Garbage - A new threat to the universe
Recently, ISS International Space Station is 15 years old. Experts say the station can still operate for a long time. If something threatens ISS, it is cosmic debris.
Experts say that more and more ISS stations must dodge cosmic debris rushing into its orbit with the speed of the bullet. Cosmic garbage is about the size of a tennis ball to the equivalent of a passenger bus. The weight of large debris can weigh up to 6 tons, while small particles are only a few grams. Clash of large objects can cause chain reactions. In this scenario, at least the most common orbit will be closed at an altitude of about 800km above the earth. Representative of the Space Research Institute Yuri Zaitsev said:
'That scenario will happen, without special measures to prevent pollution and clean up the space environment. This involves not only near-earth orbit, but even geostationary orbits. That is unquestionable. "
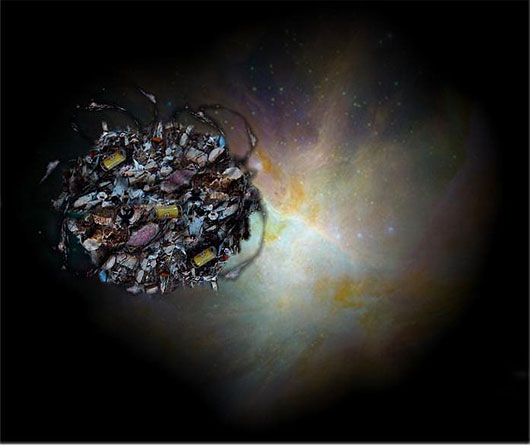
Photo: Flickr.com/sammydavisdog/cc-by
According to some experts, satellites collide and melt into thousands of fragments, which in turn will cause a series of new collisions. However, the editor of the 'Universe News' Igor Afanasyev is not so pessimistic:
'There cannot be such chain reactions. Satellite fragments collide with other satellites to create a giant cloud with different behavior. For the amount of space equipment operating in orbit 800 kilometers high, it can not be said that cosmic garbage here is like an avalanche. The number of satellite launches of this type starts or stabilizes annually or decreases. Because modern satellites have strong enough potential and do not need to be replaced as often as before. Most small orbits in low orbit tend to burn and self-destruct in the atmosphere. Large satellites with propulsion systems can adjust their trajectories. There are databases that allow predicting and adjusting trajectories to avoid collisions. "
To protect the spacecraft with the driver avoiding hitting the debris in space, experts track the movement of cosmic garbage and calculate its flight trajectory. But they only "see" about 15% of garbage objects, ie tracking space debris is not entirely effective.
Meanwhile, scientists from different countries have come up with their own initiatives. For example, Japan proposed cleaning the orbit by using giant metal grids. As planned, the network with linear dimensions a few kilometers will be put into orbit by special method. After the net obtains a large amount of garbage, it will burn itself with the garbage in the atmosphere.
Americans propose to create in the space near the dust cloud from tungsten particles, which will reduce the speed of small debris and entice them to follow. According to project authors, clearing garbage near the earth in this way will take about 25 years. Russian experts are more realistic and ready to build new generation spacecraft that can handle garbage in space.
However, experts doubt the sustainability of the proposed options. Therefore, the amount of cosmic waste is likely to increase. And in the future the mission for ISS will not be easy. But that has no reason to prevent the development of human conquest of space.
- Space waste - threat exists
- Clear up garbage on the vast universe
- Alarm on garbage on the universe
- Electronic garbage - a threat to people
- Turn garbage in the universe into radiation shield
- Russia developed a system to eliminate cosmic garbage
- How does Japan handle garbage security?
- How to sort garbage at home, you know?
- Clearing garbage on the universe
- Which country discharges the most waste into the universe?
- Universe garbage weighs more than 6 tons about to fall to earth
- Hong Kong charged the garbage tax
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people 'Strange smell' detected on cargo spacecraft to ISS
'Strange smell' detected on cargo spacecraft to ISS  After 4 years of being sent into space by Elon Musk, what is the fate of the $100,000 Tesla Roadster now?
After 4 years of being sent into space by Elon Musk, what is the fate of the $100,000 Tesla Roadster now?  The Shape of the Universe Isn't What You Think: From Ancient Round Sky to Modern Three-Dimensional Donut
The Shape of the Universe Isn't What You Think: From Ancient Round Sky to Modern Three-Dimensional Donut  How to get back to the spacecraft if the astronauts leave the cabin to work and accidentally drift away?
How to get back to the spacecraft if the astronauts leave the cabin to work and accidentally drift away?  Announcement of discovery of micro-asteroid population in the Solar System
Announcement of discovery of micro-asteroid population in the Solar System  Solving 'traffic jams' in space
Solving 'traffic jams' in space 