ESA probe detects water near the surface of Mars
ESA's ExoMars spacecraft discovered "significant amounts of water" hidden under the Martian surface in the Grand Canyon system.
The probe discovered water less than 1 meter from the surface of Valles Mariners, in a huge canyon system stretching more than 3,862km on Mars.
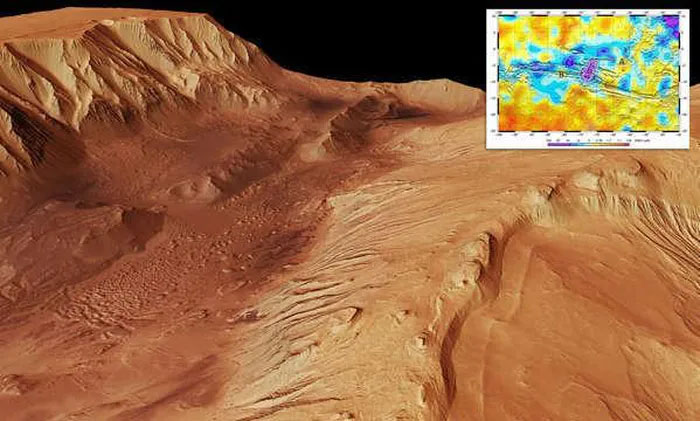
The body of water is less than 1 meter from the surface of Valles Mariners
The watery area is about the size of the Netherlands and overlaps the deep valleys of Candor Chaos.
This is part of a canyon system that scientists say holds promise in the hunt for water on Mars.
"We found that a central part of Valles Marineris contains a lot of water, which is beyond our expectations. This is very similar to closed regions," said Alexey Malakhov, Russian Academy of Sciences, co-author of the study. permafrost on Earth, water ice that exists permanently under dry land because of the constant low temperature".
The researchers analyzed FREND observations from May 2018 to February 2021, mapping the hydrogen content of Mars' soil. FREND reveals an area of unusually large amounts of hydrogen in the massive Valles Marineris canyon system.
Assuming the hydrogen they see is bound to water molecules, the researchers hypothesize, up to 40% of the near-surface matter in this region is water, and most likely exists in the form of ice.
Researchers have long found evidence of water on Mars, but only in the form of deep-earth ice. However, the recent discovery is one of the first to look for water near the red planet's surface.
The first evidence of water on Mars was announced by the US space agency NASA in 2006. It is an image showing the presence of water in two craters Terra Sirenum and Centauri Montes.
On July 31, 2008, NASA's Mars Phoenix lander confirmed the presence of water ice on Mars, containing similar compositions to water on Earth.
The red planet has a number of valleys and river channels that have dried up, and scientists have long looked at the possibility of liquid water flowing there.
NASA's probe is currently walking across Mars to explore Jezero Crater, a lake filled with water about 3.5 billion years ago.
- Detects significant amount of water in the soil on Mars
- Water flows on Mars - the discovery changes the cosmic perception
- The water below the surface of Mars is only 2.5cm: The Dream of the Red Planet is not far away?
- The photos prove there is water flowing on Mars
- Mars contains more groundwater than Earth?
- NASA confirmed that there was water flowing on Mars
- Curiosity is about to drill a third nose on Mars
- The third nose is Mars on Mars
- Mars may contain a giant ice lake
- Is water still below the surface of Mars?
- Mars once existed drinkable water
- NASA launched the Mars probe
 Announced 3 houses on the Moon and Mars
Announced 3 houses on the Moon and Mars Science proves: Mars also knows 'deflated'
Science proves: Mars also knows 'deflated' Elon Musk announced the price for a Mars trip was 11.6 billion VND, free of charge
Elon Musk announced the price for a Mars trip was 11.6 billion VND, free of charge NASA discovered strange 'gate' on Mars, is the hiding place found?
NASA discovered strange 'gate' on Mars, is the hiding place found?