The secrets hidden in the human genome
Genes are the basic biological unit of genetics, which define physical characteristics on human bodies such as hair color, eye color, face shape . Only certain types of cell genes are always work. When the cell matures, many of its genes will become permanently inactive. Errors in the process of 1 gene can cause disease.
Human genome and unexplored mysteries

It has been more than 15 years since the ambitious $ 3 billion project - the Human Genome Mapping Project - came into operation to decipher the human genome, thereby understanding the causes of disease and find a cure. This project has made a big turning point, facilitating human health studies at the molecular level.
Let us explore some of the many hidden secrets in our genome.
Blood group
Blood is one of the essential components of the body determined by genetic code . Blood type is determined by genes inherited from parents.
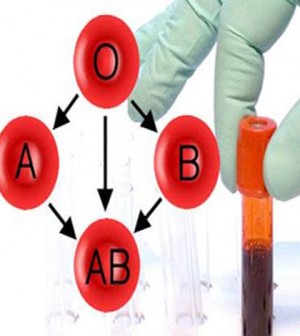
Human blood is divided into several groups - based on a number of specific carbohydrates and proteins on red blood cells. There are 4 main blood groups: O, A, B, AB.
Thanks to scientific advances, it was discovered in each blood group that there were 2 sub-groups called: Secretion and No secretion. In the excretion type, only a saliva test can identify the blood type, because the blood antigens of that group pass through the body fluids like saliva. The type that does not produce excretion requires a direct blood test. In general, the secretion type is able to help the body fight higher disease and adapt more easily to circumstances compared to the non-excretion type.
Sort by Rh system
Rh stands for Rhesus factor. There are 2 types: Rh + and Rh-. In it, Rh- blood type is very rare. In Vietnam, Rh blood group accounts for only 0.4 ‰, while Rh + group accounts for 99.96%.
The characteristic of this Rh blood group is that they can only receive and give to people of the same blood type, especially women with Rh blood type - it is very easy to die.
A woman with Rh- is still able to have a normal child, but if the Rh + husband is born, the baby can be Rh +/-. If the baby is Rh +, then when he is born, he will be in danger because when the baby gives birth to the mother's blood and the baby's will be in contact, then the Rh- mother will create antibodies against her Rh + factor, cancel Red blood cells of the baby and causing severe anemia, can be life-threatening.
Blood type is an important information for blood transfusions, or for the forensic industry. In addition, information on blood types is helpful in preventing and treating many diseases effectively, as well as adjusting the lifestyle to the best of health.
Physical characteristics

All of our physical characteristics are regulated by genes. We inherit genetic traits from parents through 23 pairs of chromosomes containing between 30,000 and 40,000 genes. This genome will regulate height, hair color, eye color, face shape, etc.
Physical characteristics inherited from parents are often described as either dominant properties or diving properties; that is, in a pair of genes there will be one gene with superiority, and if both are present in the genome, the dominant gene will express its characteristic through body characteristics.
Family history and ancestral lineage

Each family's history is recorded in the genome distributed on chromosomes . The types of cells in the human body have 46 chromosomes, combined into 23 pairs, containing all of a person's genetic information. The fact that the baby inherits a chromosome from a parent is completely random, but modern DNA testing techniques can now determine a person's parent with an accuracy of 99 , 9%.
Genealogy is a study of science, observing the changes in the genome of a certain population over time from hundreds to thousands of years. From these studies about the time of 60,000 years ago, we will find that all races share the same ancestral origin as a group of people in Africa.
Currently, there are many private companies that provide genetic screening services for ancestors for individuals wishing to identify their lineage.
Genetic disorders
Genetic disorders, or genetic diseases, are caused by adverse mutations in DNA. Some common mutations are Down syndrome , cystic fibrosis, and some types of cancer. Thanks to the human genome decoding work, scientists have initially identified the cause of some mutations, but there are still some other diseases that are still unknown.
Genetic disorders are generally divided into 4 groups: gene mutations, chromosomal mutations, multi-factor disorders, mitochondrial disorders. In particular, gene mutations are disorders that occur in a single gene; Chromosomal mutations are abnormalities that occur in some chromosomes, or when a chromosome is lost or duplicated; Multifactorial disorders are changes that occur due to many genetic causes, including external causes such as frequent exposure to toxic chemicals. Many types of cancers, such as breast cancer and colon cancer, are classified as multi-factor disorders. Mitochondrial disorders are quite rare, but are quite dangerous, and affect many internal organs and nerve functions.
Relationship with other species
Decoding the human genome map provides the basic data for many studies of human-to-primate linkages, especially the association with chimpanzees, and many other animals. .
 Orangutan Gina is the first primate belonging to a family of people who, besides humans, are also confirmed to undergo menopause.(Photo: Daily Mail)
Orangutan Gina is the first primate belonging to a family of people who, besides humans, are also confirmed to undergo menopause.(Photo: Daily Mail)
The human genome has a similarity of 98% compared to large primates , and 85% compared to mice. Although the level of similarity is so great, there are still huge differences in thousands of other genes that lead to many important differences.
Middle-aged diseases
Current genetic tests give us many opportunities to learn and predict the health status of ourselves in the future. In other words, thanks to these tests, we know in the future whether we have certain diseases related to the genome that we own.

