The US successfully tested the type of 'glue' in cancer treatment
US scientists have identified a lumican protein molecule that can bind chemicals that kill cells into cancer tissue, opening up the possibility of developing a low-toxicity cancer therapy.
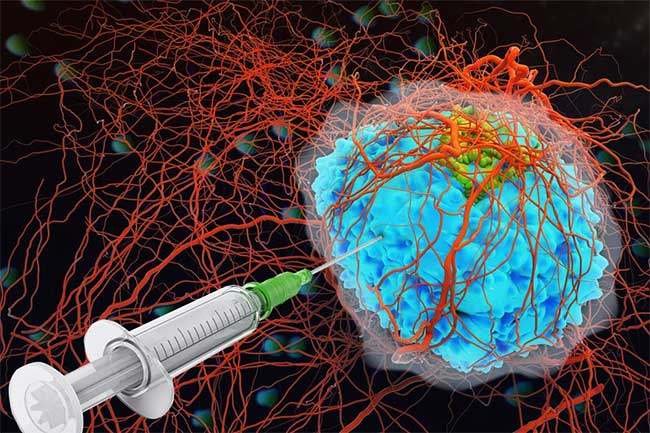
Using the lumican as the collagen-binding lumican, more than 90% of the mice survived the cytokine injection - (Photo: MIT news).
According to Science Translational Medicine , scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have found a molecule that can bind chemicals to destroy cells into cancer tissue, opening up the possibility of developing a cancer treatment. Low-toxicity mail. In particular, this protein molecule does not allow cytokines to leave the tumor because the Velcro-like protein (Velcro-like protein) can prevent cytokines from escaping after they are injected into the tumor.
Previous studies have determined that cytokines - small proteins released by immune cells to communicate with each other, have the potential to treat cancer if combined with other immunotherapies. but they are highly toxic to both healthy tissues.
Oncologists have tried to inject cytokine directly into the tumor, but those compounds within minutes have left the tumor. In the latest study, scientists screened different proteins in the tumor. They focused their attention on collagen in solid tumors. They then attached a collagen-binding protein called lumican to the cytokines.
In the trial, 2 cytokines were introduced into tumors of malignant cancerous mice. In its pure form, the inclusion of cytokines leads to the death of all rats, and if combined with immunotherapy, only a few lives will be saved. But when using lumican as the collagen-binding lumican , more than 90% of rats survived.
- Egypt successfully tested gold cancer treatment
- Food poisoning bacteria help treat pancreatic cancer
- Successfully tested new cancer drugs
- Successfully tested 10 new compounds against cancer
- Successfully developed gravel glue that breaks down is sticky
- Glue helps wound heal after surgery
- Australia successfully prepared new drugs to treat melanoma
- For the first time, implant successful cancer treatment beads in Vietnam
- Test cancer medicine on patients
- Treat cervical cancer with ... cow sperm
- Cuba develops a new cancer treatment drug
- Vietnam has successfully treated liver cancer with radioactive microspheres
 Why is Australia the country with the highest cancer rate in the world while Vietnam ranks 100th?
Why is Australia the country with the highest cancer rate in the world while Vietnam ranks 100th? New drug causes cancer to 'starve'
New drug causes cancer to 'starve' Common cancers in men
Common cancers in men America's incredible discovery: The most feared cancer cell is love
America's incredible discovery: The most feared cancer cell is love