The way the submarine sends a signal for help in distress
Immediately after the ship was in distress, the crew will broadcast emergency calls to the center, and at the same time launch signal buoys to inform the ship's position of distress. Depending on the severity of the problem, the battery may be disconnected and only the battery will be used, according to Howstuffworks.
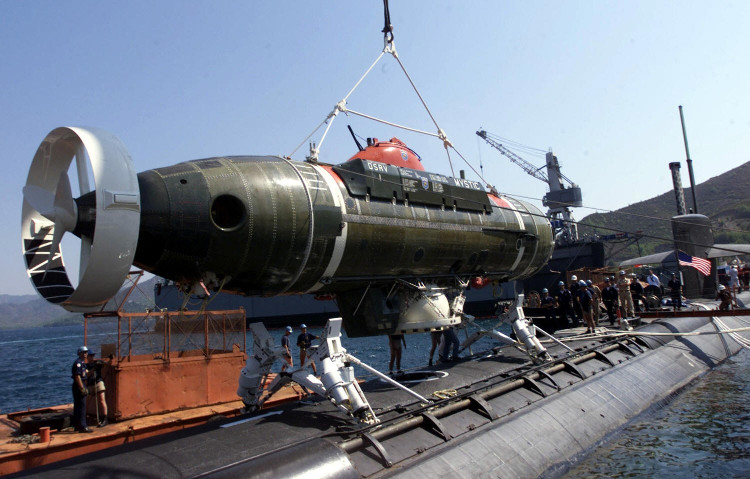

Deep diving rescue ship (DSRV).(Photo: Howstuffworks).
Rescue efforts must take place urgently, usually within 48 hours of the incident, because the crew faces a lot of risk when the submarine falls into the ocean.The most dangerous is the risk of sea water entering the ship. Besides, they also face a lack of oxygen , high levels of carbon dioxide and a sharp drop in temperature as the on-board heating system stops working.
After receiving the rescue signal, a large ship carrying rescue facilities such as a deep-diving rescue ship (DSRV) , diving bell and steam buoy were quickly dispatched to the ship's distress. The DSRV will dive into submarine positions, cling to the upper side of the ship and connect to the "escape compartment" to create an escape route (the escape compartment is usually located on the upper side, the top of the submarine, is Special design in case of rescue).
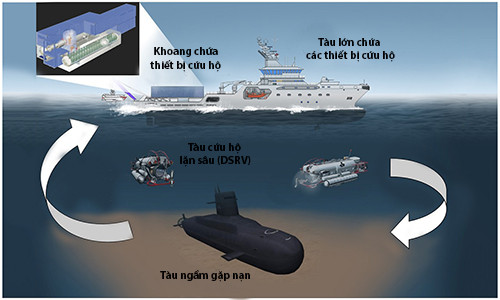
The large ship contains rescue equipment such as deep-diving lifeboats, diving bell and steam buoys approaching the position of the submarine in distress.(Photo: Thinkdefence).
The enemy corpses trapped in the submarine will be evacuated to the DSRV through the emergency exit. In many cases, dive bells (deep diving equipment for divers) can be sent down to support rescue operations. When all crews are removed from the submarine, steam buoys will be mounted around the hull and then inflated to bring the submarine to the surface.
Rescue operations and salvage submarines also depend on many factors such as the depth of the ship in distress, weather conditions at sea, flow conditions and seabed topography.
- 17 submarine and one-man submarine surprises you
- Stingray ray submarine
- The truth about Chinese submarine technology
- Submarine K-27 - Soviet
- The Arecibo message is the first 'letter' sent to the aliens
- The historical secret of the world's first submarine
- The Nereus submarine exploded at a depth of 10,000m
- German submarine explosion: Mysteriously challenging the maritime industry for nearly 100 years
- New personal submarine
- HMS Artful - World's largest nuclear submarine
- Mini submarine explores Jupiter's moon
- Students of grade III American private submarine 2,000 USD
 'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times
'Fine laughs' - Scary and painful torture in ancient times The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why?
The sequence of numbers 142857 of the Egyptian pyramids is known as the strangest number in the world - Why? History of the iron
History of the iron What is alum?
What is alum? The Ship of Theseus Paradox: Who Are You?
The Ship of Theseus Paradox: Who Are You?  Ghost ship 'appears' in coal mine after 1,700 years missing
Ghost ship 'appears' in coal mine after 1,700 years missing  China installs world's longest undersea steel-casing concrete pipe tunnel
China installs world's longest undersea steel-casing concrete pipe tunnel  The most catastrophic maritime accident in human history, more than 9,000 people died in just one night
The most catastrophic maritime accident in human history, more than 9,000 people died in just one night  The surprising discovery of 'MH370 hunters' at the site of the mysterious missing plane crash
The surprising discovery of 'MH370 hunters' at the site of the mysterious missing plane crash  Why has the Titanic wreckage not been salvaged after 111 years?
Why has the Titanic wreckage not been salvaged after 111 years? 