Some diseases in the common eye socket
Common symptoms of eye sore: swollen eyelids, protruding eyes and double vision (double vision). Sometimes there is both pain and vision loss. In it, protrusion and restriction of labels are the main sign, easy to identify.
The eye socket is a pyramidal cavity, the apex toward the back, the opening extending to the front due to the skull and facial bones. The soft organization of eye sockets does not apply directly to the periosteum but is encased by weight. Thus pathological processes can progress either in or out of weight.
The eye socket organization consists of: a tenon bag wrapped around the eyeball from the edge of the cornea to the optic nerve. From the tenon sack to the eye sockets and the fat organization, there are many fibers that help the eyeball stand in a certain position and is easy to transport when the muscles work; labeled motor muscles include 4 straight muscles and 2 cross muscles; eye socket vein system; lymphatic system. These are factors that keep the eyeball standing in a certain position in the eye socket, when there is a change in the eye socket, it is easy to identify it.
Here are some common eye sores:
Thyroid eye disease (graves disease): causes protrusion
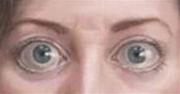
Eye protrusion in graves disease
(Photo: TTO)
eye. Patients often feel painless unless there is an open corneal disease. The eyes of the patient often convex both sides at once. Computerized layer saw thickening muscles but not associated with tendon and muscle damage.
Fake u sore eyes : patients often have pain, fever but the number of leukocytes is normal. Computerized tomography images showed thickening of the motor muscles and associated with muscle tendon damage. Sheaths, eye sockets and lacrimal glands may also be affected. Acute disease usually responds well to systemic steroids.
Ocular cell tissue inflammation : patients often have fever and leukocytosis. Computerized tomography usually shows sinusitis, especially sinusitis.
Eye sores : when examined, the doctor may palpate the eye socket. Eyeballs can be moved away from the tumor position. The lesion is seen more clearly when a computerized tomography is taken.
Injury : such as hemorrhagic hemorrhage, foreign object in the eye socket. Both occur at an injury, but the object may not cause signs in the eye socket for a long time. Therefore, to correctly diagnose, there are a number of support measures such as ultrasound or computerized tomography.
Ocular vascular inflammation : such as wegener granulomatous disease, polyarthritis with nodules . When sick, patients often have signs and symptoms of the whole body, especially in the sinuses, kidneys, lungs and disease skin, patients have fever, blood sedimentation rate increases.
Mucoriasis : disease manifested in the eye socket, nose and sinus disease in people with diabetes, immunodeficiency or systemic weakness. The patient has a high risk of death.
Varicose veins : widening veins in the eye sockets cause protrusion when it is full of blood and dilating. When it is not stagnant, blood is not protruding. Computerized tomography images clearly showed enlarged veins. If a computerized tomography does not show varicose veins and still has suspicious signs, then a vein scan is needed.
When the patient is convex, the eye should be distinguished from the disease caused by systemic disease and the changes of the eye socket caused by false eye protrusion. False eye protrusions may be encountered in the following cases:
Unusual shape and size of the eyeball: severe myopia due to piercing (especially when myopia is on one side). Congenital glaucoma, also known as buffalo eye, water retention eyeball, corneal protrusion or whole feeling - sclera.
- Size and shape of eye sockets on either side due to congenital or after-treatment.
- The amount of fat organization increases significantly in obese people and older people.
In contrast to the convex symptom, the eyeball is normal in size and shape but indentates the eye socket. The corneal peak compared to the outer corner of the eye socket is about 2-9mm shorter than usual. Prosthetic concave is usually in the case of small eyes, small cornea, atrophic atrophy, severe hyperopia, eyelashes or weak patients.
These are some of the eye-related diseases. The clinical situation is extremely diverse. Treatment also depends on the individual pathology in the eye socket. When suspected to have an eye infection, the patient needs to go to the right eye department to determine the right pathology and appropriate treatment.
- iSocket 3G: Ổ power with SIM slot, automatic messaging when power outage
- Symptoms of 5 common skin diseases in the summer
- 8 prone skin diseases in summer heat
- Children often encounter Winter-Spring season and preventive methods
- 5 common diseases that people need to know
- The disease is common in the rainy season and prevention
- Learn and prevent common diseases in the spring
- Common diseases can become
- Deal with 4 common diseases of hot season in young children
- Dangerous diseases Vietnamese people often encounter
- Extremely unique inventions of popular products
- 6 types of diseases are often easily misdiagnosed to other diseases
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking