Planetary mystery Vesta
The first images of the asteroid vesta sent from the space probe Dawn were announced by the US Aviation Agency (NASA) on August 1.
The first images sent by Dawn show surprising terrain and some unknown geological features. The chaotic terrain at the South Pole is dominated by a central peak and large trenches extending around the equator.
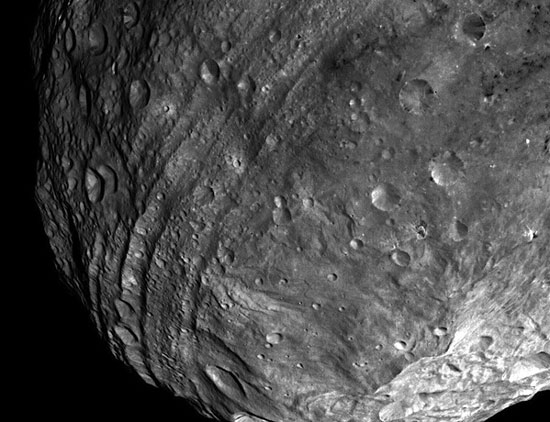
The grooves around Vesta's equator are thought to form after the giant geological vibrations at Vesta's southern pole. Photos were taken at a distance of 5,200km. (NewScientist Source)
Bright spots, black holes and craters are covered by inexplicable black and white streaks. The grooves in the northern terrain seem to be deeper and wider.
Scientists believe that Vesta formed from a cloud of gas and dust that remained after the formation of the sun 4.65 billion years ago in a crystal superfluous explosion.
After leaving Vesta, Dawn will approach Ceres thanks to an innovative ion-propulsion engine that consumes relatively little energy and only speeds up gradually during flight.
NASA spent $ 466 million on the Vesta asteroid exploration project and Ceres dwarf planet for 10 years.
- Asteroid Vesta 'very similar to the Earth
- Vesta is the newborn planet
- Asteroid 800,000km2 fly near the Earth
- NASA explores the abandoned planet Vesta
- Images of two asteroids Ceres and Vesta sent by Hubble
- Little planet with huge mountains
- Revealing mysteries about the Solar System
- The NASA spacecraft first explored asteroids
- Planetary nebula
- Discover new planetary system formed in the universe
- Find a new planetary system containing 3
- Strange planetary system has 3 'Venus'
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people