For example, BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are usually genes that control and prevent abnormal cell division; That means they help the body prevent the growth of tumors. However, if there are some unfavorable mutations in these two genes, the owner is likely to have a higher chance of developing breast cancer.
In addition, there are many other genes that are thought to be associated with many different types of cancer . The interaction and behavior of these genes has not yet been determined, but the discovery of these genes through genetic tests can help us take precautions such as a regime. Eating appropriately, taking vaccines, or even conducting surgery in the tissue area is at risk of developing tumors before the toxic tumor can form.
Pharmaceutical genetics
With the current medical achievements, there is a concept of much interest that is ' personal medicine a little'. Genetic pharmacies will study the individual's genetic profile, checking how each individual's response to different drugs will determine the dose and treatment accordingly. .
Although there have not been many significant breakthroughs yet, the genetic pharmaceutical industry promises a potential future along with the development of gene technology and widely used genetic tests.
Gene therapy
Gene therapy is a treatment by introducing genetic material (DNA or RNA) into cells to compensate for old genes that cause disease or produce useful proteins, to fight disease, instead of cure. Traditional treatment is medication or surgery.
Researchers are testing a number of directions for gene therapy, including:
- Replace the disease gene (mutant gene) with a copy of a healthy gene
- Destroy the mutant gene completely
- Bringing a new gene into the body helps fight disease
Although gene therapy is a promising treatment option for a number of diseases (including genetic diseases, certain types of cancer, and viral infections), this method is still potentially dangerous and needed. More research is done to make sure this technique is safe and effective. Currently, gene therapy is only being studied in clinical trials in many different cancers and some have no other treatment.
Life expectancy

In the past, people all wanted the river for a long time and said that long life was a rare and precious thing. Most medical research and treatment also focuses on increasing the life of the community.
Life expectancy changes according to the influence of many factors, in which, in addition to external factors such as accidents, climate, natural disasters, living environment, nutrition, health ., genetic factors also contribute to important. Many studies in recent years have discovered some genes that affect aging, the immune system, and other factors that affect life expectancy. For example, in a 2009 study by Tokyo Agricultural University, a special gene was discovered, which works in men but does not work in women, and the activity of this gene explains for women. usually live longer than men. The researchers say that the gene helps men have a larger and more robust body, but the exchange price is shorter than the weaker one.
In 2010, a team of researchers at Birmingham University, England, studied worms, also found that worms with active DAF-16 genes will live longer and be able to prevent better disease.
- Genetic secrets make other monkeys
- Human genome sheds light on the mystery of human history
- Science says: More than half of your body is not human!
- International publication of the Vietnamese genome sequence
- Research on the Vietnamese genome found many rare diseases
- The Cray XC30 super computer helps build the human genome in 9 minutes
- The first complete map of human gene activity
- 1/5 human genome is a fake gene
- Lice 'write' human history
- Cooperation in human genome research
- The genome of a marine creature carries the secret of the unicellular ancestor of human beings
- Wukong recognizes the benefits of decoding human genes
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum?