How to detect pus meningitis early
Meningitis is a disease that can be encountered at any time of the year. The disease is common in children (especially children under 5 years old). Without early detection and timely treatment will leave sequelae such as deafness, dumbness, nerve damage .
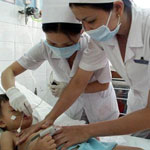 Meningitis is common in children under 5 years old (Photo: Star) Doctor Nguyen Van Loc - Deputy Director of the National Hospital of Pediatrics said that the cause of pleurisy (VMNM) can be germ or virus, headed by Haemophilus Influenzae.
Meningitis is common in children under 5 years old (Photo: Star) Doctor Nguyen Van Loc - Deputy Director of the National Hospital of Pediatrics said that the cause of pleurisy (VMNM) can be germ or virus, headed by Haemophilus Influenzae.
Meningitis: Need early hospitalization .
This type of bacteria causes 70% of cases of childhood meningitis. This disease usually occurs after an infection of the ear, nose and throat area, bacteria entering the meninges and causing VMN.
Besides, VMNM often enters the blood and follows the blood to the focal brain. The disease is common in children (especially children under 5 years old). However, older children and adults may also get VMNM. When the child shows signs of coryza, stiff neck, headache, high fever, vomiting into a hose, headache (with unspoken babies will shake his head back and forth when headache), bulging fontanel (with newborns) , children sleeping should be taken to a medical facility. Children under 3 months of age may not have a fever, but only show breast-feeding, crying or sleeping a lot.
Children with the disease are mostly aged 0-36 months. VMNM is transmitted through respiratory, nasal, saliva, need to isolate sick children. If not detected early and treated promptly. In case of late detection, even if the disease is treated, it still leaves complications such as deafness, paralysis, nervousness, dumbness, dumbness . If detected early, the child will return to normal after being treated cured.
In order to cure and without sequelae, it is necessary for children to be hospitalized early, use strong antibiotics and stay in hospital for many days. While viral meningitis is necessary, antibiotic treatment is required and the duration of treatment at the hospital only lasts 3 to 5 days.
Dr. Loc recommends that VMNM is a very dangerous disease and very expensive to treat, so prevention is very important. Parents can use the vaccine to prevent bacteria Haemophilus Influenzae, pneumococcus.
Even when there is a VMNM happening, parents can still send their children to vaccination because after 3 - 4 days after vaccination, the body has produced antibodies to prevent disease.
On the days of weather changes, to prevent VMNM disease, children should be kept warm, take good care of children at times when weather changes and especially when flu outbreak occurs.
Prevention is better than cure
Treatment should be promptly avoided to prevent children with prolonged nasopharyngitis as well as treatment as soon as the child is drooling. If the child shows signs of flu, fever should be taken to the hospital for immediate treatment. Doctors also note that parents have one thing: Japanese VMNM and Japanese encephalitis are two different diseases. So even though the Japanese encephalitis vaccine was vaccinated, the child could still be VMN.
Vaccination can be started for children at 2-3 months of age or any time in children under 5 years of age according to the following schedule: Children from 2 months to 6 months inject 3 doses each dose 1 month apart, possibly booster at 18 months. Children from 7 months to 11 months inject 2 doses at 1 month interval, can be re-vaccinated at 18 months. Children from 12 to 14 months receive 1 dose and repeat 1 dose at 18 months. Children aged 15-59 months receive a single dose.
- Decode misunderstandings about meningitis
- Many children with meningitis enter the hospital
- Find out how to detect cancer early
- Handbook 'must know' to fight meningococcal meningitis
- The North started season inflammation of the brain and meninges
- Early signs of meningitis
- What is meningeal syndrome?
- Signs of differentiation of encephalitis with meningitis
- Distinguishing brain-meningeal disease
- Many children are hospitalized with meningitis
- Hanoi recorded the first case of dangerous meningococcal encephalitis
- Fungal meningitis continues to spread in the United States
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking Seeds became the 'secret weapon' that helped 4 children in a plane crash survive 40 days in the forest
Seeds became the 'secret weapon' that helped 4 children in a plane crash survive 40 days in the forest  Dangerous diseases that require vaccination from a young age
Dangerous diseases that require vaccination from a young age  If you put babies together without anyone teaching them to speak, will a new language emerge?
If you put babies together without anyone teaching them to speak, will a new language emerge?  The concubines, though favored by the king, had no children: An autopsy revealed the truth!
The concubines, though favored by the king, had no children: An autopsy revealed the truth!  How important are micronutrients to the human body?
How important are micronutrients to the human body?  Ancient Handprints on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Unique Evidence of Human Evolution
Ancient Handprints on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Unique Evidence of Human Evolution 