Warning signs of oral cancer
Carcinoma of the oral cavity is a disease arising from malignant changes of the oral mucosa covering the entire oral cavity including: cancer of the lips (including upper lip, lower lip, margin), maxillary gums, mandibular gums, cleft intermaxillary, hard palate, tongue (mobile part), buccal mucosa and floor of the mouth.
According to the doctor of Central K Hospital, patients can detect oral cancer because the signs are quite easy to notice as soon as they appear. However, patients are often subjective. Therefore, most of the patients with oral cancer come to the hospital at a late stage, when the cancer lesions have spread, destroying many nearby structures, so the patient's prognosis is greatly reduced.
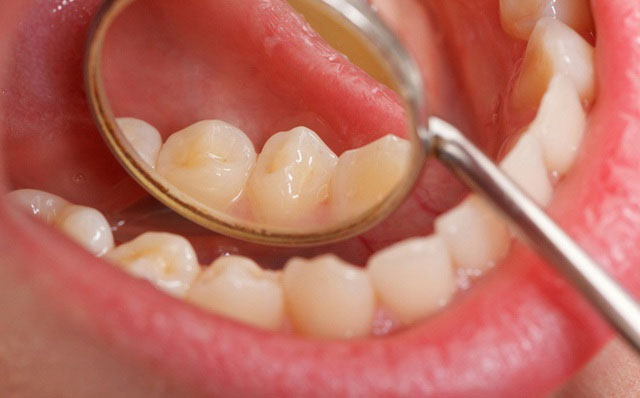
Patients can detect oral cancer because the signs are quite easy to see as soon as they appear.
The most common cancer in the oral cavity is squamous cell carcinoma (95%) and usually occurs in the oral mucosa. Squamous cell carcinoma is divided into 3 types: highly differentiated, moderately differentiated, and poorly differentiated. There are also other types of cancer such as follicular adenocarcinoma, connective tissue cancer and melanoma .
The cause to the illness
Smoking and drinking are the main causes of head and neck cancers, including cancers of the oral cavity. The habit of eating betel nut, misaligned teeth, poor oral hygiene. can cause mechanical damage in the oral cavity, creating favorable conditions for cancer development.
In addition, some other risk factors such as Herpes virus infection, HPV (Human Papilloma Virus), Xeroderma pigmentosum syndrome, Fanconi anemia. are also thought to be related to oral cancer.
Signs of oral cancer
You should pay attention if you have the following symptoms:
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing.
- Mouth has sclerotic, broccoli bud-like lesions.
- Difficulty moving the tongue or jaw.
- Unwanted weight loss.
- Pain or ulcers that do not heal or bleed
- Loose teeth do not find the cause.
- Appearance of white or black, red patches in the oral cavity.
The assessment of lesions is based on many factors such as clinical examination, taking medical history. If needed, your doctor may order a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head, neck, or chest to assess the spread of disease in the area and see if the disease has spread. Has it spread to the lungs?
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a biopsy of the lesion. In addition, patients will be asked to endoscopy of the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, trachea to look for lesions because up to 5-15% of patients with cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx or larynx have a secondary cancer. 2 at another location in the head and neck region.
- 7 signs of 'sneaking' on oral cancer
- Warning signs of tongue cancer
- Signs for early detection of oral cavity cancer
- Do not confuse tongue cancer and mouth heat
- Diagnosing oral cancer by telephone
- 10 signs of cancer are growing in the body, everyone must be satisfied
- The culprit for tonsil cancer you need to avoid
- The relevance of oral bacteria and cancers
- The cancer has no symptoms early
- Warning signs of breast cancer in men
- Warning signs of skin cancer that you cannot see with the naked eye
- Oral cancer test using bio-nano chips
 Why is Australia the country with the highest cancer rate in the world while Vietnam ranks 100th?
Why is Australia the country with the highest cancer rate in the world while Vietnam ranks 100th? New drug causes cancer to 'starve'
New drug causes cancer to 'starve' Common cancers in men
Common cancers in men America's incredible discovery: The most feared cancer cell is love
America's incredible discovery: The most feared cancer cell is love