Dangerous cancer - cause and prevention
Every year, nearly 8 million people worldwide die from cancer. Currently, science has discovered more than 200 different types of cancer, each with its own symptoms, treatments and diagnosis.
What is cancer?
Cancer begins to work when the cells' bodies are constantly being produced by the body and cannot be controlled, leading to the formation of new cells with many abnormal manifestations. These abnormal cells form plaques, large lumps and are often called tumors.
What is cancer, why is it difficult to prevent?
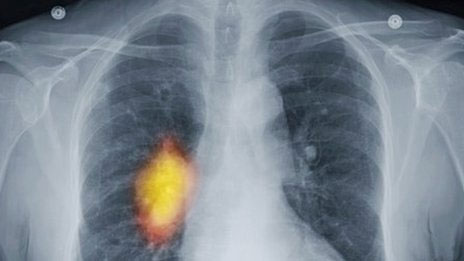
A chest x-ray of a person with cancer, a cancerous tumor in yellow
If the tumor cells do not spread and develop, they are called benign tumors, they are not cancer and can often be removed. Conversely, if cells can penetrate into healthy organs or organs, or spread throughout the body through blood or leukocytes and continue to thrive, these tumors are also called malignant tumors. is cancer. Now the cancer cells will spread faster if the tumor is not treated.
What causes cancer?
Every cell in the human body contains DNA sequences (short for the phrase deoxyribonucleic acid - the genetic material in humans and most living organisms). DNA carries the genetic code of the living organism and performs the activity according to the cell's instructions.
If the DNA in the cells is damaged, the activity instructions will be misleading. In fact, damaging or sudden DNA is a continuous thing in living cells when cells divide or reproduce themselves. Most cells can identify themselves when a mutation occurs then can repair DNA sequences or self-destruct and die.
Video causes and treatments for cancer
When a number of mutations occur in a cell's DNA just enough, the cell's growth control function may be lost but the cells still do not die. Instead, they begin to develop according to unusual instructions that cause them to reproduce and develop, producing more and more mutated cells - this is the first stage of cancer.
There are many factors such as smoking or exposure to sunlight that causes DNA damage - mutation accumulation leads to faster cancer. In addition, a family history of many people with cancer also increases the risk of serious disease, because people themselves have inherited a number of DNA mutations that can cause them to have cancer.
Even when the illness has subsided, cancer is still very easy to grow back. However, in many cases, scientists have yet to find out the exact cause or sequence of events that causes a person to have cancer.
A recent study found that more than 80 genetic markers (ie genetic mutations) may increase the risk of developing cancer such as breast, prostate, or ovarian cancer. Scientists believe that these studies may soon be used as a basis for widespread application of DNA testing to predict and treat cancer variants.
How dangerous is cancer?
Cancer cells can invade other parts of the body, where they can settle and develop to form new tumors with the name of secondary tumors, tumors originally called blocks Primary tumor. Cells spread through blood vessels that can travel throughout the body.
For example, bowel cancer can spread through the intestinal wall itself, it begins to develop on photosensitivity. If the vascular cells can move to other parts like the lungs or brain. Over time, tumors will gradually replace normal tissues.
The spread of cancer cells is called metastasis. Once the cancer starts to spread, the chances of treating the disease usually begin to decrease, because it becomes very difficult to treat with a variety of different pathologies.
Cancer damages the body in many ways. The size of the tumor may affect nearby organs or compress blood vessels or parts around it. For example, a tumor in the pancreas can develop and pinch bile ducts, resulting in patients with biliary obstruction. A tumor in the brain can suppress important parts of the brain causing memory loss, seizures, and a host of other serious health problems.
Cancer is also the cause of a number of other common problems such as loss of appetite and increased use of energy that reduces weight or changes the blood coagulation system in the body leading to deep vein thrombosis.
Why is cancer difficult to treat?
Cancer is one of the most complexly treated diseases. Biologically the types of cancer are very different. For example, skin cancer is different from blood cancer called lymphoma, because there are many different types of lymphoma.
Early surgery is considered the best method to remove cancer-causing tumors. But cancer can still grow again if any disease-causing cells are missed. Cancer may also return if cells break from the primary tumor and form a secondary secondary tumor in other parts of the body before surgery to remove the primary tumor.
And because cancer cells are cells of the human body, many treatments that kill cancer cells are at risk of destroying healthy cells in the living body.
New achievements in cancer treatment
Cancer research scientists are slowly giving up the diagnosis of the origin of the disease by monitoring the locations of abnormal manifestations on the body, because some types of breast cancer may have many characteristics. It is more common with ovarian cancer than other types of breast cancer.
Instead, scientists are looking for ways to study the differences in cancer cells, because a tumor may have 100,000 gene mutations and they change over time. And when identifying the mutations that cause cancer, scientists say they will choose drugs that are more likely to treat each type of tumor individually.
In addition, molecular-level cancer treatments are currently under development. This treatment will prevent the development of cancer by interfering with the genetic and molecular processes especially related to the progress and development of tumors.
Clinical trials using gene therapy are also underway. This experimental treatment involves adding genetic material to human cells to fight or prevent cancer.
- 10 most dangerous cancers of all time
- How to eat to prevent cancer
- Why does cancer attack kill humans?
- Answer 11 common questions about cancer
- The secret of cancer room consists of only 2 things, everyone can do it
- Dangerous skin cancer from habit of using deodorant roller
- You are throwing away the first pharmaceutical preventative cancer
- Prevention of throat cancer
- Men 'peak' enough times during the month will be less likely to suffer from a dangerous type of cancer
- Prevention of prostate cancer, eating a lot of broccoli
- Preventing stomach cancer from coffee
- Cancer will increase strongly in Vietnam in the next 5 years
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking