Artificial red blood cells
UC Santa Barbara and Michigan University (USA) have collaborated to successfully synthesize artificial red blood cells (sRBCs), replicating key features and functions of natural red blood cells, including flexibility and transport. oxygen gas.
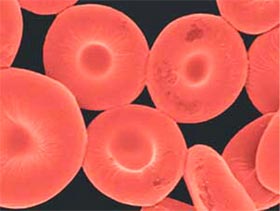 The team created spherical polymer particles and coated a protein layer (including hemoglobin) of 7µm thick.
The team created spherical polymer particles and coated a protein layer (including hemoglobin) of 7µm thick.
When the polymer core is removed, the remaining protein shell will have natural red blood cell-like properties.
They can stretch to squeeze through capillaries smaller than their diameter and return to disk shape when they leave capillaries.
These hemoglobin-coated particles can absorb oxygen in high concentrations and release oxygen at lower concentrations.
Synthetic red blood cells are capable of transporting drugs or contrast materials, opening many useful applications in diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
- Artificial blood can save patients' lives like real blood
- Artificial blood will be tested in humans in 2016
- Producing artificial blood from stem cells
- A way to produce artificial blood has been found on an industrial scale
- India announced the successful development of artificial blood
- Processing artificial blood from ... deep sea
- Study artificial blood test
- Japanese scientists successfully tested artificial blood on rabbits
- Using artificial blood on human body
- Breakthrough in the production of large-scale artificial blood
- Artificial blood - From idea to reality
- Scientists for the first time can turn blood cells into egg cells in humans
 Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash?
Green tea cleans teeth better than mouthwash? Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips
Death kiss: This is why you should not let anyone kiss your baby's lips What is salmonellosis?
What is salmonellosis? Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking
Caution should be exercised when using aloe vera through eating and drinking