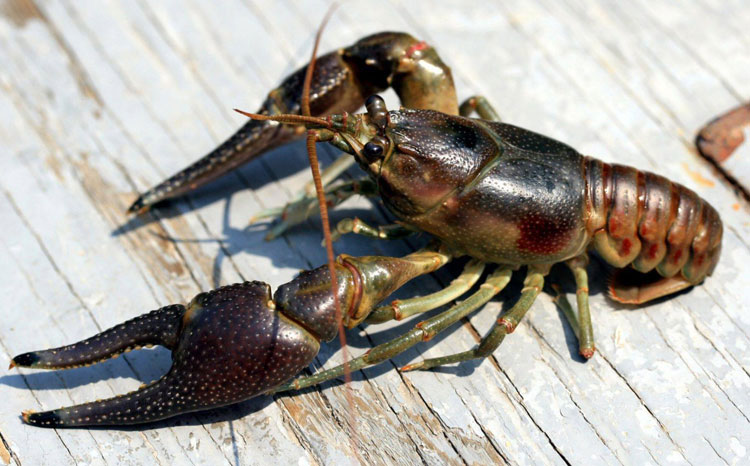

Orenectes rusticus lobster soil.
Orenectes rusticus is native animals on the Ohio River in Ohio, Kentucky, Michigan, and Indiana. They are seen as invasive species in many states from Maine to New Mexico and the Five Lakes region. Like P. clarkii, they also spread through use as bait and released by aquariums. O. rusticus lives in small lakes and streams.
This lobster species has dark iron spots on both sides of the armor. Males are about 10 cm long. O. rusticus has a larger and smoother pair of blue-gray or reddish-brown. The large size and aggressive nature of the O. rusticus turns into prey hunting for native fishes. Thanks to their ability to avoid good predators, their numbers increase extremely fast, becoming invasive species in the northern United States and many areas in Canada. They colonize native habitats, causing many local lobster species to drop sharply in quantity in the past 50 years.
Soil lobster signal (Pacifastacus leniusculus)
Pacifastacus leniusculus, native lobster species in the northwest Pacific, is harming aquatic animals everywhere from Alaska to Japan, Finland and Greece. Nearly 18 cm long and possessing a larger pair, P. leniusculus can easily defeat frogs, fish and other lobster species.

Ground lobster Pacifastacus leniusculus.
This lobster species is not only harmful due to voracious nature but also because they specialize in digging burrows beneath mud, sand and gravel. Their caves alter the stability of the riverbank, the flow of water and the amount of sediment in the water. A study in 2013 found that the quality of spring water became much worse when P. leniusculus started digging burrows and digging sediments in the dark.
Through introduction, P. leniusculus appears in many countries such as Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal , Spain, Russia Sweden, Switzerland, England and even Japan. They are resistant to high temperature fluctuations, high salinity and resistance to major epidemic of lobster soil. They also have a fast reproductive rate, maturity after two years and produce more than twice as many eggs than other lobster species. Currently, P. leniusculus is considered an invasive species in Europe and Japan, dominating native species.
- The truth about the lobster species
- Origin and nutritional value of earth lobster
- The truth about the lobster species
- Origin and nutritional value of earth lobster
- Why does American lobster become one of the most luxurious dishes in the world?
- Lobster lobster 4 is rarely seen
- Rare blue lobster has a net in America
- Lobster grows again in a month
- Decode the mysterious lobster age
- To boil lobster live: Forget it if you're in Switzerland!
- Rare and precious blue lobster is caught by American fishermen
- Finding lobster has 6 fangs
- The world's largest freshwater lobster is about to become extinct
- Catching an unusual 2-color lobster in America
 Animal 'suffering' after hibernation
Animal 'suffering' after hibernation Why do goats climb well?
Why do goats climb well? Scientists were surprised to see chimpanzees eating turtles
Scientists were surprised to see chimpanzees eating turtles Giant catfish died deadly due to drought in Thailand
Giant catfish died deadly due to drought in Thailand Strange species in Southeast Asia becomes the first marine fish species 'extinct due to humans'
Strange species in Southeast Asia becomes the first marine fish species 'extinct due to humans'  Ancient humans may still live on Indonesia's Flores island
Ancient humans may still live on Indonesia's Flores island  The 'dragon' species that was thought to only exist in myths is one of the rarest on the planet.
The 'dragon' species that was thought to only exist in myths is one of the rarest on the planet.  How many animals have ever existed on Earth?
How many animals have ever existed on Earth?  Treasure of Southeast Asia: Rare animal species found in only 9 countries in the world, Vietnam just received good news!
Treasure of Southeast Asia: Rare animal species found in only 9 countries in the world, Vietnam just received good news!  'Ghost humans' discovered leaving 'hybrid offspring' in 3 modern countries
'Ghost humans' discovered leaving 'hybrid offspring' in 3 modern countries 