Explain the viability of humanity on Earth
Humans have existed with some of the others, but so far we are the only species alive on Earth.
Answers about the viability of humanity on Earth
According to the BBC, millions of years ago, some species of the Hominin (hominin ) lived together and mostly ate plants. According to researcher John Shea of Stony Brook University in the US, there is no evidence that they hunt large animals.
When living conditions change, hominins begin to migrate from habitat in the forest to the arid savannah and develop the habit of eating meat. The problem is that the animals they hunt are increasingly scarce along with plants, so food shortages often occur and fierce competition causes some species to become extinct.
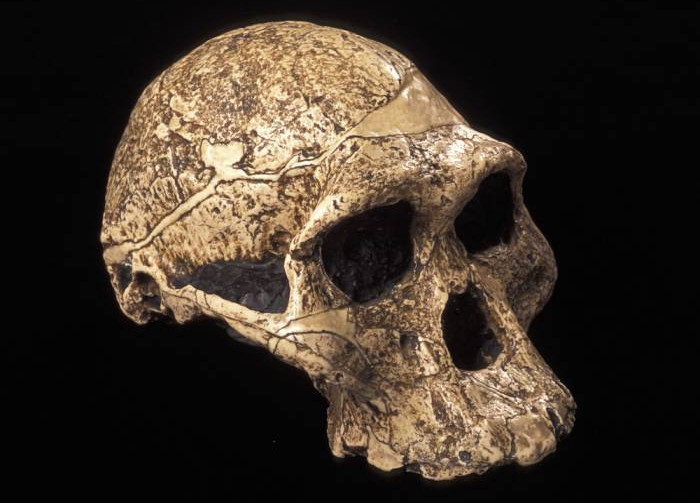
A skull identified as genus Australopithecus.(Photo: Pascal Goetgheluck / SPL).
30,000 years ago, modern people lived at the same time as three other hominins, Neanderthals in Europe and Western Asia, Denisovan in Asia and "Hobbit" in Flores island of Indonesia. Archaeological traces show that hobbits may have been wiped out in a massive volcanic eruption about 18,000 years ago. Meanwhile, the Denisovan traces are very modest, so scientists cannot conclude why they are extinct.
Overwhelms
Archaeological evidence indicates that Neanderthals have been overwhelmed by modern humans . According to Jean-Jacques, Germany's Max Planck Institute for Anthropology, the Neanderthals were soon "occupied" when modern humans from Africa migrated to Europe and this could not be a coincidence.
Neanderthals evolved before modern humans and lived in Europe before we arrived 40,000 years ago. When humans were in Europe, the Neanderthals lived here for more than 200,000 years, long enough to adapt to the cold climate. They wear warm clothes, are excellent hunters and have sophisticated stone tools.
Some scientists argue that when Europe began to undergo a period of rapid climate change, Neanderthals had many difficulties to survive . Specialist John Stewart, Bournemouth University, England, judges that temperature is not the main problem, but colder climates have changed the habitat, while they have not changed traditional hunting ways to adapt.
Compared to modern humans, Neanderthals are more adaptable to hunting in mountain forests. But climate change makes forests more and more and more like African savannahs, where modern people once hunted. Forests that provide staple food for Neanderthals shrink and cannot help them sustain life.

The hobbit skull (left) was discovered in Indonesia.(Photo: Equinox Graphics / SPL).
Modern people hunt more animals, including small animals like rabbits. In contrast, according to an analysis of the archaeological sites of Iberia, where Neanderthals live for the longest time, there is little evidence that they hunt small mammals. Neanderthal tools are suitable for capturing large animals, so even when trying, they can hardly catch small ones.
"When living in a stressful environment, modern people seem to be able to do more. Rapid innovation helps them exploit and achieve greater efficiency in their living environment, and the fertility rate is also higher." , Stewart said, asserting the ability to innovate and adapt could explain why they could replace Neanderthals so quickly.
Social evolution
Neanderthal tools are remarkably effective in some missions, but when it comes to Europe, modern people have better tools, causing more damage. In addition to hunting tools, modern people also create art - features that surpass any species on Earth. Scientists have found evidence that not long after leaving Africa, modern people have crafted jewelry, ornaments, and drawings that symbolize mythical animals and even musical instruments.
"When modern people arrived in Europe, their population increased rapidly," said Nicholas Conard, a researcher at the University of Tübingen in Germany. As the population increases, people start living in more complex social units and have more sophisticated communication and communication ways.
Art traces of modern people in Europe date back about 40,000 years. One of them is a wooden sphinx named Löwenmensch , found in a cave in Germany. Similar sculptures of the same time were found in some other places in Europe.
According to Conard, it shows that we know how to share information from different regional cultural groups instead of keeping to ourselves and art seems to play an important role in life, bringing people closer to people. . In contrast, Neanderthals hunt, cook, go to sleep, maintain breeds, rest and do not need iconic artifacts.
Evolution is often illustrated with images from monkeys-like species to modern humans with a growing brain. But in fact, the evolution story is much more complicated.

Löwenmensch wooden statue is 30,000 years old.(Photo: Alamy).
Homo erectus lived for a long time and was the first hominin to step outside Africa, even before the Neanderthals, but had a relatively small brain. Large brains may play an important role in human success, but Neanderthals also have relatively large brains compared to their body size.
In some cases, living conditions and behaviors may affect genetic characteristics. For example, most Europeans only absorb lactose when our ancestors started eating more dairy products. Genetic changes can also happen when many people face major epidemics like Black Death in the 14th century.
Similarly, Hublin believes that modern people have inherited some important genetic changes. In the first 100,000 exist, modern humans have Neanderthal-like behaviors. However, genetic evidence suggests that our DNA has changed and differentiated after being separated from common ancestors with Neanderthals.
Geneticists determine many points in the human genome and some are related to brain development. Neanderthals have a similarly large brain size, but the development of the brain in modern humans has made a difference.
From language, culture, to war and love, the most characteristic human behaviors are social. In other words, the tendency of human social life has led to the ability to use symbols and artistic creation.
- 20,000 scientists simultaneously warned about the fate of humanity
- The vain assumptions about the day the Earth was destroyed
- Does Earth destroy humanity?
- 80% of the chances of people dying in 2100
- How is the world if people completely disappear?
- Humanity exploits resources beyond the capacity of the Earth
- Which species will 'inherit' the Earth when humans become extinct?
- What if the animal world does not appear?
- Earth Overshoot Day - the time when humanity abused resources exceeded Earth's recovery threshold
- There are many caves on Mars?
- Humanity is alien
- The mystery about the Earth has not been answered
 Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old
Discovered an ancient centipede fossil 99 million years old Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China
Discovered bat-like dinosaurs in China Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast
Discovered a 200-year-old bronze cannon of the coast Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils
Discover 305 million-year-old spider fossils