Why is young blood a medicinal god helping
A series of experiments have shown that it is possible to rejuvenate old mice by using the blood of young mice. So what is the solution to the operation of this strange mechanism?
Researchers have discovered an enzyme that can 'rescue' the old brain from weakened cognitive decline. This has been demonstrated in mice, but similar mechanisms have been found in humans. The results of this study may lead to new generation anti-aging therapies.
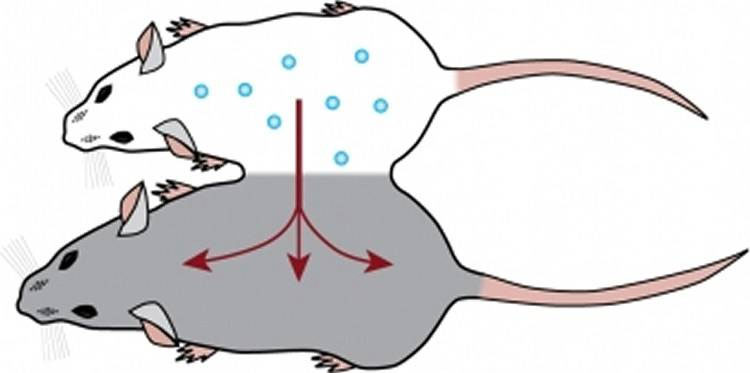
Scientists have used parabiosis to understand the mystery of how young mice 'blood works to improve memory for older mice.(Photo: Villeda lab).
A group of researchers led by neuroscientist Saul Villeda of the University of California, San Francisco, found that the memory and learning ability of old mice improved significantly after when they are given blood from young mice. The reason is that the connections in the hippocampus of these mice have a positive change. Similarly, the brains of young mice will also be weakened if they are injected with blood from long-lived mice.
Since then, Villeda's lab has been working hard to find the secret behind this mysterious, seemingly "fresh spring" , and now they have grasped the results in their hands. The team used a technique called parabiosis - surgery that connects the circulatory systems of a pair of mice of relatively different ages. They then analyzed their brains to measure the level of an enzyme involved in age-related diseases.
The main author of this study is Geraldine Gontier, a UCSF scientist. He said: "At first I did not believe this was true. I did the experiment over and over again to make sure I got a right result. And obviously some circulatory factors in the blood. can change Tet2 levels in the brain ".
Tet2 (eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenase 2) plays a role in epigenetic regulation in some genes. As we get older, the mutations in genes that contain this enzyme increasingly accumulate, increasing the risk of cancer, stroke and cardiovascular disease.
The blood of young people can recover old, weak brains.(Photo: Sciencealert).
There are some genes that are thought to be responsible for regenerating brain cells. And as we age, they become less effective - this is the cause of cognitive decline in people who are entering the last pages of their lives. Later, the researchers did a second experiment using short RNA sequences to block Tet2 activity in a 3-month-old juvenile mouse.
Experimental results show that many new neurons in the hippocampus in these young mice have reduced function. They are also worse than normal in tests of memory and learning ability. In the final test, the team implanted a 6-month-old adult mouse with a virus capable of causing cells in the hippocampus to remove Tet2. Once again, high levels of Tet2 enzymes have demonstrated the ability to increase epigenetic activities and create new brain cells.
Being rejuvenated does not completely help older mice perform all memory tests excellently, but their results are moderately progressive."This is great because it's like we can improve memory like a healthy 30-year-old man ," Villeda said excitedly.

Researchers have discovered that a blood enzyme can "rescue" the aging brain from weakened cognitive decline.(Photo: CBC).
Gontier said: "I spent all my time working on my doctoral thesis and now it's a postdoctoral degree to try to understand the aging process of the brain and find ways to 'improve old people'. And in this study, we found that Tet2 molecules can prevent memory impairment and enhance some cognitive functions in adult mouse brains. "
Although the results of this study are really interesting, it has only been recently proved in mice. There are good reasons for researchers to think that this process is similar in humans, but more research is needed. If there is a simple way to fill the memory's aging regression, then we humans will live for many more meaningful years, so this is a valuable study.
Research has been published on Cell Reports.
- Young blood - the key to preventing aging?
- Discovering new plants for medicinal plants
- These foods are better than medicine
- High blood pressure is
- Donating blood helps avoid serious diseases
- Tens of thousands of medicinal plants are about to disappear forever
- Lam Dong: Discovering extremely rare medicinal plants that treat Alzheimer's disease
- Archaeological bottle of medicinal wine
- Researching
- Artificial blood from prehistoric elephants
- Canon gun 'blood' - fake death scene for Halloween
- Can humans be immortal by blood transfusion technology?
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking