Huge fresh water is discovered deep below the sea floor
A rare freshwater reserve has been discovered off the southern coast of New Zealand, which can help combat drought and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Fresh offshore offshore groundwater (OFG) was discovered through a combination of seismic and electromagnetic wave scanning techniques, which were used to develop 3D maps of the subterranean aquifer.

This rare freshwater reserve was discovered in southern New Zealand.
While the exact amount of water has not been confirmed yet, the researchers estimate the system can contain up to 2,000 cubic kilometers of fresh water (nearly 480 cubic miles) - the equivalent of 800 million Olympic standard swimming pools or more lakes. Ontario.
These offshore aquifers are locked in rocks, which can be found in many different parts of the world although they are not common. In this case, most of the water is likely left behind after the last three ice ages, the scientists said.
"One of the most important aspects of this research is the improvement in understanding of water management," said geologist Joshu Mountjoy, from the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Administration (NIWA). .
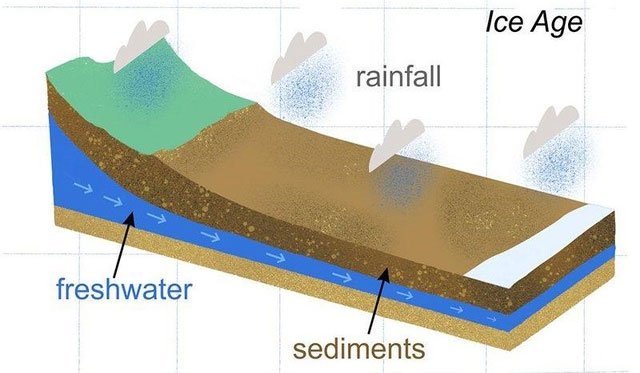
These offshore aquifers are locked in rocks.
Further investigations were started on a research vessel in 2017. The abnormally shallow aquifer is only 20 meters below the sea floor. It can extend about 60km from the coast.
According to the researchers, the same techniques used in this study could also be used to evaluate similar aquifers around the globe.
Local authorities are keen to discover how the newly discovered aquifer can help provide fresh water, without any damage to the surrounding environment or ecosystems that depend on it.
- Huge ice wall along the largest freshwater lake in the Far East
- Discover more fresh sea water in the seabed in Norway
- Create fresh water with solar energy
- 8th graders make devices that turn seawater into fresh water
- Find boiling water in the middle of the cold Arctic
- Unexpectedly discovered 'huge treasure' in the 13m deep hole
- 50% of the world's population lacks fresh water by 2050
- Detecting large groundwater bags
- The 10 most shocking mysteries of the ocean floor
- Turning seawater into fresh water for Truong Sa soldiers
- Video: The scenery on the ocean floor if the water is dry
- Successfully tried the fresh water treatment system in Ly Son
- Don't worry about lack of water even in the desert with this device
- The two boys turned seawater into fresh water thanks to the waves
 Surprised: Fish that live in the dark ocean still see colors
Surprised: Fish that live in the dark ocean still see colors Japan suddenly caught the creature that caused the earthquake in the legend
Japan suddenly caught the creature that caused the earthquake in the legend A series of gray whale carcasses washed ashore on California's coast
A series of gray whale carcasses washed ashore on California's coast Compare the size of shark species in the world
Compare the size of shark species in the world