What is glass bone disease?
TS.BS. Dao Hung Hanh (Bach Mai Hospital)
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Osteogenesis Imperfecta , or OI for short, is a rare, hereditary bone disease that is caused by damage to the collagen fibers of the bone that make the bones very brittle and brittle after a Very minor collisions such as coughing, sneezing . or even when there is no recurrence of fractures and fractures many times, it is also called ' glass bone disease ' or crunchy bone disease.
Because it is a genetic disease, so far there is no specific treatment, but only treatment and supportive treatment. Today, the advancement of pre-natal diagnostic techniques allows us to detect the disease early in the fetal period, especially in severe cases with multiple and early fractures.
Why is there a glass bone phenomenon?
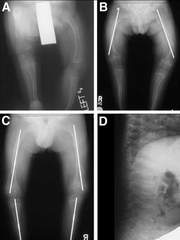
Fractures due to glass bone disease.(Photo: SK & D)
As we know, bone is a special connective tissue consisting of cells and bone matrix, in which the bone matrix consists of collagen fibers and other connective tissue rich in glucoaminoglycin. Bone tissue has solid bone (bone shell) and spongy bone. 80% -90% of solid bone mass is calcified; 15-25% of the volume of porous bone is calcified. Concentrated bone has the function of protecting the body while the bone has the function of metabolism, homeostasis.
Bone cells include destroying the osteoclasts (multi-nucleus giant cells, responsible for bone destruction) and creating cell bones (the rhombic cells, which are responsible for producing the components of the substrate). bones: collagen fibers and substrates, which play an important role in calcification.
In the body, the process of bone formation and bone destruction takes place continuously according to the mechanism of replacing old bone with new bone. In dysfunctional bone disease, due to damage to the commanding genes of type 1 collagen production (COL1A1 and COL1A2), the amount or quality of the reduced collagen fibers causes the bone to lose its capacity, deform and easy to break. On the other hand, collagen is also the main component of many connective tissue, so the clinical picture is not only in bone but also in other organs such as skin, ligaments, sclera, teeth .
How does the disease manifest?
This is a rare disease studied in the United States, the incidence is about 1 / 20,000, the frequency of disease does not depend on race and gender. Our country so far has no specific data on the number of people suffering from this disease.
The disease is divided into 4 clinical types with different severity levels.
Type 1 : is the lightest and most common form. Patients with normal or relatively normal stature, manifestations of muscle weakness, spinal column may be bent, sclera may be blue or purple, fractures usually occur before puberty.
Type 2 : is the heaviest. Patients often die immediately after birth or live only a short time due to respiratory dysfunction (low lung production, broken ribs), patients with small stature, broken bones.
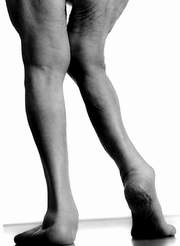
Foot of the person with glass bone.(Photo: SK & D)
Type 3 : is relatively severe, children often born with fractures. The eye patch is usually too white or gray, blue, reduces respiratory function, hearing loss and abnormal teeth.
Type 4 : is an intermediary between type 1 and 3. Bone deformities are mild to moderate.
Sorting from mild to severe order will be type 1, type 4, type 3, type 2. Some new studies have been classified more types 5, 6, 7.
Bone density testing is usually lower than normal. Fetal ultrasound can detect abnormalities in fetal limb length from the 15th week and fractures, but for mild forms it is difficult to detect.
Treatment measures
As mentioned above, the disease has no specific treatment, the therapeutic gene is a thorough and hopeful treatment in the future. Currently, treatment measures aimed at improving the quality of life for patients: minimizing fractures and complications, helping patients to be independent in life and life.
Orthopedic treatment: The majority of fractures in this disease are usually treated with orthopedic methods such as immobilization, splint, and cast. One thing in particular is that the fractures are usually faster than normal cases.
Surgical treatment: Less applicable, indicated for severe deformed bones.
Drug therapy: There are many drugs that have been studied but so far, drugs that inhibit bone resorption like bisphosphonate group are the most studied drugs and give quite satisfactory results. Pamidronate is given intravenously every 3 months, which helps reduce pain, increase density and limit fractures. However, the price of medicines is too high for the income of many sick families, so it is difficult to treat.
- Glass bone disease
- New glass can decompose and release calcium into the body
- Google Glass applies bone-streaming technology
- Experimental injection of stem cells to prevent glass bone disease
- The strange disease caused the patient's bones to
- The world's first 3D jaw bone graft surgery
- Things you don't know about bone calcification
- Nine genes were found to be related to bone density
- What is glass?
- Detecting and treating osteomalacia
- Unexpected uses of Gorilla Glass
- Drinking too much tea causes calcified bones
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking