What is the benefit of mini ice age?
The sunspot cycle is about to enter the first hibernation period since the 17th century. This means humanity will lessen the safety of the electrical and satellite networks.
>> The sun is about to . disappear?
Clear signs
A study published by experts from the National Solar Observatory (USA) at the annual meeting of the Sun Physics major of the American Astronomical Society showed that the Sun is about to enter a period irregular and prolonged hibernation. The sunspot field has gradually decreased in intensity since 1998 and by 2020, black spots may disappear in a few years or even decades. The most recent similar period lasted for 70 years (1645 - 1715), known as the Maunder Period or Little Ice Age.
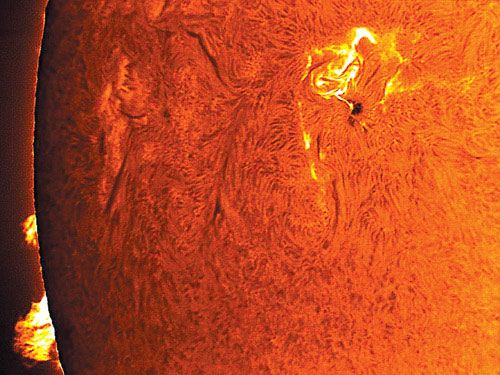
Sunspots are about to disappear in a few years or even decades.
Scientists do not know why the Sun suddenly became so quiet. But there are at least three clear signs that show: the black marks are weakening, the activity at the poles of the coronary rim decreases and the solar winds are disappearing. Lead researcher Dr Frank Hill said: " If we are right, this is the last maximum period of sun activity that we will witness in the next few decades. This can affect every things, from cosmic expeditions to Earth's climate " .
Positive impact
In a 22-year cycle, the sun's magnetic field changes in the North - South direction, creating a black streak cycle lasting 11 years. At peak times, like 2001, dark spots appear every day, while the fire and solar storms occur regularly. The blade of fire and the Sun's bursts can launch large amounts of high-charged particles towards the Earth, causing satellite communication, GPS systems and air traffic control devices. Therefore, when the Sun declines and the black marks disappear, we can be more secure about these technology infrastructures.
Reducing black spot activity means that solar radiation will have lower energy levels, ultraviolet rays, solar winds and weaker magnetic fields, but light and warmth for the Earth will not decrease. This phenomenon can also produce a small effect on the climate, but not significantly compared to human influence through carbon dioxide and methane emissions.
A study published in early 2010 found that by 2100, the Sun's long minimum period of activity could only reduce the Earth's temperature by 0.3 degrees Celsius compared to the normal period. Meanwhile, global warming due to human activity will increase the temperature by 4.5 0 C by the end of the century. One obvious example we just witnessed, is that in 2010 there was virtually no Sun activity, but still holds the record for the hottest year in about a century.
- Video: How to make a high speed mini drill
- Bombard the mini moon to test Earth defenses
- Mini-rat brains in mice raise concerns about intelligent hybridization
- New push system for mini satellites
- Reconnaissance aircraft from unique biodegradable material
- Prepare car at home
- Farmers make their own cheap mini hydroelectric plants
- Scientists successfully developed lung 'mini'
- Truong Sa 02 submarine gradually formed: New ambition!
- The American scientists raised 'mini brains' to live up to 9 months in vitro
- Climate change: The place to benefit, where it is
- Mini heart culture for effective cardiovascular treatment
 Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth
Van Allen's belt and evidence that the Apollo 11 mission to the Moon was myth The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale)
The levels of civilization in the universe (Kardashev scale) Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned
Today Mars, the sun and the Earth are aligned The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people
The Amazon owner announced a secret plan to build a space base for thousands of people Top 5 lands where the sun never sets, where 'sunset never reaches'
Top 5 lands where the sun never sets, where 'sunset never reaches'  Rare detailed image of sunspot
Rare detailed image of sunspot  Why are the sun's outer rings so much hotter than the inner core?
Why are the sun's outer rings so much hotter than the inner core?  'Planet 9' left its mark on Earth before disappearing?
'Planet 9' left its mark on Earth before disappearing?  Could the Sun Capture a New Planet, Changing Life on Earth?
Could the Sun Capture a New Planet, Changing Life on Earth?  Mysterious comet flies close to the Sun without melting, leaving scientists puzzled
Mysterious comet flies close to the Sun without melting, leaving scientists puzzled 