
A piece of bone accidentally discovered on the shore of a river in Siberia has provided the most modern human genome ever.

According to the British journal Nature, a group of international scientists with Russian involvement confirms that modern humans may be descended from some ancient human species.

Studying the genome of the remains found in the famous Denisov cave today, scientists have determined a 17% coincidence with the Neanderthal gene, another 4% of the hominid gene

Scientists believe they have found the first evidence of mating behavior between Nealderthals and our ancestors.

A relative from Tianyuan Cave: a human being who lived 40,000 years ago seems to be a relative of many Asians and native Americans today.

A new study shows that prehistoric people living in caves draw four-legged animals better than today's artists.

The last mating between Neanderthals was extinct with modern people taking place from 47,000 to 65,000 years ago.

Most Neanderthals are right-handed like modern humans, and this shows the possibility

After analyzing the finger bone fragment gene of an ancient girl, Denisova's hair, skin and eyes were all brown. At the same time, scientists also shed light on genetic

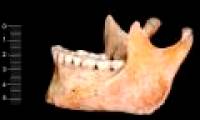
Archaeologists believe that the skulls of two caveman people were excavated in Spain containing the oldest DNA of modern humans. The remains were found by accident in 2006 in the
 A piece of bone accidentally discovered on the shore of a river in Siberia has provided the most modern human genome ever.
A piece of bone accidentally discovered on the shore of a river in Siberia has provided the most modern human genome ever. According to the British journal Nature, a group of international scientists with Russian involvement confirms that modern humans may be descended from some ancient human species.
According to the British journal Nature, a group of international scientists with Russian involvement confirms that modern humans may be descended from some ancient human species. Studying the genome of the remains found in the famous Denisov cave today, scientists have determined a 17% coincidence with the Neanderthal gene, another 4% of the hominid gene
Studying the genome of the remains found in the famous Denisov cave today, scientists have determined a 17% coincidence with the Neanderthal gene, another 4% of the hominid gene Scientists believe they have found the first evidence of mating behavior between Nealderthals and our ancestors.
Scientists believe they have found the first evidence of mating behavior between Nealderthals and our ancestors. A relative from Tianyuan Cave: a human being who lived 40,000 years ago seems to be a relative of many Asians and native Americans today.
A relative from Tianyuan Cave: a human being who lived 40,000 years ago seems to be a relative of many Asians and native Americans today. A new study shows that prehistoric people living in caves draw four-legged animals better than today's artists.
A new study shows that prehistoric people living in caves draw four-legged animals better than today's artists. The last mating between Neanderthals was extinct with modern people taking place from 47,000 to 65,000 years ago.
The last mating between Neanderthals was extinct with modern people taking place from 47,000 to 65,000 years ago. Most Neanderthals are right-handed like modern humans, and this shows the possibility
Most Neanderthals are right-handed like modern humans, and this shows the possibility After analyzing the finger bone fragment gene of an ancient girl, Denisova's hair, skin and eyes were all brown. At the same time, scientists also shed light on genetic
After analyzing the finger bone fragment gene of an ancient girl, Denisova's hair, skin and eyes were all brown. At the same time, scientists also shed light on genetic Archaeologists believe that the skulls of two caveman people were excavated in Spain containing the oldest DNA of modern humans. The remains were found by accident in 2006 in the
Archaeologists believe that the skulls of two caveman people were excavated in Spain containing the oldest DNA of modern humans. The remains were found by accident in 2006 in the



 Do signals from extraterrestrial civilizations detected by Sky Eye really exist?
Do signals from extraterrestrial civilizations detected by Sky Eye really exist? 'City without air conditioning' in China: People don't know what heat is!
'City without air conditioning' in China: People don't know what heat is! The element of the sun god is giving scientists a headache
The element of the sun god is giving scientists a headache Unique Village: Roofs Become Roads for Residents!
Unique Village: Roofs Become Roads for Residents! Top 7 strange psychological effects of the brain that we all have without knowing
Top 7 strange psychological effects of the brain that we all have without knowing Which is the most terrifying bedroom elixir in Chinese history?
Which is the most terrifying bedroom elixir in Chinese history? Earth's core may start rotating in reverse
Earth's core may start rotating in reverse A day in Japan can be up to 30 hours long, does this country live in a different 'timeline'?
A day in Japan can be up to 30 hours long, does this country live in a different 'timeline'?