How dangerous is liver fluke infection?
Flukes multiply in the bile ducts, causing pain, inflammation, bleeding, biliary tract cancer, worse than liver abscess .
Flukes are a chronic parasitic disease in the bile ducts, which are infected when eating food containing tapeworms, drinking unboiled water . causing infections. The main hosts of parasitic parasites are humans and some animals such as dogs, cats, tigers, foxes, otters and mice. The vector that transmits the disease is snails and freshwater fish. The flukes are bisexual, with both testes and ovaries. Liver fluke eggs have thin shells, so they exist in a very poor external environment.
Doctor Pham Truong Giang, Head of the General Department of General Surgery, Hanoi Post Hospital, said that eating uncooked foods from fish, snails, vegetables . is an opportunity for infective tapeworm larvae to enter. into the body. First they enter the stomach, duodenum and then back up the bile to the liver, develop into liver fluke maturation, parasite and cause biliary tract disease. Here, adult flukes can parasitize and cause disease for up to decades without recognizing symptoms.
Young flukes will develop into adult worms, laying eggs in the bile ducts. Eggs are excreted in the stool, into the water, develop in a closed cycle and then continue to spread through eating raw food containing cysts.
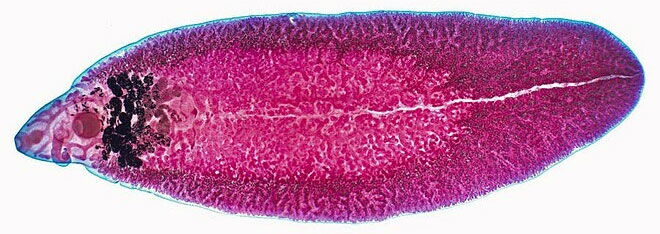
The picture of the parasite is dense in the liver.(Photo: Fine Art America).
Fascioliasis includes small liver fluke and small liver fluke. Small liver fluke has 3 types: clonorchis sinensis, opisthorchis viverrini, opisthorchis felineus. Fascioliasis has 2 types of fasciola hepatica, fasciola gigantica. The incubation period for both types depends on the number of larvae ingested and the host's response. For small liver fluke infection, infection of more than 100 new flukes appears clear.
Flukes of small liver due to parasites in the bile ducts, young flukes will develop into adult flukes, continue to produce, lay eggs in the bile ducts. The size of an adult flukes is only 10-20 mm long and 2-4 mm wide. People infected with flukes are at risk of clogged bile ducts in the liver, leading to initial symptoms such as pain in the liver, digestive disorders, anorexia. Flukes usually cling to bile ducts, use their mouths to suck food, so over time the liver will be scaly spread and degenerative fat. Some cases manifest jaundice depending on the severity of the disease. Flukes, which produce too much in the long run, can cause biliary tract inflammation, bleeding of the bile ducts, and biliary tract cancer.
Fascioliasis is about 20 - 30 mm long and about 5 - 12 mm wide. Because of its large size, in addition to painful expressions such as small liver fluke, large liver fluke can cause liver abscess, causing severe pain. If the abscess bursts into the lungs, it can cause pleural effusion, ectopic parasites such as under the chest skin, lungs . life-threatening. The pathological status of the patient depends on the number of infected flukes, the duration of infection, the location of parasite .
Doctor Giang said that the diagnosis of the first liver fluke was based on clinical symptoms such as fever, hepatic-biliary colic, symptoms of biliary tract inflammation, etc. immune response. Treatment of fascioliasis has many specific drugs such as emetine, dehydroemetine, bithionol, hexachloroparaxylol, niclorofan, mebendazole .
If you are suspected of being infected with a tapeworm infection, you need to go to the hospital to get tested immediately, to prevent the development of the fluke for a long time. The doctor recommends eating boiled and boiled food. Some vegetables, if you want to eat raw, need to be handled very clean to ensure safety.
- Eating habits that can keep you from getting flukes may also lead to liver failure
- Attendance of vegetables that help hand the flukes to nest in the body
- Eating habits that can make you not infected with fluke also have days of losing your liver
- Flukes invade the human brain
- Eating raw fish is prone to liver cancer
- Liver fluke and helminths appear in the south
- Parasitic species attach to the brain to control suicide ants
- List of types of vegetables to help the fluke nest in the body
- Triclabendazole is effective for treatment of large liver fluke
- The first baby from deadly liver disease thanks to new technology
- Using the right amount of coffee can help protect the liver
- Things to know about liver cancer
- Watch out for signs of fatty liver disease
- The worms of the flukes of snail chewed away the human skin
 13 causes of non-itchy rash
13 causes of non-itchy rash How the mouse with human ears changed the world?
How the mouse with human ears changed the world? The truth about 'fried rice syndrome!
The truth about 'fried rice syndrome! What is dental implant?
What is dental implant? Remarkable findings about liver function related to fasting
Remarkable findings about liver function related to fasting  Unexpected link discovered between coffee and liver cancer
Unexpected link discovered between coffee and liver cancer  First successful pig liver transplant to a living person
First successful pig liver transplant to a living person  Developing a new liver in the human body from cell sacs
Developing a new liver in the human body from cell sacs  New discovery: The age of most people's liver is only... 3 years old
New discovery: The age of most people's liver is only... 3 years old  The unexpected reason why skinny people still have fatty liver
The unexpected reason why skinny people still have fatty liver 