Laparoscopic knee surgery
When you have arthritis in your knee, suffer from an object of the knee joint, joint pain due to early degeneration . endoscopic surgery is a method that can interfere with these symptoms.
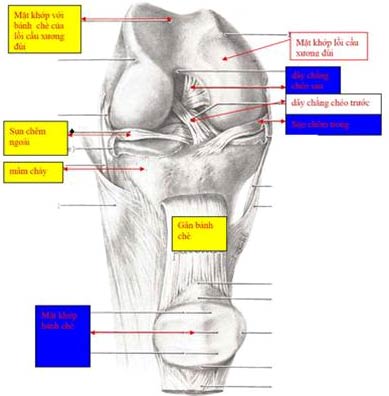
Structure of the knee joint
The knee joint consists of two joints that are the convex joint of the thigh and tibial plateau and the joint between the thigh and tea cake convex. Between the convex joint of the thigh and the tibial plateau, there is a cartilage structure called a cartilage. Clinged cartilage between the cartilage joint of the femoral bridge and the tibial plateau aims to reduce shock when cartilage joints of the femoral convex and tibial plateau are exposed during movement.
On the other hand, wedge cartilage also works to keep the knee joint stable when moving. There are two meniscus including inner and outer warts located in the inner or outer joint cavity.
The knee joint is held on by the inner, outer ligament system and the two front and rear cross ligaments are located inside the knee joint. The frontal ligament has the main effect of keeping the tibial plateau sliding forward and the posterior cross ligament keeping the tibial plateau not slipping back. The outer ligament helps the pillow not bend in, the inner ligament helps the pillow not bend out.
The entire knee is covered by a synovial membrane that acts to produce fluid that fits in sufficient amount to lubricate the movement of the knee joint like a car viscosity. However, the synovial membrane has an anti-inflammatory effect. Once an injury or an infection occurs, the synovial fluid can become thicker, more fluid in the joint makes the knee joint swell. The thickening of the synovial fluid also prevents the drug from penetrating the joint, reducing the therapeutic effect.
(Illustration: NA, TTO)
The role of laparoscopic surgery
In recent decades, with the development of technical branches, small and accurate surgical instruments have been born, including the endoscopic industry. Knee arthroscopy is using a cold light source inserted into the pillow, through a small camera (camera) all images in the knee will be shown on a television screen with a certain magnification. The surgeon will see clearly all structures in the knee joint.
Figure of knee arthroscopic surgery, a hole for camera, another hole used to allow instruments to perform surgical operations. Physiological saline is used to inflate the knee joint.
One or more other small incisions will be made to bring the devices into the knee joint to perform the procedure. The advantage of this type of surgery is that it causes less pain due to the small incision, recovery time earlier, and in some cases more accurate than open surgery. Increasingly, arthroscopic surgery in general and knee joint in particular have more indications. For knee joints, endoscopy can be used to support in the following cases:
1. Used for diagnosis when learning with diagnostic imaging tools does not make an accurate decision. Endoscopy allows the surgeon to see and "touch" the internal structures of the knee joint so that the diagnosis is accurate. Endoscopy is used to verify the reliability of other diagnostic imaging devices.
2. Surgery to cut the cartilage or suture the cartilage is torn when surgery is indicated. So far, it has been proved that endoscopic cleavage surgery is better than open surgery.
A typical symptom of tearing of the cartilage in the knee joint is pain when walking or "getting stuck" in the knee joint, meaning that the patient can bend the knee but cannot stretch the knee and must choose to stretch the knee, sometimes not You can stretch your knees and have emergency endoscopy to cut the cartilage.
3. Surgery to reconstruct anterior cruciate ligament in the anterior cruciate ligament damage of the knee. This is the technique of using a tendon or anemone tendon to replace a broken cross ligament (anterior cruciate ligament does not heal when stitched).
Symptoms of anterior cruciate ligament rupture in the knee joint are painful or unstable when walking. Starting with a knee injury is sometimes not severe but in a rotating position, the knee is swollen, unable to bend or very painful when bending the knee. X-ray films often do not detect anything and are often diagnosed with a knee sprain. Later, the pillow can be folded well but begins to appear painful or unstable, the patient is often "pillow" when walking, up and down the difficult ladder.
Clinical examination is usually found with Lachman or jerk test. An MRI scan usually allows confirmation of the diagnosis but is not mandatory when the visit has clearly seen the symptoms. Breaking the cross ligament first if not treated will damage the knee joint and cause pain.
4. Endoscopy supports the removal of foreign bodies in the knee joint as cartilage fragments in separated cartilage disease.
5. In arthritis-related diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis causes thickening of the synovium, the knee joint is swollen due to effusion, reducing the effect of anti-inflammatory drugs, people use tools and with support of endoscopic circumcision, improving treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs.
6. In simple fractures of tibial plateau or tea wheel, with the help of endoscopy, surgeons can surgically correct and combine bone with high accuracy due to seeing directly the joint surface.
7. Cases of knee pain due to degeneration in the early stages, the cutting of cartilage pieces, the joints are torn due to degeneration, washing the knee joints to prolong the painless time of the knee joint. It is possible to transplant cultured cartilage cells to restore joint surface. This is a surgery that promises to improve in the fight against degeneration of articular cartilage due to old age or for some reason such as trauma . before going to appoint an artificial knee joint.
BS UP HA NAM ANH
Lecturer of Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy
- What is endoscopic surgery?
- 6 signs of pathological warning about joints
- First successful surgery endoscopic endothelial tumors
- The knee can identify the person who replaced the fingerprint
- Causes and treatments for knee pain in the elderly
- The doctor has a surgical method named after himself 'Dr Luong' receiving Vietnamese record certification
- 5 most amazing surgical methods in the world
- Successfully fabricated laser device in laparoscopic surgery
- 12 walking tips for people with knee pain
- The knee throbbed like an electric shock, the woman accidentally discovered a strange disease
- Detection of arthritis by listening to the knee
- The benefits and harms of new 'no touch' myopia surgery in Vietnam
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking