What are antibiotics and classify antibiotics
As you know, the current situation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is growing strongly, but if we cannot find a way to prevent this situation, even a mild infection can make us quick death. Because it has been over 30 years, people have not found a new mineral. But what is antibiotics, not everyone understands.
What are antibiotics?
Antibiotics are chemical compounds - regardless of origin - that have a specific effect on an essential metabolic stage of microorganisms. With therapeutic doses, antibiotics can inhibit or kill pathogenic microorganisms.
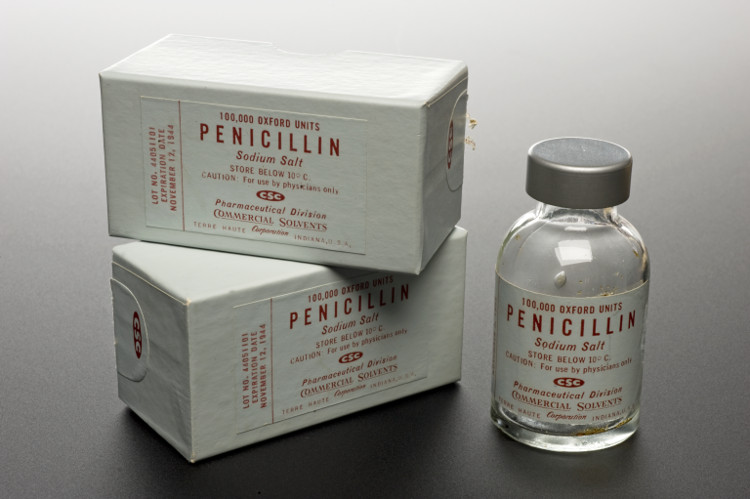
Antibiotics are found by Alexander Fleming.
Who finds antibiotics?
In 1928, Alexander Fleming, a scientist from Scottland, was experimenting with influenza viruses. When he rummaged through the experimental plates full of different bacteria he discovered a strange thing.
A type of mold that attaches to one of the experimental plates seems to destroy the bacteria it touches. Or in modern interpretation, the mold contains antibiotic properties.
After years of searching for the "miraculous" remedy , Fleming naturally found it in the most accidental situation possible.
Just a few weeks later, the professor classified the mold and found it to be of the Penicillium strain. He named the disinfectant ingredient "Penicillin". And from there the first antibiotic in the world was born.
Classification of antibiotics
Each type of antibiotic (antibiotics) only works with a certain bacterium. In choosing antibiotics to treat infected people, doctors will guess the type of bacteria that causes the disease. For example, some infections are caused only by certain types of bacteria. If an antibiotic is expected to work against all types of bacteria, there is no need for further testing.
If the infection can be caused by a variety of bacteria or a type of bacteria that is expected to be unaffected by antibiotics, the test will be required to determine the type of bacteria. The bacteria cause an infection from a sample of blood, urine, or tissue from that patient. These types of bacteria that cause this infection are then tested for susceptibility to different antibiotics.
The results of the tests usually take one to two days and therefore cannot guide the initial choice of antibiotic use.
Each type of antibiotic (antibiotics) that is effective in the laboratory does not necessarily work with an infected person. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the extent to which the drug is absorbed into the bloodstream, the amount of drug taken to the place of infection and the rate at which the body excretes the drug. These factors vary from person to person, depending on the different drug being used, the presence of another disorder and the person's age.
In the selection of antibiotics (antibiotics), doctors also consider the nature and extent of the risk of infection, the ability to cause side effects, allergens and severe reactions. weight of drugs and drug prices.
The combination of antibiotics (antibiotics) is sometimes necessary to treat the following cases:
- For serious infections, especially during the early days when antibiotic effects on bacteria are unknown.
- Some infections caused by bacteria that quickly develop resistance to a single antibiotic.
- Infections are caused by many types of bacteria if each type of bacteria is affected by a different type of antibiotic.












- 'Heavenly' facts about antibiotics
- Find new antibiotics under the ocean
- Why do you know that antibiotics do not treat flu, many people continue to abuse?
- Antibiotics from dirt
- Bad habits of parents hurt the liver and kidneys, endanger children
- 7 mistakes we often make when talking about antibiotics
- Understand disease to use antibiotics correctly
- Find a new drug that can replace antibiotics
- When do you need to say 'no' to antibiotics?
- Children under 2 years of age use many antibiotics prone to obesity
- The world is depleted of new generation antibiotics
- Risk from fluoroquinolones
 The United Nations' all-human warning: All antibiotics are becoming useless
The United Nations' all-human warning: All antibiotics are becoming useless How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics?
How did bacteria learn to fight antibiotics? 10 million deaths are one of the startling numbers about 'Antibiotic resistance'.
10 million deaths are one of the startling numbers about 'Antibiotic resistance'. 7 principles when using antibiotics
7 principles when using antibiotics The dangers of using antibiotics indiscriminately to treat sore throats
The dangers of using antibiotics indiscriminately to treat sore throats  Using AI to prescribe antibiotics helps curb drug resistance
Using AI to prescribe antibiotics helps curb drug resistance  What you need to know about antibiotic-associated diarrhea
What you need to know about antibiotic-associated diarrhea  The CDC report states: The United States has entered a post-antibiotic period
The CDC report states: The United States has entered a post-antibiotic period  Making a liquid first aid bandage, the 'little scientist' won a $ 25,000 prize
Making a liquid first aid bandage, the 'little scientist' won a $ 25,000 prize  Rivers are infected with antibiotics
Rivers are infected with antibiotics 